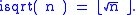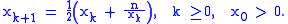Integer square root
Encyclopedia
In number theory
, the integer square root (isqrt) of a positive integer n is the positive integer m which is the greatest integer less than or equal to the square root
of n,
For example, because
because 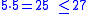 and
and 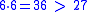 .
.
 and
and  is to use Newton's method
is to use Newton's method
to find a solution for the equation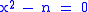 , giving the recursive
, giving the recursive
formula
The sequence
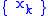 converges
converges
quadratically
to as
as  . It can be proven that if
. It can be proven that if  is chosen as the initial guess, one can stop as soon as
is chosen as the initial guess, one can stop as soon as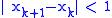
to ensure that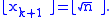
 is irrational
is irrational
for almost all
 , the sequence
, the sequence 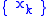 contains only rational
contains only rational
terms when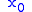 is rational. Thus, with this method it is unnecessary to exit the field
is rational. Thus, with this method it is unnecessary to exit the field
of rational numbers in order to calculate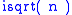 , a fact which has some theoretical advantages.
, a fact which has some theoretical advantages.
 is the largest possible number for which the stopping criterion
is the largest possible number for which the stopping criterion
ensures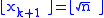
in the algorithm above.
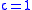
Since actual computer calculations involve roundoff errors, a stopping constant less than 1 should be used, e.g.
Number theory
Number theory is a branch of pure mathematics devoted primarily to the study of the integers. Number theorists study prime numbers as well...
, the integer square root (isqrt) of a positive integer n is the positive integer m which is the greatest integer less than or equal to the square root
Square root
In mathematics, a square root of a number x is a number r such that r2 = x, or, in other words, a number r whose square is x...
of n,
For example,
 because
because 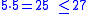 and
and 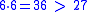 .
.Algorithm
One way of calculating and
and  is to use Newton's method
is to use Newton's methodNewton's method
In numerical analysis, Newton's method , named after Isaac Newton and Joseph Raphson, is a method for finding successively better approximations to the roots of a real-valued function. The algorithm is first in the class of Householder's methods, succeeded by Halley's method...
to find a solution for the equation
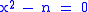 , giving the recursive
, giving the recursiveRecursion
Recursion is the process of repeating items in a self-similar way. For instance, when the surfaces of two mirrors are exactly parallel with each other the nested images that occur are a form of infinite recursion. The term has a variety of meanings specific to a variety of disciplines ranging from...
formula
The sequence
Sequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an ordered list of objects . Like a set, it contains members , and the number of terms is called the length of the sequence. Unlike a set, order matters, and exactly the same elements can appear multiple times at different positions in the sequence...
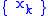 converges
convergesLimit (mathematics)
In mathematics, the concept of a "limit" is used to describe the value that a function or sequence "approaches" as the input or index approaches some value. The concept of limit allows mathematicians to define a new point from a Cauchy sequence of previously defined points within a complete metric...
quadratically
Rate of convergence
In numerical analysis, the speed at which a convergent sequence approaches its limit is called the rate of convergence. Although strictly speaking, a limit does not give information about any finite first part of the sequence, this concept is of practical importance if we deal with a sequence of...
to
 as
as  . It can be proven that if
. It can be proven that if  is chosen as the initial guess, one can stop as soon as
is chosen as the initial guess, one can stop as soon as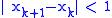
to ensure that
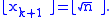
Domain of computation
Although is irrational
is irrationalIrrational number
In mathematics, an irrational number is any real number that cannot be expressed as a ratio a/b, where a and b are integers, with b non-zero, and is therefore not a rational number....
for almost all
Almost all
In mathematics, the phrase "almost all" has a number of specialised uses."Almost all" is sometimes used synonymously with "all but finitely many" or "all but a countable set" ; see almost....
 , the sequence
, the sequence 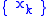 contains only rational
contains only rationalRational number
In mathematics, a rational number is any number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction a/b of two integers, with the denominator b not equal to zero. Since b may be equal to 1, every integer is a rational number...
terms when
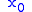 is rational. Thus, with this method it is unnecessary to exit the field
is rational. Thus, with this method it is unnecessary to exit the fieldField (mathematics)
In abstract algebra, a field is a commutative ring whose nonzero elements form a group under multiplication. As such it is an algebraic structure with notions of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, satisfying certain axioms...
of rational numbers in order to calculate
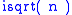 , a fact which has some theoretical advantages.
, a fact which has some theoretical advantages.Stopping criterion
One can prove that is the largest possible number for which the stopping criterion
is the largest possible number for which the stopping criterion
ensures
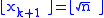
in the algorithm above.
Since actual computer calculations involve roundoff errors, a stopping constant less than 1 should be used, e.g.

External links
- A geometric view of the square root algorithm
- Integer Square Roots, an article by Jack Crenshaw explaining a fast, direct method.