
Immersed boundary method
Encyclopedia
The immersed boundary method is an approach – in computational fluid dynamics
– to model and simulate mechanical systems in which elastic structures (or membranes) interact with fluid flows. Treating the coupling (the elastic boundary changes the flow of the fluid and the fluid moves the elastic boundary simultaneously) of the structure deformations and the fluid flow poses a number of challenging problems for numerical simulations
. In the immersed boundary method approach the fluid is represented in an Eulerian coordinate frame
and the structures in a Lagrangian coordinate frame
. For Newtonian fluids governed by the Navier–Stokes equations the immersed boundary method fluid equations are
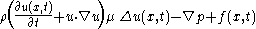
with incompressibility condition
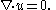
The immersed structures are typically represented by a collection of interacting particles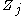 with a prescribed force law, where
with a prescribed force law, where 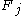 is the force acting on the
is the force acting on the 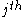 particle. The forces are accounted for in the fluid equations by the force density
particle. The forces are accounted for in the fluid equations by the force density
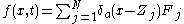
where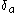 is an approximation of the Dirac
is an approximation of the Dirac 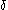 -function
-function
smoothed out over a length scale . The immersed structures are then updated using the equation
. The immersed structures are then updated using the equation
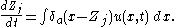
Variants of this basic approach have been applied to simulate a wide variety of mechanical systems involving elastic structures which interact with fluid flows. See the references for more details.
Computational fluid dynamics
Computational fluid dynamics, usually abbreviated as CFD, is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical methods and algorithms to solve and analyze problems that involve fluid flows. Computers are used to perform the calculations required to simulate the interaction of liquids and gases with...
– to model and simulate mechanical systems in which elastic structures (or membranes) interact with fluid flows. Treating the coupling (the elastic boundary changes the flow of the fluid and the fluid moves the elastic boundary simultaneously) of the structure deformations and the fluid flow poses a number of challenging problems for numerical simulations
Computer simulation
A computer simulation, a computer model, or a computational model is a computer program, or network of computers, that attempts to simulate an abstract model of a particular system...
. In the immersed boundary method approach the fluid is represented in an Eulerian coordinate frame
Lagrangian and Eulerian coordinates
In fluid dynamics and finite-deformation plasticity the Lagrangian specification of the flow field is a way of looking at fluid motion where the observer follows an individual fluid parcel as it moves through space and time. Plotting the position of an individual parcel through time gives the...
and the structures in a Lagrangian coordinate frame
Lagrangian and Eulerian coordinates
In fluid dynamics and finite-deformation plasticity the Lagrangian specification of the flow field is a way of looking at fluid motion where the observer follows an individual fluid parcel as it moves through space and time. Plotting the position of an individual parcel through time gives the...
. For Newtonian fluids governed by the Navier–Stokes equations the immersed boundary method fluid equations are
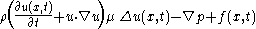
with incompressibility condition
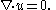
The immersed structures are typically represented by a collection of interacting particles
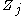 with a prescribed force law, where
with a prescribed force law, where 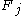 is the force acting on the
is the force acting on the 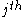 particle. The forces are accounted for in the fluid equations by the force density
particle. The forces are accounted for in the fluid equations by the force density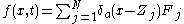
where
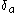 is an approximation of the Dirac
is an approximation of the Dirac 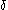 -function
-functionDirac delta function
The Dirac delta function, or δ function, is a generalized function depending on a real parameter such that it is zero for all values of the parameter except when the parameter is zero, and its integral over the parameter from −∞ to ∞ is equal to one. It was introduced by theoretical...
smoothed out over a length scale
 . The immersed structures are then updated using the equation
. The immersed structures are then updated using the equation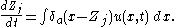
Variants of this basic approach have been applied to simulate a wide variety of mechanical systems involving elastic structures which interact with fluid flows. See the references for more details.
See also
- Stokesian dynamics
- Volume of fluid methodVolume of fluid methodIn computational fluid dynamics, the volume of fluid method is a numerical technique for tracking and locating the free surface . It belongs to the class of Eulerian methods which are characterized by a mesh that is either stationary or is moving in a certain prescribed manner to accommodate the...
- Level set methodLevel set methodThe level set method is a numerical technique for tracking interfaces and shapes. The advantage of the level set method is that one can perform numerical computations involving curves and surfaces on a fixed Cartesian grid without having to parameterize these objects...
- Charles S. PeskinCharles S. PeskinCharles S. Peskin is a professor of mathematics at the Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences, New York University. He is a MacArthur Fellow, and a member of the National Academy of Science....

