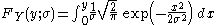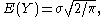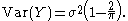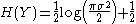Half-normal distribution
Encyclopedia
The half-normal distribution is the probability distribution
of the absolute value
of a random variable
that is normally distributed with expected value
0 and variance
σ2. I.e. if X is normally distributed with mean 0 and variance
σ2, then Y = |X| is half-normally distributed.
The cumulative distribution function
(CDF) is given by
Using the change-of-variables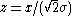 , the CDF can be written as
, the CDF can be written as
Probability distribution
In probability theory, a probability mass, probability density, or probability distribution is a function that describes the probability of a random variable taking certain values....
of the absolute value
Absolute value
In mathematics, the absolute value |a| of a real number a is the numerical value of a without regard to its sign. So, for example, the absolute value of 3 is 3, and the absolute value of -3 is also 3...
of a random variable
Random variable
In probability and statistics, a random variable or stochastic variable is, roughly speaking, a variable whose value results from a measurement on some type of random process. Formally, it is a function from a probability space, typically to the real numbers, which is measurable functionmeasurable...
that is normally distributed with expected value
Expected value
In probability theory, the expected value of a random variable is the weighted average of all possible values that this random variable can take on...
0 and variance
Variance
In probability theory and statistics, the variance is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out. It is one of several descriptors of a probability distribution, describing how far the numbers lie from the mean . In particular, the variance is one of the moments of a distribution...
σ2. I.e. if X is normally distributed with mean 0 and variance
Variance
In probability theory and statistics, the variance is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out. It is one of several descriptors of a probability distribution, describing how far the numbers lie from the mean . In particular, the variance is one of the moments of a distribution...
σ2, then Y = |X| is half-normally distributed.
The cumulative distribution function
Cumulative distribution function
In probability theory and statistics, the cumulative distribution function , or just distribution function, describes the probability that a real-valued random variable X with a given probability distribution will be found at a value less than or equal to x. Intuitively, it is the "area so far"...
(CDF) is given by
Using the change-of-variables
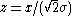 , the CDF can be written as
, the CDF can be written as-
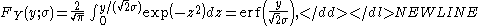
where erf(x) is the error functionError functionIn mathematics, the error function is a special function of sigmoid shape which occurs in probability, statistics and partial differential equations...
, a standard function in many mathematical software packages.
The expectation is then given by
The variance is given by
Since this is proportional to the variance σ2 of X, σ can be seen as a scale parameterScale parameterIn probability theory and statistics, a scale parameter is a special kind of numerical parameter of a parametric family of probability distributions...
of the new distribution.
The entropy of the half-normal distribution is exactly one bit less the entropy of a zero-mean normal distribution with the same second moment about 0. This can be understood intuitively since the magnitude operator reduces information by one bit (if the probability distribution at its input is even). Alternatively, since a half-normal distribution is always positive, the one bit it would take to record whether a standard normal random variable were positive (say, a 1) or negative (say, a 0) is no longer necessary. Thus,
Related distributions
- The distribution is a special case of the folded normal distributionFolded Normal DistributionThe folded normal distribution is a probability distribution related to the normal distribution. Given a normally distributed random variable X with mean μ and variance σ2, the random variable Y = |X| has a folded normal distribution. Such a case may be encountered if only the magnitude of some...
with μ = 0. - (Y/σ)^2 has a chi square distribution with 1 degree of freedom.
External links
- Half-Normal Distribution at MathWorldMathWorldMathWorld is an online mathematics reference work, created and largely written by Eric W. Weisstein. It is sponsored by and licensed to Wolfram Research, Inc. and was partially funded by the National Science Foundation's National Science Digital Library grant to the University of Illinois at...
-