
Habitability of red dwarf systems
Encyclopedia

Extraterrestrial life
Extraterrestrial life is defined as life that does not originate from Earth...
, as red dwarfs make up most stars in the Milky Way Galaxy. While the relatively little energy output, small habitable zone
Habitable zone
In astronomy and astrobiology, a habitable zone is an umbrella term for regions that are considered favourable to life. The concept is inferred from the empirical study of conditions favourable for Life on Earth...
s, probability of tidally locked planets, and high stellar variation are postulated impediments to habitability
Planetary habitability
Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia...
, the ubiquity and longevity of red dwarfs are possible positive factors.
Habitability around brown dwarf
Brown dwarf
Brown dwarfs are sub-stellar objects which are too low in mass to sustain hydrogen-1 fusion reactions in their cores, which is characteristic of stars on the main sequence. Brown dwarfs have fully convective surfaces and interiors, with no chemical differentiation by depth...
s, which are likely more numerous, is considered unlikely, since what little heat they emit is quickly dispersed.
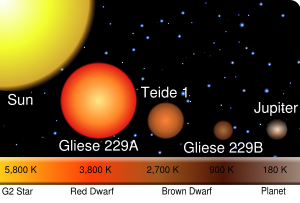
Red dwarf characteristics
Red dwarfs are the smallest, coolest, and most common type of star. Estimates of their abundance range from 70% to more than 90% of all stars in the galaxy, an often quoted median figure being 73%. Red dwarfs are either late K or M spectral type. Given their low energy output, red dwarfs are never visible by the unaided eye from Earth; neither the closest red dwarf star to the Sun when viewed individually, Proxima CentauriProxima Centauri
Proxima Centauri is a red dwarf star about 4.2 light-years distant in the constellation of Centaurus. It was discovered in 1915 by Robert Innes, the Director of the Union Observatory in South Africa, and is the nearest known star to the Sun, although it is too faint to be seen with the naked eye...
(which is also the closest star to the Sun), nor the closest solitary red dwarf, Barnard's star
Barnard's star
Barnard's Star, also known occasionally as Barnard's "Runaway" Star, is a very low-mass red dwarf star approximately six light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Ophiuchus . In 1916, the American astronomer E.E...
, is anywhere near visual magnitude.
Light emission and tidal lock
Nuclear reaction
In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, a nuclear reaction is semantically considered to be the process in which two nuclei, or else a nucleus of an atom and a subatomic particle from outside the atom, collide to produce products different from the initial particles...
s proceed exceptionally slowly and they emit very little light (from 3% of that produced by the Sun to as little as 0.01%). Any planet in orbit around a red dwarf would have to orbit very close to its parent star to attain Earth-like surface temperatures; from 0.3 AU (just inside the orbit of Mercury
Mercury (planet)
Mercury is the innermost and smallest planet in the Solar System, orbiting the Sun once every 87.969 Earth days. The orbit of Mercury has the highest eccentricity of all the Solar System planets, and it has the smallest axial tilt. It completes three rotations about its axis for every two orbits...
) for a star like Lacaille 8760, to as little as 0.032 AU
Astronomical unit
An astronomical unit is a unit of length equal to about or approximately the mean Earth–Sun distance....
for a star like Proxima Centauri
Proxima Centauri
Proxima Centauri is a red dwarf star about 4.2 light-years distant in the constellation of Centaurus. It was discovered in 1915 by Robert Innes, the Director of the Union Observatory in South Africa, and is the nearest known star to the Sun, although it is too faint to be seen with the naked eye...
(such a world would have a year lasting just 6.3 days).
Planets that are close enough to red dwarfs to receive a sufficient amount of radiation for liquid water are likely to have long been tidally locked to their respective stars so that the planet rotates only once for every time it completes an orbit; this means that one face always points at the star (creating perpetual day) and one face always points away (creating perpetual night). Potential life could be limited to a ring-like region, known as the terminator
Terminator (solar)
A terminator, twilight zone or "grey line" is a moving line that separates the illuminated day side and the dark night side of a planetary body...
, where the sun would always appear on the horizon.
Should the planet have a moon massive enough to hang on to an atmosphere, however, the moon could be tidally locked with the more massive planet instead of with the star, and as such it could have a day-and-night cycle, increasing chances of habitability on the moon. Tidal forces between the two bodies would also keep the centers of both the planet and its moon liquid, which should result in a strong enough magnetic field to protect the planet and its moon from outbursts coming from the parent star.
The tidally locked planet would likely need an atmosphere thick enough to transfer some of the star's heat from the day side to the night side; this would prevent the colder night side's atmospheric temperature from dropping below condensation point, causing a drop in atmospheric pressure that would draw more of the atmosphere towards the night side until all of the atmosphere gets frozen on the night side. It was long assumed that an atmosphere would need to be so thick as to impede photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a chemical process that converts carbon dioxide into organic compounds, especially sugars, using the energy from sunlight. Photosynthesis occurs in plants, algae, and many species of bacteria, but not in archaea. Photosynthetic organisms are called photoautotrophs, since they can...
from any plants on the day side surface. However, more recent research has suggested otherwise. A 2010 study concluded that Earth-like aquaplanets tidally locked to their stars would still have temperatures above -33 Celsius on the night side. Studies by Robert Haberle and Manoj Joshi of NASA
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...
's Ames Research Center in California have shown that a planet's atmosphere (assuming it included greenhouse gases CO2
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
and H2O) need only be 100 mb
Bar (unit)
The bar is a unit of pressure equal to 100 kilopascals, and roughly equal to the atmospheric pressure on Earth at sea level. Other units derived from the bar are the megabar , kilobar , decibar , centibar , and millibar...
, or 10% of Earth's atmosphere, for the star's heat to be effectively carried to the night side. This is well within the levels required for photosynthesis on the day side, though some of their models still had water frozen on the dark side. Martin Heath of Greenwich Community College
Greenwich Community College
Greenwich Community College is a post-secondary educational institution located in Greenwich, South East of Greater London, England.The Quad at Greenwich College's Plumstead Centre features a tropical fish pond and a cannon which dates back to when the College was a training provider for the Royal...
, has shown that seawater, too, could effectively circulate without freezing solid if the ocean basins were deep enough to allow free flow beneath the night side's ice cap. Geothermal heat might also help keep the lower parts of any ocean liquid. Further research—including a consideration of the amount of photosynthetically active radiation—has suggested that tidally locked planets in red dwarf systems might at least be habitable for higher plants.
Photosynthesis
Size and brightness are not the only factors in making red dwarfs potentially unsuitable for life. If the planet is tidally locked, on the day side, because the sun does not rise or set, areas in the shadows of mountains would remain so forever. Photosynthesis as we understand it would be complicated by the fact that a red dwarf produces most of its radiation in the infraredInfrared
Infrared light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of visible light, measured from the nominal edge of visible red light at 0.74 micrometres , and extending conventionally to 300 µm...
, and on the Earth the process depends on visible light. Photosynthesis on a red dwarf planet would require additional photons to achieve excitation potentials comparable to those needed in Earth photosynthesis for electron transfers, due to the lower average energy level of near-infrared photons compared to visible. Having to adapt to a far wider spectrum to gain the maximum amount of energy, foliage on a habitable red dwarf planet would probably appear black if viewed in visible light.
Weather conditions and habitability
Due to differential heating, a tidally locked planet would experience fierce winds blowing continually towards the night side with permanent torrential rain at the point directly opposite the local star, the solar pole. In the opinion of one author this makes complex life improbable. But the scientists who worked on the Aurelia and Blue MoonAurelia and Blue Moon
Aurelia and Blue Moon are hypothetical examples of a planet and a moon on which extraterrestrial life could evolve. They are the outcome of a collaboration between television company Blue Wave Productions Ltd. and a group of American and British scientists who were collectively commissioned by...
series disagree.
Plant life would have to adapt to this constant gale, e.g. by anchoring securely into the soil and sprouting long flexible leaves that do not snap. Plants would probably be less productive in the dim red sunlight, so consequently there would be less oxygen in the atmosphere and animal life would be constrained in size. Animals would likely rely on infrared vision as signaling by calls or scents would be difficult over the din of the planet-wide gale. Underwater life would, however, be protected from fierce winds and flares, and vast blooms of black photosynthetic plankton and algae could support the sea life. There may not even be enough water for habitable planets around many red dwarf stars.
Variability
Red dwarfs are far more variable and violent than their more stable, larger cousins. Often they are covered in starspotStarspot
Starspots are equivalent to sunspots but located on other stars. Spots the size of sunspots are very hard to detect since they are too small to cause fluctuations in brightness...
s that can dim their emitted light by up to 40% for months at a time. On Earth life has adapted in many ways to the similarly reduced temperatures of the winter. Life may survive by hibernating and/or by diving into deep water where temperatures could be more constant. More serious is that the oceans could perhaps freeze over during cold periods. After the cold has ended the planet’s albedo
Albedo
Albedo , or reflection coefficient, is the diffuse reflectivity or reflecting power of a surface. It is defined as the ratio of reflected radiation from the surface to incident radiation upon it...
would be higher causing light from the red dwarf to be reflected. This could cause conditions similar to Snowball Earth
Snowball Earth
The Snowball Earth hypothesis posits that the Earth's surface became entirely or nearly entirely frozen at least once, some time earlier than 650 Ma . Proponents of the hypothesis argue that it best explains sedimentary deposits generally regarded as of glacial origin at tropical...
so cold could last millions of years.
At other times, red dwarf stars emit gigantic flares that can double their brightness in a matter of minutes. Indeed, as more and more red dwarfs have been scrutinized for variability, more of them have been classified as flare stars to some degree or other. Such variation in brightness could be very damaging for life. Flares might also blow off sizable portions of the planet's atmosphere.
- "No one found any showstoppers to habitability," says Gibor Basri of the University of CaliforniaUniversity of CaliforniaThe University of California is a public university system in the U.S. state of California. Under the California Master Plan for Higher Education, the University of California is a part of the state's three-tier public higher education system, which also includes the California State University...
, Berkeley. One concern was that because M dwarfs frequently produce flares, the resulting torrents of charged particles could strip the atmosphere off any nearby planet. If the planet had a magnetic field, though, it would deflect the particles from the atmosphere. And even the slow rotation of a tidally locked M-dwarf planet—it spins once for every time it orbits its star—would be enough to generate a magnetic field as long as part of the planet's interior remained molten. http://www.sciam.com/article.cfm?id=red-star-rising
However, the violent flaring period of a red dwarf's lifecyle is estimated to only last roughly the first 1.2 billion years of its existence. If a planet forms far away from a red dwarf so as to avoid tidelock, and then migrates into the star's habitable zone after this turbulent initial period, it is possible that life may have a chance to develop.
Life could initially protect itself from radiation by remaining underwater until the star had passed through its early flare stage, assuming the planet could retain enough of an atmosphere to produce liquid oceans. The scientists who wrote Aurelia believed that life could survive on land despite a red dwarf star flaring. Once life reached onto land, the low amount of UV produced by a quiescent red dwarf means that life could thrive without an ozone layer, and thus never need to produce oxygen.
Other scientists disagree that red dwarf stars could sustain life. See Rare Earth hypothesis. Tidal-locking would likely result in a relatively low planetary magnetic moment
Magnetic moment
The magnetic moment of a magnet is a quantity that determines the force that the magnet can exert on electric currents and the torque that a magnetic field will exert on it...
. Active red dwarfs that emit coronal mass ejection
Coronal mass ejection
A coronal mass ejection is a massive burst of solar wind, other light isotope plasma, and magnetic fields rising above the solar corona or being released into space....
s would bow back the magnetosphere
Magnetosphere
A magnetosphere is formed when a stream of charged particles, such as the solar wind, interacts with and is deflected by the intrinsic magnetic field of a planet or similar body. Earth is surrounded by a magnetosphere, as are the other planets with intrinsic magnetic fields: Mercury, Jupiter,...
until it contacted the planetary atmosphere. As a result, the atmosphere would undergo strong erosion, possibly leaving the planet uninhabitable.
Abundance
There is, however, one major advantage that red dwarfs have over other stars as abodes for life: they live a long time. It took 4.5 billion years before humanity appeared on Earth, and life as we know it will see suitable conditions for as little as half a billion years more. Red dwarfs, by contrast, could live for trillions of years, because their nuclear reactions are far slower than those of larger stars, meaning that life both would have longer to evolve and longer to survive. Further, while the odds of finding a planet in the habitable zone around any specific red dwarf are unknown, the total amount of habitable zone around all red dwarfs combined is equal to the total amount around sun-like stars given their ubiquity. The first super-EarthSuper-Earth
A super-Earth is an extrasolar planet with a mass higher than Earth's, but substantially below the mass of the Solar System's gas giants. The term super-Earth refers only to the mass of the planet, and does not imply anything about the surface conditions or habitability...
with a mass of a 3 to 4 times that of the Earth's found in the potentially habitable zone
Habitable zone
In astronomy and astrobiology, a habitable zone is an umbrella term for regions that are considered favourable to life. The concept is inferred from the empirical study of conditions favourable for Life on Earth...
of its star is Gliese 581 g
Gliese 581 g
Gliese 581 g , also Gl 581 g or GJ 581 g, is a hypothesized extrasolar planet proven nonexistent by the Geneva Team, orbiting the red dwarf star Gliese 581, 20.5 light-years from Earth in the constellation of Libra. It is the sixth planet discovered in the Gliese 581 planetary system and the fourth...
, and its star, Gliese 581
Gliese 581
Gliese 581 is a red dwarf star with spectral type M3V, located 20.3 light years away from Earth in the constellation Libra. Its estimated mass is about a third of that of the Sun, and it is the 89th closest known star system to the Sun. Observations suggest that the star has at least six planets:...
, is indeed a red dwarf. Although tidally locked, it is thought possible that at its terminator
Terminator (solar)
A terminator, twilight zone or "grey line" is a moving line that separates the illuminated day side and the dark night side of a planetary body...
liquid water may well exist. The planet is thought to have existed for approximately 7 billion years and has a large enough mass to support an atmosphere.
Tidally locked planets in red dwarf systems in fiction
In Olaf StapledonOlaf Stapledon
William Olaf Stapledon was a British philosopher and author of several influential works of science fiction.-Life:...
's 1937 science fiction
Science fiction
Science fiction is a genre of fiction dealing with imaginary but more or less plausible content such as future settings, futuristic science and technology, space travel, aliens, and paranormal abilities...
novel Star Maker
Star Maker
-External links:*...
, one of the many alien civilizations in our galaxy he describes is one in the terminator zone of a tidally locked planet of a red dwarf system. This planet is inhabited by intelligent plants that look like carrot
Carrot
The carrot is a root vegetable, usually orange in colour, though purple, red, white, and yellow varieties exist. It has a crisp texture when fresh...
s with arms, legs, and a head that "sleep" part of the time by inserting themselves in soil
Soil
Soil is a natural body consisting of layers of mineral constituents of variable thicknesses, which differ from the parent materials in their morphological, physical, chemical, and mineralogical characteristics...
on plots of land and absorbing sunlight by photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a chemical process that converts carbon dioxide into organic compounds, especially sugars, using the energy from sunlight. Photosynthesis occurs in plants, algae, and many species of bacteria, but not in archaea. Photosynthetic organisms are called photoautotrophs, since they can...
, and that are awake part of the time, emerging from their plots of soil as locomoting beings who participate in all the complex activities of a modern industrial civilization. Stapledon also describes how life evolved on this planet.
See also
- AstrobiologyAstrobiologyAstrobiology is the study of the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe. This interdisciplinary field encompasses the search for habitable environments in our Solar System and habitable planets outside our Solar System, the search for evidence of prebiotic chemistry,...
- Aurelia and Blue MoonAurelia and Blue MoonAurelia and Blue Moon are hypothetical examples of a planet and a moon on which extraterrestrial life could evolve. They are the outcome of a collaboration between television company Blue Wave Productions Ltd. and a group of American and British scientists who were collectively commissioned by...
- Gliese 581 gGliese 581 gGliese 581 g , also Gl 581 g or GJ 581 g, is a hypothesized extrasolar planet proven nonexistent by the Geneva Team, orbiting the red dwarf star Gliese 581, 20.5 light-years from Earth in the constellation of Libra. It is the sixth planet discovered in the Gliese 581 planetary system and the fourth...
- Habitable zoneHabitable zoneIn astronomy and astrobiology, a habitable zone is an umbrella term for regions that are considered favourable to life. The concept is inferred from the empirical study of conditions favourable for Life on Earth...
- Planetary habitabilityPlanetary habitabilityPlanetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia...
- SETISETIThe search for extraterrestrial intelligence is the collective name for a number of activities people undertake to search for intelligent extraterrestrial life. Some of the most well known projects are run by the SETI Institute. SETI projects use scientific methods to search for intelligent life...

