
Hybrid coil
Encyclopedia

Transformer
A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through inductively coupled conductors—the transformer's coils. A varying current in the first or primary winding creates a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core and thus a varying magnetic field...
that has three winding
Coil
A coil is a series of loops. A coiled coil is a structure in which the coil itself is in turn also looping.-Electromagnetic coils:An electromagnetic coil is formed when a conductor is wound around a core or form to create an inductor or electromagnet...
s, and which is designed to be configured as a circuit
Electrical network
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical elements such as resistors, inductors, capacitors, transmission lines, voltage sources, current sources and switches. An electrical circuit is a special type of network, one that has a closed loop giving a return path for the current...
having four branches, (i.e. ports) that are conjugate in pairs.
A signal arriving on one branch is divided between the two adjacent branches but does not appear at the opposite branch. In the schematic diagram, the signal into W splits between X and Z, and no signal passes to Y. Similarly, signals into X split to W and Y with none to Z, etc.
Correct operation requires matched characteristic impedance
Characteristic impedance
The characteristic impedance or surge impedance of a uniform transmission line, usually written Z_0, is the ratio of the amplitudes of a single pair of voltage and current waves propagating along the line in the absence of reflections. The SI unit of characteristic impedance is the ohm...
at all four ports.
Explanation
Voiceband
In electronics, voiceband means the typical human hearing frequency range that is from 20 Hz to 20 kHz. In telephony, it means the frequency range normally transmitted by a telephone line, generally about 200–3600 Hz. Frequency-division multiplexing in telephony normally uses...
hybrid coil
Coil
A coil is a series of loops. A coiled coil is a structure in which the coil itself is in turn also looping.-Electromagnetic coils:An electromagnetic coil is formed when a conductor is wound around a core or form to create an inductor or electromagnet...
is to convert between 2-wire
Two-wire circuit
In telecommunication, a two-wire circuit is characterized by supporting transmission in two directions simultaneously, as opposed to four-wire circuits, which have separate pairs for transmit and receive. In either case they are twisted pairs. Telephone lines are almost all two wire, while trunks...
and 4-wire
Four-wire circuit
In telecommunication, a four-wire circuit is a two-way circuit using two paths so arranged that the respective signals are transmitted in one direction only by one path and in the other direction by the other path...
operation in sequential sections of a communications
Information transfer
In telecommunications, information transfer is the process of moving messages containing user information from a source to a sink.Note: The information transfer rate may or may not be equal to the transmission modulation rate.-See also:...
circuit, for example in a four-wire terminating set
Four-wire terminating set
A four-wire terminating set is a balanced transformer used to perform a conversion between 4-wire and 2-wire operation in telecommunication systems.For example, a 4-wire circuit may, by means of a 4-wire terminating set, be connected to a 2-wire telephone set...
. Such conversion was necessary when repeater
Repeater
A repeater is an electronic device that receives asignal and retransmits it at a higher level and/or higher power, or onto the other side of an obstruction, so that the signal can cover longer distances.-Description:...
s were introduced in a 2-wire circuit, a frequent practice at early 20th century telephony
Telephony
In telecommunications, telephony encompasses the general use of equipment to provide communication over distances, specifically by connecting telephones to each other....
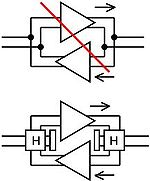
. Without hybrids, the output of one amplifier feeds directly into the input of the other, resulting in a howling situation (upper diagram). By using hybrids, the outputs and inputs are isolated, resulting in correct 2-wire repeater operation. Late in the century, this practice became rare but hybrids continued in use in line card
Line card
A line card or Digital Line Card is a modular electronic circuit on a printed circuit board, the electronic circuits on the card interfacing the telecommunication lines coming from the subscribers to the rest of the telecommunications access network.A line card commonly interfaces the twisted pair...
s.
Hybrid coil circuit diagrams
Hybrids are realized using transformersTransformer
A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through inductively coupled conductors—the transformer's coils. A varying current in the first or primary winding creates a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core and thus a varying magnetic field...
. Two versions of transformer hybrids were used, the single transformer version providing unbalanced outputs with one end grounded
Ground (electricity)
In electrical engineering, ground or earth may be the reference point in an electrical circuit from which other voltages are measured, or a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth....
, and the double transformer version providing balanced ports
Balanced circuit
A balanced circuit is circuitry for use with a balanced line or the balanced line itself. Balanced lines are a common method of transmitting many types of electrical communication signals between two points on two wires...
.
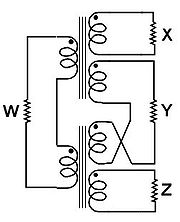
Single transformer hybrid
Two-wire circuit
In telecommunication, a two-wire circuit is characterized by supporting transmission in two directions simultaneously, as opposed to four-wire circuits, which have separate pairs for transmit and receive. In either case they are twisted pairs. Telephone lines are almost all two wire, while trunks...
repeater
Repeater
A repeater is an electronic device that receives asignal and retransmits it at a higher level and/or higher power, or onto the other side of an obstruction, so that the signal can cover longer distances.-Description:...
s, the single transformer version suffices, since amplifiers in the repeaters have grounded inputs and outputs. X, Y, and Z share a common ground
Ground (electricity)
In electrical engineering, ground or earth may be the reference point in an electrical circuit from which other voltages are measured, or a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth....
. As shown at left, signal into W, the 2-wire port, will appear at X and Z. But since Y is bridged from center of coil to center of X and Z, no signal appears. Signal into X will appear at W and Y. But signal at Z is the difference of what appears at Y and, through the transformer coil, at W, which is zero. Similar reasoning proves both pairs, W & Y, X & Z, are conjugates.
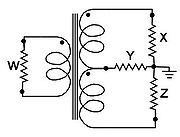
Double transformer hybrid
When both the 2-wireTwo-wire circuit
In telecommunication, a two-wire circuit is characterized by supporting transmission in two directions simultaneously, as opposed to four-wire circuits, which have separate pairs for transmit and receive. In either case they are twisted pairs. Telephone lines are almost all two wire, while trunks...
and the 4-wire circuits
Four-wire circuit
In telecommunication, a four-wire circuit is a two-way circuit using two paths so arranged that the respective signals are transmitted in one direction only by one path and in the other direction by the other path...
must be balanced
Balanced circuit
A balanced circuit is circuitry for use with a balanced line or the balanced line itself. Balanced lines are a common method of transmitting many types of electrical communication signals between two points on two wires...
, double transformer hybrids are used, as shown at right. Signal into port W splits between X and Z, but due to reversed connection to the windings, cancel at port Y. Signal into port X goes to W and Y. But due to reversed connection to ports W and Y, Z gets no signal. Thus the pairs, W & Y, X & Z, are conjugates.
Applications
Hybrids are used in telephoneTelephone
The telephone , colloquially referred to as a phone, is a telecommunications device that transmits and receives sounds, usually the human voice. Telephones are a point-to-point communication system whose most basic function is to allow two people separated by large distances to talk to each other...
s (see telephone hybrid
Telephone hybrid
Telephone hybrids are an essential functional component of the Public Switched Telephone Network . The term also describes the piece of equipment used in broadcast facilities to enable the airing of telephone callers....
) to reduce the sidetone
Sidetone
Sidetone is audible feedback to someone who is speaking. The term is most used in telecommunication contexts.-Telephony:In telephony, sidetone is the effect of sound that is picked up by the telephone's mouthpiece and in real-time introduced at a low level into the earpiece of the same handset,...
, or volume of microphone output that was fed back to the earpiece. Without this, the phone user's own voice would be louder in the earpiece than the other party's. Such hybrids also had their windings so arranged as to act as an impedance matching
Impedance matching
In electronics, impedance matching is the practice of designing the input impedance of an electrical load to maximize the power transfer and/or minimize reflections from the load....
transformer, matching the low-impedance carbon button transmitter
Carbon microphone
The carbon microphone, also known as a carbon button microphone or a carbon transmitter, is a sound-to-electrical signal transducer consisting of two metal plates separated by granules of carbon. One plate faces outward and acts as a diaphragm...
to the higher impedance parts of the system. Today, the transformer version of the hybrid has been replaced by resistor networks and compact IC versions, which uses integrated circuit
Integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is an electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material...
electronics to do the job of the hybrid coil.
Radio-frequency hybrids are used to split radio signals, including television. The splitter divides the antenna
Antenna (radio)
An antenna is an electrical device which converts electric currents into radio waves, and vice versa. It is usually used with a radio transmitter or radio receiver...
signal to feed multiple receivers.

