
Gyroradius
Encyclopedia
The gyroradius is the radius
of the circular motion of a charged particle
in the presence of a uniform magnetic field
.
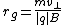
where
(All units are in SI
)
Similarly, the frequency
of this circular motion is known as the gyrofrequency or cyclotron frequency, and is given in radian/second by: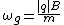
and in Hz by: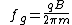
For electrons, this works out to be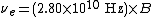
. In that case, the velocity and mass of the moving object has to be replaced by the relativistic momentum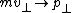 :
:
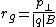
For rule-of-thumb calculations in accelerator
and astroparticle
physics, the physical quantities can be expressed in proper units, which results in the simple numerical formula
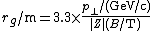
where
given by:
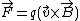
where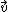 is the velocity vector,
is the velocity vector, 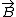 is the magnetic field vector, and
is the magnetic field vector, and 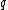 is the particle's electric charge
is the particle's electric charge
.
Notice that the direction of the force is given by the cross product
of the velocity and magnetic field. Thus, the Lorentz force will always act perpendicular to the direction of motion, causing the particle to move in a circle (gyrate
). The radius of this circle can be determined by equating the magnitude of the Lorentz force to the centripetal force
can be determined by equating the magnitude of the Lorentz force to the centripetal force
:

where is the particle mass
is the particle mass
(for high velocities the relativistic mass),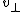 is the velocity component perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field, and
is the velocity component perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field, and is the strength of the field.
is the strength of the field.
Solving for , the gyroradius is determined to be:
, the gyroradius is determined to be: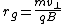
Thus, the gyroradius is directly proportional to the particle mass and velocity, and inversely proportional to the particle electric charge, and the magnetic field strength.
Radius
In classical geometry, a radius of a circle or sphere is any line segment from its center to its perimeter. By extension, the radius of a circle or sphere is the length of any such segment, which is half the diameter. If the object does not have an obvious center, the term may refer to its...
of the circular motion of a charged particle
Charged particle
In physics, a charged particle is a particle with an electric charge. It may be either a subatomic particle or an ion. A collection of charged particles, or even a gas containing a proportion of charged particles, is called a plasma, which is called the fourth state of matter because its...
in the presence of a uniform magnetic field
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
.
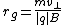
where
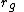 is the gyroradius,
is the gyroradius,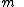 is the mass of the charged particle,
is the mass of the charged particle,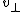 is the velocity component perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field,
is the velocity component perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field,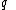 is the charge of the particle, and
is the charge of the particle, and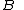 is the constant magnetic field.
is the constant magnetic field.
(All units are in SI
Si
Si, si, or SI may refer to :- Measurement, mathematics and science :* International System of Units , the modern international standard version of the metric system...
)
Similarly, the frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
of this circular motion is known as the gyrofrequency or cyclotron frequency, and is given in radian/second by:
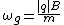
and in Hz by:
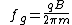
For electrons, this works out to be
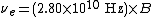
Relativistic case
The formula for the gyroradius also holds for relativistic motionSpecial relativity
Special relativity is the physical theory of measurement in an inertial frame of reference proposed in 1905 by Albert Einstein in the paper "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies".It generalizes Galileo's...
. In that case, the velocity and mass of the moving object has to be replaced by the relativistic momentum
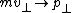 :
: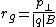
For rule-of-thumb calculations in accelerator
Particle accelerator
A particle accelerator is a device that uses electromagnetic fields to propel charged particles to high speeds and to contain them in well-defined beams. An ordinary CRT television set is a simple form of accelerator. There are two basic types: electrostatic and oscillating field accelerators.In...
and astroparticle
Astroparticle physics
Astroparticle physics, the same as particle astrophysics, is that branch of particle physics that studies elementary particles of astronomical origin, and their relation to astrophysics and cosmology. It is a relatively new field of research emerging at the intersection of particle physics,...
physics, the physical quantities can be expressed in proper units, which results in the simple numerical formula
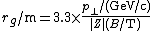
where
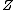 is the charge of the moving object in elementary units.
is the charge of the moving object in elementary units.
Derivation
If the charged particle is moving, then it will experience a Lorentz forceLorentz force
In physics, the Lorentz force is the force on a point charge due to electromagnetic fields. It is given by the following equation in terms of the electric and magnetic fields:...
given by:
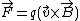
where
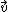 is the velocity vector,
is the velocity vector, 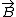 is the magnetic field vector, and
is the magnetic field vector, and 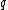 is the particle's electric charge
is the particle's electric chargeElectric charge
Electric charge is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter. Electric charge comes in two types, called positive and negative. Two positively charged substances, or objects, experience a mutual repulsive force, as do two...
.
Notice that the direction of the force is given by the cross product
Cross product
In mathematics, the cross product, vector product, or Gibbs vector product is a binary operation on two vectors in three-dimensional space. It results in a vector which is perpendicular to both of the vectors being multiplied and normal to the plane containing them...
of the velocity and magnetic field. Thus, the Lorentz force will always act perpendicular to the direction of motion, causing the particle to move in a circle (gyrate
Gyration
In geometry, a gyration is a type of rotation.The center of a rotational symmetry is a rotation point. A rotation point that does not lie on a mirror is called a gyration point. A rotocenter is a rotation point with an integral number of rotational symmetries.-See also:*Terms starting with...
). The radius of this circle
 can be determined by equating the magnitude of the Lorentz force to the centripetal force
can be determined by equating the magnitude of the Lorentz force to the centripetal forceCentripetal force
Centripetal force is a force that makes a body follow a curved path: it is always directed orthogonal to the velocity of the body, toward the instantaneous center of curvature of the path. The mathematical description was derived in 1659 by Dutch physicist Christiaan Huygens...
:

where
 is the particle mass
is the particle massMass
Mass can be defined as a quantitive measure of the resistance an object has to change in its velocity.In physics, mass commonly refers to any of the following three properties of matter, which have been shown experimentally to be equivalent:...
(for high velocities the relativistic mass),
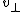 is the velocity component perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field, and
is the velocity component perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field, and is the strength of the field.
is the strength of the field.Solving for
 , the gyroradius is determined to be:
, the gyroradius is determined to be: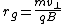
Thus, the gyroradius is directly proportional to the particle mass and velocity, and inversely proportional to the particle electric charge, and the magnetic field strength.

