
Home birth
Encyclopedia

Childbirth
Childbirth is the culmination of a human pregnancy or gestation period with the birth of one or more newborn infants from a woman's uterus...
in a non-clinical setting, typically using natural childbirth
Natural childbirth
Natural Childbirth is a philosophy of childbirth that is based on the notion that women who are adequately prepared are innately able to give birth without routine medical interventions. Natural childbirth arose in opposition to the techno-medical model of childbirth that has recently gained...
methods, that takes place in a residence rather than in a hospital
Hospital
A hospital is a health care institution providing patient treatment by specialized staff and equipment. Hospitals often, but not always, provide for inpatient care or longer-term patient stays....
or a birth centre
Birthing center
A birthing center or centre is a healthcare facility, staffed by nurse-midwives, midwives and/or obstetricians, for mothers in labor, who may be assisted by doulas and coaches. By attending the laboring mother, the doulas can assist the midwives and make the birth easier. The midwives monitor the...
, and usually attended by a midwife or lay attendant with expertise in managing home births.
Women with access to high-quality medical care may choose home birth because they prefer the intimacy of a home and family-centered experience or desire to avoid a medically-centered experience typical of a hospital or clinical setting. Professionals attending home births can be obstetricians, certified nurse midwives and doulas . Home birth was, until the advent of modern medicine, the only method of delivery. In developing countries, where women may not be able to afford medical care or it may not be accessible to them, a home birth may be the only option available, and the woman may or may not be assisted by an attendant of any kind.
The safety of home birth has been a subject of some controversy, especially among professional physicians groups in the U.S. A number of studies have shown that the safety of an attended home birth for low-risk women is equal to the risks of giving birth in the hospital or a birthing center, though the quality and reliability of the available data has been called into question. The American Medical Association
American Medical Association
The American Medical Association , founded in 1847 and incorporated in 1897, is the largest association of medical doctors and medical students in the United States.-Scope and operations:...
and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists oppose home birth on the basis that a seemingly uncomplicated birth can still potentially become a medical emergency without warning, and they assert that home birth makes the birth experience a greater priority than safety.
Legal regulations in some Western nations, especially the United States, limit a woman's ability to choose an attended home birth. Attended home births are supported in much of Europe.
The majority of all infants in developing countries are born at home with mothers attended by lay midwives, nurse/midwives, or family members but due to poor medical care and other cultural and socio-economic reasons, the risks of perinatal death
Perinatal mortality
Perinatal mortality , also perinatal death, refers to the death of a fetus or neonate and is the basis to calculate the perinatal mortality rate. Variations in the precise definition of the perinatal mortality exist specifically concerning the issue of inclusion or exclusion of early fetal and...
or maternal death
Maternal death
Maternal death, or maternal mortality, also "obstetrical death" is the death of a woman during or shortly after a pregnancy. In 2010, researchers from the University of Washington and the University of Queensland in Brisbane, Australia, estimated global maternal mortality in 2008 at 342,900 , of...
are very high.
Types of home births
Home births are either attended or unattended. Women are attended when they are assisted through labor and birth by a professional, usually a midwife, and rarely a general practitionerGeneral practitioner
A general practitioner is a medical practitioner who treats acute and chronic illnesses and provides preventive care and health education for all ages and both sexes. They have particular skills in treating people with multiple health issues and comorbidities...
. Women who are unassisted or only attended by a lay person, perhaps their spouse, family, friend, or a non-professional birth attendant
Doula
A Doula is someone who provides non-medical support to women and their families during labour and childbirth, and also the postpartum period. The term can also be used to describe other supportive roles for other life events such as abortion, death and more....
, are sometimes called freebirths.
Factors in opting for a home birth
Many women choose home birth because delivering a baby in familiar surroundings is important to them. Others choose home birth because they dislike a hospital or birthing center environment, do not like a medically-centered birthing experience, are concerned about exposing the infant to hospital-borne pathogens, or dislike the presence of strangers at the birth. Others prefer home birth because they feel it is more natural and less stressful. In a study published in the Journal of Midwifery and Women's Health, women were asked, Why did you choose a home birth? The top five reasons given were safety, avoidance of unnecessary medical interventions common in hospital births, previous negative hospital experiences, more control, and a comfortable and familiar environment.One study found that women experience pain inherent in birth differently, and less negatively, in a home setting.
Many midwives are prepared with oxygen, if needed, to assist the mother or newborn. Midwives are usually trained to provide neonatal resuscitation, start intravenous solutions
Intravenous therapy
Intravenous therapy or IV therapy is the infusion of liquid substances directly into a vein. The word intravenous simply means "within a vein". Therapies administered intravenously are often called specialty pharmaceuticals...
, and can administer oxytocin
Oxytocin
Oxytocin is a mammalian hormone that acts primarily as a neuromodulator in the brain.Oxytocin is best known for its roles in sexual reproduction, in particular during and after childbirth...
and other medications as needed to halt postpartum hemorrhaging. They carry the supplies needed and are trained to suture. Births necessitating other interventions must be transferred to a hospital. Home births do not offer access to pharmaceutical pain relief or pharmaceutical labor induction. They do not provide ready access to the equipment and supplies required for emergency cesarean section. Most midwives develop working relationships with obstetricians and hospitals in case these options become necessary. Depending on the midwifery practice, transfer rates range from 5% to 40%, with most studies citing a transfer rate of about 16%.
Home birth trends
Home birth was until the advent of modern medicine the de facto method of delivery.Developed countries
In many developed countries, home birth declined rapidly over the 20th century. In the United States home birth declined from 50% in 1938 to fewer than 1% in 1955; in the United Kingdom a similar but slower trend happened with approximately 80% of births occurring at home in the 1920s and only 1% in 1991. In Japan the change in birth location happened much later, but much faster: home birth was at 95% in 1950, but only 1.2% in 1975.The decline was due in large part to the expansion of private insurance coverage in the US and taxpayer-funded medical care in Europe and Canada, changes which included policies about where birth should take place. In addition, there was a large population migration from rural to urban areas, an increased accessibility to hospitals, and unwillingness by doctors to attend to women in their homes.
One doctor described birth in a working class home in the 1920s:
This experience is contrasted with a 1920s hospital birth by Adolf Weber:
Midwifery
Midwifery
Midwifery is a health care profession in which providers offer care to childbearing women during pregnancy, labour and birth, and during the postpartum period. They also help care for the newborn and assist the mother with breastfeeding....
, the practice supporting a natural approach to birth, enjoyed a revival in the United States during the 1970s. However, although there was a steep increase in midwife-attended births between 1975 to 2002 (from less than 1.0% to 8.1%), most of these births occurred in the hospital and the US rate of out-of-hospital birth has remained steady at 1% of all births since 1989 with 27.3% of these in a free-standing birth center
Birthing center
A birthing center or centre is a healthcare facility, staffed by nurse-midwives, midwives and/or obstetricians, for mothers in labor, who may be assisted by doulas and coaches. By attending the laboring mother, the doulas can assist the midwives and make the birth easier. The midwives monitor the...
and 65.4% in a residence. Hence, the actual rate of home birth in the United States has remained remarkably low (0.65%) over the past twenty years.
Home birth in the United Kingdom has also received some press over the past few years as there has been a movement, most notably in Wales, to increase home birth rates to 10% by 2007. Between 2005 to 2006, there was an increase of 16% of home birth rates in Wales, but the total home birth rate is still 3% even in Wales (double the national rate) and in some other counties of Great Britain the home birth rate is still under 1%. In Australia, birth at home has fallen steadily over the years and is currently 0.3%, ranging from nearly 1% in the Northern Territory
Northern Territory
The Northern Territory is a federal territory of Australia, occupying much of the centre of the mainland continent, as well as the central northern regions...
to 0.1% in Queensland
Queensland
Queensland is a state of Australia, occupying the north-eastern section of the mainland continent. It is bordered by the Northern Territory, South Australia and New South Wales to the west, south-west and south respectively. To the east, Queensland is bordered by the Coral Sea and Pacific Ocean...
. The New Zealand
New Zealand
New Zealand is an island country in the south-western Pacific Ocean comprising two main landmasses and numerous smaller islands. The country is situated some east of Australia across the Tasman Sea, and roughly south of the Pacific island nations of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga...
rate for births at home is nearly three times Australia's with a rate of 2.5% and increasing.
In the Netherlands, an opposite trend has taken place: in 1965, two-thirds of Dutch births took place at home, but that figure has dropped to less than a third—about 30%.
In Korea, well-known Actress Kim Se-ah-I made headlines in January 2010 when she delivered a baby girl at home. Less than one percent of Korean infants are born at home.
Research on safety

In 2007, after a comprehensive review of the literature, the UK's National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
The National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence is a special health authority of the English National Health Service , serving both English NHS and the Welsh NHS...
(NICE) expressed concern for the lack of quality evidence comparing the potential risks and benefits of home and hospital birthing environments. Their report also noted that intrapartum-related perinatal mortality was low in all settings. In conclusion, the report recommended that women should be offered the choice of planning birth at home, in a midwifery unit or in an obstetric unit, and informed of the potential risks and benefits of each birth setting.
The NICE report concluded that women who give birth at home are more likely to deliver vaginally and to have greater satisfaction from the experience when compared with women who plan to give birth in a hospital. The report compared women's home birth experience to birth in a consultant-led unit. It concluded that the consultant-led setting increased the likelihood that the woman would receive analgesia
Analgesic
An analgesic is any member of the group of drugs used to relieve pain . The word analgesic derives from Greek an- and algos ....
, obstetrical intervention and a delivery using instruments, and decreased the woman's satisfaction with the experience. It reported that women who give birth at home may experience an equal or lower risk of perinatal mortality equal when they receive care in a consultant-led unit.
Since the 2007 review, a study of 529,688 low-risk planned home and hospital births was reported in the British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology in 2009. The study concluded:
Further, the study noted there was evidence that "low risk women with a planned home birth are less likely to experience referral to secondary care and subsequent obstetric interventions than those with a planned hospital birth." The study has been criticised on several grounds, including that some data might be missing and that the findings may not be representative of other populations.
In North America, a 2005 study found "similar mortality rates for low-risk hospital births and planned home births." The study found that mothers who gave birth at home were less likely to require medical interventions like a caesarean section
Caesarean section
A Caesarean section, is a surgical procedure in which one or more incisions are made through a mother's abdomen and uterus to deliver one or more babies, or, rarely, to remove a dead fetus...
or forceps delivery
Forceps in childbirth
Forceps are a surgical instrument that resembles a pair of tongs and can be used in surgery for grabbing, maneuvering, or removing various things within or from the body...
. About 12 percent of women intending to give birth at home needed to be transferred to the hospital for reasons such as a difficult labor or pain relief. However, women in the study were more likely to already have had a child, tended to be older, of lower socioeconomic classes, better educated, and less likely to be African-American or Hispanic.
A 2010 meta-analysis of studies which compared home births with planned hospital births among healthy, low-risk mothers in industrialized countries found no difference in the home and hospital rates of perinatal death, but also found that "planned home birth is associated with a tripling of the neonatal mortality rate." The authors wrote that they found this increase "striking" since women planning home births generally had fewer risk factors than those planning hospital births — lower rates of obesity, fewer prior Caesarean sections, and fewer previous pregnancy complications. This study was controversial for many reasons, most notably that it included a large U.S. study that contained both planned and unplanned home births, the latter of which are known to have much higher rates of perinatal mortality.
Study design
Randomized controlled trials are the "gold standard" of research methodology with respect to applying findings to populations; however, such a study design is not feasible or ethical for location of birth. The studies that do exist, therefore, tend to be cohort studies conducted either retrospectively (by selecting hospital records that match the characteristics of the home birth records), by matched pairs (by pairing study participants based on their background characteristics), or by using multivariate analysis to control for background variables. The Midwives Alliance of North America is collecting prospective data from out of hospital births for future research.There are many differences between women who choose to give birth at home versus in hospital. There are unquantifiable differences in home birth patients, such as maternal attitudes towards medical involvement in birth, and demographically, home birth patients tend towards being more multiparous
Parity (medicine)
In biology, parity is a technical term that refers to the number of times a female has given birth to a fetus.It can lead to some ambiguity for events occurring between 20 and 24 weeks, and for multiple pregnancies.-Enumeration:...
, less ethnic minorities, attend more prenatal visits, be slightly taller and lighter, of better educational background, and have fewer previous obstetric complications, including cesarean sections. None of the studies conducted were able to study a large enough group of matched births to make definitive statements concerning perinatal mortality and other rare complications.
The Cochrane database
Cochrane Library
The Cochrane Library is a collection of databases in medicine and other healthcare specialties provided by the Cochrane Collaboration and other organisations. At its core is the collection of Cochrane Reviews, a database of systematic reviews and meta-analyses which summarize and interpret the...
, first published in 1998, is a study of Home versus hospital birth, Systematically reviewed in May 2010, it "found only one small trial, which provided no strong evidence to favour either planned hospital birth or planned home birth for low-risk pregnant women."
However, in a study of over four hundred Cochrane entries, C. H. Hofmeyr reported that, "The relative benefits and risks of different settings are difficult to quantify. For a woman and her baby with no complications, the risk of an unexpected adverse event during a home birth may be smaller than risks specific to hospitalization, such as hospital-acquired infections."
Olsen and Jewell (2000), the authors of the systematic review also state: "In countries where it is possible to establish a home birth service backed up by a modern hospital system, all low-risk women should be offered the possibility of considering a planned home birth...." (Olsen & Jewell: 2000 (CD000352) in Buckley:2005:230).
Maternal safety
Evaluations of maternal safety are based on studies of developed countries where professionals are available to attend to women giving birth at home. Women who do not receive prenatal care and give birth unattended have a much higher risk for maternal deathMaternal death
Maternal death, or maternal mortality, also "obstetrical death" is the death of a woman during or shortly after a pregnancy. In 2010, researchers from the University of Washington and the University of Queensland in Brisbane, Australia, estimated global maternal mortality in 2008 at 342,900 , of...
s and perinatal mortality
Perinatal mortality
Perinatal mortality , also perinatal death, refers to the death of a fetus or neonate and is the basis to calculate the perinatal mortality rate. Variations in the precise definition of the perinatal mortality exist specifically concerning the issue of inclusion or exclusion of early fetal and...
.
All medical interventions were substantially decreased in the home birth sample, including the use of any pain medication or analgesics including epidural
Epidural
The term epidural is often short for epidural analgesia, a form of regional analgesia involving injection of drugs through a catheter placed into the epidural space...
s, forceps
Forceps in childbirth
Forceps are a surgical instrument that resembles a pair of tongs and can be used in surgery for grabbing, maneuvering, or removing various things within or from the body...
or vacuum extraction
Ventouse
Ventouse is a vacuum device used to assist the delivery of a baby when the second stage of labour has not progressed adequately. It is an alternative to a forceps delivery and caesarean section. It cannot be used when the baby is in the breech position or for premature births. This technique is...
, episiotomy
Episiotomy
An episiotomy , also known as perineotomy, is a surgically planned incision on the perineum and the posterior vaginal wall during second stage of labor. The incision, which can be midline or at an angle from the posterior end of the vulva, is performed under local anaesthetic , and is sutured...
and cesarean sections. Accordingly, the likelihood of normal vaginal birth was also greatly increased in the home birth sample. The studies were able to establish that there was no difference between the home birth and the hospital birth groups in the incidence of pre-eclampsia
Pre-eclampsia
Pre-eclampsia or preeclampsia is a medical condition in which hypertension arises in pregnancy in association with significant amounts of protein in the urine....
, premature rupture of membranes, or premature birth
Premature birth
In humans preterm birth refers to the birth of a baby of less than 37 weeks gestational age. The cause for preterm birth is in many situations elusive and unknown; many factors appear to be associated with the development of preterm birth, making the reduction of preterm birth a challenging...
. Except in the 1989-1992 Zurich
Zürich
Zurich is the largest city in Switzerland and the capital of the canton of Zurich. It is located in central Switzerland at the northwestern tip of Lake Zurich...
study. the length of labor tended to be longer during home birth, which is unsurprising given the fivefold lower incidence of labor induction in the home birth populations.
In terms of maternal outcome, no study found any statistically significant difference between the number of women that had third-degree perineal lacerations or postpartum hemorrhage
Obstetrical hemorrhage
Obstetrical hemorrhage refers to heavy bleeding during pregnancy, labor, or the puerperium. Bleeding may be vaginal and external, or, less commonly but more dangerously, internal, into the abdominal cavity...
. However, the 1998-1999 British Columbia
British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost of Canada's provinces and is known for its natural beauty, as reflected in its Latin motto, Splendor sine occasu . Its name was chosen by Queen Victoria in 1858...
study did find a three- to fourfold less likelihood of infection for both the infant and the mother, and all studies reported a substantially higher likelihood of an intact perineum
Perineum
In human anatomy, the perineum is a region of the body including the perineal body and surrounding structures...
in the home birth sample.
Infant safety
Perinatal outcome is more complicated to assess due to the low incidence of mortality and the subjectivity of Apgar scoringApgar score
The Apgar score was devised in 1952 by the eponymous Dr. Virginia Apgar as a simple and repeatable method to quickly and summarily assess the health of newborn children immediately after birth...
. Most studies found a slight, but statistically significant, difference in Apgar score for infants at five minutes. However, the 1994 UK National Birthday Trust study found a slight advantage for home birthed infants at one minute and no difference at five minutes. No cohort study has conducted long-term follow up on the infants. The perinatal mortality figure still remains controversial. The Zurich study showed an equal perinatal death rate between the home birth group and the hospital birth group (2.3 / 1000), and the Birthday Trust study found a slightly higher perinatal death rate in the hospital birth group (1 / 1000 vs. 0.8/1000). However, two other studies found a slightly higher perinatal mortality in the home birth group as compared to the hospital birth group. None of these results were seen to be statistically significant, since the actual mortality rate and the sample sizes were both so low, these figures have been the subject of much debate regarding the relative safety of home birth compared to hospital birth.
Legal situation
While a woman in developed countries may choose to deliver her child at home, in a birthing center, or at hospital, legal issues influence her options.Australia
In April 2007, the Western Australian Government expanded coverage for birth at home across the State. Other state governments in Australia, including the Northern Territory, New South Wales and South Australia, also provide government funding for independent, private home birth.The 2009 Federal Budget provided additional funds to Medicare to allow more midwives to work as private practitioners, allow midwives to prescribe medication under the Medicare Benefits Schedule, and assist them with medical indemnity insurance. However, this plan only covers hospital births. There are no current plans to extend Medicare and PBS funding to home birth services in Australia.
As of July 2010, all health professionals must show proof of liability insurance. Midwives who attend home births will be excluded from the indemnity requirement for two years while the government seeks to make affordable insurance available.
Canada
Public health coverage of home birth services varies from province to province as does the availability of doctors and midwives providing home birth services. The Provinces of Ontario, British Columbia, Saskatchewan, Manitoba, Alberta, and Quebec currently cover home birth services.A comprehensive four-year study of all home births attended by midwives in British Columbia, published in August 2009, found "Planned home birth attended by a registered midwife was associated with very low and comparable rates of perinatal death and reduced rates of obstetric interventions and other adverse perinatal outcomes compared with planned hospital birth attended by a midwife or physician."
United Kingdom
There are few legal issues with a home birth in the UK. There is no way a woman can be forced to go to hospital, if she does not want to. Both the RCM (Royal College of MidwivesRoyal College of Midwives
The Royal College of Midwives is a British midwives organisation which has existed under its present name since 1947.-History:The Matrons' Aid Society, renamed the Midwives' Institute in 1881, was founded by Louisa Hubbard and Zepharina Veitch to raise the training and status of midwives...
) and the RCOG (Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists
Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists
The Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists is a professional association based in the UK. Its members, including people with and without medical degrees, work in the field of obstetrics and gynaecology, that is, pregnancy, childbirth, and female sexual and reproductive health...
) support home births where there are no expected complications. The support of the various Health Authorities of the National Health Service
National Health Service
The National Health Service is the shared name of three of the four publicly funded healthcare systems in the United Kingdom. They provide a comprehensive range of health services, the vast majority of which are free at the point of use to residents of the United Kingdom...
may vary, but in general the Government is pro home birth - the Parliamentary Under-Secretary of State for Health, Lord Hunt of King's Heath
Philip Hunt, Baron Hunt of Kings Heath
Philip Hunt, Baron Hunt of Kings Heath OBE, PC is a former health administrator and a Labour member of the House of Lords.-Early life and career:...
has stated
and
United States
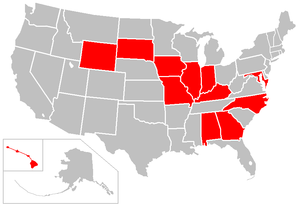
Practising as a direct-entry midwife is still (as of May 2006) illegal under certain circumstances in Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly referred to as Washington, "the District", or simply D.C., is the capital of the United States. On July 16, 1790, the United States Congress approved the creation of a permanent national capital as permitted by the U.S. Constitution....
and the following states: Alabama
Alabama
Alabama is a state located in the southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Tennessee to the north, Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gulf of Mexico to the south, and Mississippi to the west. Alabama ranks 30th in total land area and ranks second in the size of its inland...
, Georgia
Georgia (U.S. state)
Georgia is a state located in the southeastern United States. It was established in 1732, the last of the original Thirteen Colonies. The state is named after King George II of Great Britain. Georgia was the fourth state to ratify the United States Constitution, on January 2, 1788...
, Hawaii
Hawaii
Hawaii is the newest of the 50 U.S. states , and is the only U.S. state made up entirely of islands. It is the northernmost island group in Polynesia, occupying most of an archipelago in the central Pacific Ocean, southwest of the continental United States, southeast of Japan, and northeast of...
, Illinois
Illinois
Illinois is the fifth-most populous state of the United States of America, and is often noted for being a microcosm of the entire country. With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and great agricultural productivity in central and northern Illinois, and natural resources like coal,...
, Indiana
Indiana
Indiana is a US state, admitted to the United States as the 19th on December 11, 1816. It is located in the Midwestern United States and Great Lakes Region. With 6,483,802 residents, the state is ranked 15th in population and 16th in population density. Indiana is ranked 38th in land area and is...
, Iowa
Iowa
Iowa is a state located in the Midwestern United States, an area often referred to as the "American Heartland". It derives its name from the Ioway people, one of the many American Indian tribes that occupied the state at the time of European exploration. Iowa was a part of the French colony of New...
, Kentucky
Kentucky
The Commonwealth of Kentucky is a state located in the East Central United States of America. As classified by the United States Census Bureau, Kentucky is a Southern state, more specifically in the East South Central region. Kentucky is one of four U.S. states constituted as a commonwealth...
, Maryland
Maryland
Maryland is a U.S. state located in the Mid Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware to its east...
, North Carolina
North Carolina
North Carolina is a state located in the southeastern United States. The state borders South Carolina and Georgia to the south, Tennessee to the west and Virginia to the north. North Carolina contains 100 counties. Its capital is Raleigh, and its largest city is Charlotte...
, South Dakota
South Dakota
South Dakota is a state located in the Midwestern region of the United States. It is named after the Lakota and Dakota Sioux American Indian tribes. Once a part of Dakota Territory, South Dakota became a state on November 2, 1889. The state has an area of and an estimated population of just over...
and Wyoming
Wyoming
Wyoming is a state in the mountain region of the Western United States. The western two thirds of the state is covered mostly with the mountain ranges and rangelands in the foothills of the Eastern Rocky Mountains, while the eastern third of the state is high elevation prairie known as the High...
. However, Certified Nurse Midwives can legally practise in these areas.
No state prosecutes mothers for giving birth outside a hospital.
Hungary
In Hungary home birth is not illegal but midwives are refused certification to aid it. Ágnes GerébÁgnes Geréb
Ágnes Geréb is a Hungarian gynaecologist/midwife, the pioneer of father's participation in deliveries at hospital and homebirth in Hungary. She founded the Napvilág birthing centre...
, an obstetrician and midwife, and main promoter of home birth in Hungary, is currently on trial.
Celebrities who chose Home Birth
Bimba Bosé (Spain),Carla Conte (Argentina),
Cindy Crawford
Cindy Crawford
Cynthia Ann "Cindy" Crawford is an American model. Known for her trademark mole just above her lip, Crawford has adorned hundreds of magazine covers throughout her career. She was named #3 on VH1's 40 Hottest Hotties of the 90s...
(USA),
Demi Moore
Demi Moore
Demi Guynes Kutcher , known professionally as Demi Moore, is an American actress. After minor roles in film and a role in the soap opera General Hospital, Moore established her career in films such as St...
(USA),
Gisele Bündchen
Gisele Bündchen
Gisele Caroline Bündchen is a Brazilian fashion model, occasional film actress and goodwill ambassador for the UN Environment Programme.In the late 1990s, Bündchen became one of the first in a wave of Brazilian models to find success...
(Brasil),
Gwyneth Paltrow
Gwyneth Paltrow
Gwyneth Kate Paltrow is an American actress and singer. She made her acting debut on stage in 1990 and started appearing in films in 1991. After appearing in several films throughout the decade, Paltrow gained early notice for her work in films such as Se7en and Emma...
(USA),
Julianne Moore
Julianne Moore
Julianne Moore is an American actress and a children's book author. Throughout her career, she has been nominated for four Oscars, six Golden Globes, three BAFTAs and nine Screen Actors Guild Awards....
(USA),
Kelly Preston
Kelly Preston
Kelly Preston is an American actress and former model.- Early years :Preston was born Kelly Kamalelehua Smith in Honolulu, Hawaii. Her mother, Linda, was an administrator of a mental health center, and her father, who worked for an agricultural firm, drowned when Preston was three years old...
(USA) wife of John Travolta
John Travolta
John Joseph Travolta is an American actor, dancer and singer. Travolta first became known in the 1970s, after appearing on the television series Welcome Back, Kotter and starring in the box office successes Saturday Night Fever and Grease...
,
Lisa Bonet
Lisa Bonet
Lisa Bonet , also known as Lilakoi Moon, is an American actress. She is best known for her role as Denise Huxtable Kendall on the long-running NBC sitcom The Cosby Show, and originally starring in its spinoff A Different World.-Early life:Bonet was born in San Francisco, California...
(USA) wife of Lenny Kravitz
Lenny Kravitz
Leonard Albert "Lenny" Kravitz is an American singer-songwriter, multi-instrumentalist, record producer and arranger, whose "retro" style incorporates elements of rock, soul, R&B, funk, reggae, hard rock, psychedelic, folk and ballads...
,
Maria Bello
Maria Bello
Maria Elena Bello is an American actress and singer known for her appearances in the movies Coyote Ugly, The Jane Austen Book Club, Permanent Midnight, Thank You for Smoking, A History of Violence, Payback, and The Mummy: Tomb of the Dragon Emperor. For television she is known for her role as Dr...
(USA),
Mary Lynn Rajskub
Mary Lynn Rajskub
Mary Lynn Rajskub is an American actress and comedian, best known for her leading role as Chloe O'Brian on the Fox action-thriller 24.-Early life:...
(USA),
Meryl Streep
Meryl Streep
Mary Louise "Meryl" Streep is an American actress who has worked in theatre, television and film.Streep made her professional stage debut in 1971's The Playboy of Seville, before her screen debut in the television movie The Deadliest Season in 1977. In that same year, she made her film debut with...
(USA),
Nelly Furtado
Nelly Furtado
Nelly Kim Furtado is a Canadian singer-songwriter, record producer and actress. Furtado grew up in Victoria, British Columbia, Canada.Furtado first gained fame with her debut album, Whoa, Nelly!, and its single "I'm Like a Bird", which won a 2001 Juno Award for Single of the Year and a 2002 Grammy...
(Canada),
Pamela Anderson
Pamela Anderson
Pamela Denise Anderson is a Canadian-American actress, model, producer, author, activist, and former showgirl, known for her roles on the television series Home Improvement, Baywatch, and V.I.P. She was chosen as a Playmate of the Month for Playboy magazine in February 1990...
(Canada),
Patricia Arquette
Patricia Arquette
Patricia T. Arquette is an American actress and director. She played the lead character in the supernatural drama series Medium for which she won the Primetime Emmy Award for Outstanding Lead Actress in a Drama Series....
(USA), Ricki Lake
Ricki Lake
Ricki Pamela Lake is an American actress, producer, and television host. She is best known for her starring role as Tracy Turnblad in the original Hairspray, her ground-breaking documentary film The Business of Being Born, and her talk show which was broadcasted internationally from...
(USA).
Material regarding safety and risk relating to birth
- Obstetric Myths versus Research Realities - a guide to the medical literature, Henci GoerHenci GoerHenci Goer is an American author who writes about pregnancy and childbirth from an evidence-based perspective. She is the author of The Thinking Woman's Guide to a Better Birth. Her previous book, Obstetric Myths Versus Research Realities is a resource for childbirth professionals...
, Bergin & Gavey, 1998 - The Thinking Woman's Guide to a Better Birth, Henci GoerHenci GoerHenci Goer is an American author who writes about pregnancy and childbirth from an evidence-based perspective. She is the author of The Thinking Woman's Guide to a Better Birth. Her previous book, Obstetric Myths Versus Research Realities is a resource for childbirth professionals...
- Pursuing the Birth Machine - the search for appropriate birth technology, Marsden Wagner, Ace Graphics, 1988
Material against home birth
The position of The American College of Obstetricians and GynecologistsSee also
- ChildbirthChildbirthChildbirth is the culmination of a human pregnancy or gestation period with the birth of one or more newborn infants from a woman's uterus...
- MidwiferyMidwiferyMidwifery is a health care profession in which providers offer care to childbearing women during pregnancy, labour and birth, and during the postpartum period. They also help care for the newborn and assist the mother with breastfeeding....
- Birth attendantBirth attendantA birth attendant, also known as “skilled birth attendant” , is a midwife, physician, obstetrician, nurse, or other health care professional who provides basic and emergency health care services to women and their newborns during pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period...
- DoulaDoulaA Doula is someone who provides non-medical support to women and their families during labour and childbirth, and also the postpartum period. The term can also be used to describe other supportive roles for other life events such as abortion, death and more....
- Natural childbirthNatural childbirthNatural Childbirth is a philosophy of childbirth that is based on the notion that women who are adequately prepared are innately able to give birth without routine medical interventions. Natural childbirth arose in opposition to the techno-medical model of childbirth that has recently gained...
- NursingBreastfeedingBreastfeeding is the feeding of an infant or young child with breast milk directly from female human breasts rather than from a baby bottle or other container. Babies have a sucking reflex that enables them to suck and swallow milk. It is recommended that mothers breastfeed for six months or...
- PregnancyPregnancyPregnancy refers to the fertilization and development of one or more offspring, known as a fetus or embryo, in a woman's uterus. In a pregnancy, there can be multiple gestations, as in the case of twins or triplets...
External links
- Home Birth Pools Resource Resource for advice on home birth products.
- International Models of Maternity Care Report on maternity care released in Scotland, 2002, includes summary of how maternity care is dealt with in other countries besides the UK. Expert Group on Acute Maternity Services: Reference Report
- Intrapartum Care Guidelines (2007) National Center for Health and Clinical Excellence, an independent health care monitoring organization in the UK, reviewing the home birth literature.
- Home Birth Reference Site, Index of Research on Home Birth
- Home Birth American Pregnancy Association, brief article outlining the pros and cons of home birth
- General Aspects of Labor World Health Organization, Care in Normal Birth: A practical guide, Chapter 2, 1997.
- ACOG Statement on Home Birth American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Reiterates its long-standing opposition to home births (Feb 6, 2008)
- Canadian Medical Association Journal, Outcomes of planned home birth with registered midwife versus planned hospital birth with midwife or physician—Jansen et al., 10.1503/cmaj.081869, August 2009. This was a 4-year study of all home births with midwives in British Columbia. Conclusion: Planned home birth attended by a registered midwife was associated with very low and comparable rates of perinatal death and reduced rates of obstetric interventions and other adverse perinatal outcomes compared with planned hospital birth attended by a midwife or physician.
- Profile of home birth pioneer Ina May Gaskin, The Guardian, September 2009
- Kirpalani, Neeta and Emily Jackson. "Birth Right." Southern Spaces, January 12, 2010, http://southernspaces.org/2010/birth-right.
- "Celebrity Homebirthers and Celebrity born at home"

