
Gramme machine
Encyclopedia

Electrical generator
In electricity generation, an electric generator is a device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy. A generator forces electric charge to flow through an external electrical circuit. It is analogous to a water pump, which causes water to flow...
which produces direct current
Direct current
Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through...
, named for its Belgian inventor, Zénobe Gramme
Zénobe Gramme
Zénobe Théophile Gramme was a Belgian electrical engineer. He invented the Gramme machine, a type of direct current dynamo capable of generating smoother and much higher voltages than the dynamos known to that point.In 1873 he and Hippolyte Fontaine accidentally discovered that the device was...
, and was built as either a dynamo or a magneto
Magneto
A magneto is a type of electrical generator.Magneto may also refer to:* Magneto , permanent magnetic alternating current rotary generator* ignition magneto, magnetos on internal combustion engines...
. It was the first generator to produce power on a commercial scale for industry. Inspired by a machine invented by Antonio Pacinotti
Antonio Pacinotti
Antonio Pacinotti was an Italian physicist, who was Professor of Physics at the University of Pisa.-Biography:Pacinotti was born in Pisa, where he also died...
in 1860, Gramme was the developer of a new induced rotor in form of a wire-wrapped ring (Gramme ring) and demonstrated this apparatus to the Academy of Sciences
Academy of Sciences
An Academy of Sciences is a national academy or another learned society dedicated to sciences.In non-English speaking countries, the range of academic fields of the members of a national Academy of Science often includes fields which would not normally be classed as "science" in English...
in Paris
Paris
Paris is the capital and largest city in France, situated on the river Seine, in northern France, at the heart of the Île-de-France region...
in 1871.
Description
The Gramme machine used a ring armature, i.e., a series of thirty armatureArmature (electrical engineering)
In electrical engineering, an armature generally refers to one of the two principal electrical components of an electromechanical machine–generally in a motor or generator, but it may also mean the pole piece of a permanent magnet or electromagnet, or the moving iron part of a solenoid or relay....
coil
Coil
A coil is a series of loops. A coiled coil is a structure in which the coil itself is in turn also looping.-Electromagnetic coils:An electromagnetic coil is formed when a conductor is wound around a core or form to create an inductor or electromagnet...
s, wound around a revolving ring of soft iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
. The coils are connected in series, and the junction between each pair is connected to a commutator
Commutator (electric)
A commutator is a rotary electrical switch in certain types of electric motors or electrical generators that periodically reverses the current direction between the rotor and the external circuit. In a motor, it applies power to the best location on the rotor, and in a generator, picks off power...
on which two brushes run. The permanent magnet
Magnet
A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets.A permanent magnet is an object...
s magnetize the soft iron ring, producing a magnetic field
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
which rotates around through the coils in order as the armature turns. This induces a voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
in two of the coils on opposite sides of the armature, which is picked off by the brushes.
Earlier electromagnetic
Electromagnetism
Electromagnetism is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three are the strong interaction, the weak interaction and gravitation...
machines passed a magnet near the poles of one or two electromagnets, creating brief spikes or pulses of DC resulting in a transient output of low average power, rather than a constant output of high average power.
With enough coils, the resulting voltage waveform is practically constant, thus producing a near direct current
Direct current
Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through...
supply. This type of machine needs only electromagnet
Electromagnet
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by the flow of electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off...
s producing the magnetic field to become a modern generator
Electrical generator
In electricity generation, an electric generator is a device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy. A generator forces electric charge to flow through an external electrical circuit. It is analogous to a water pump, which causes water to flow...
.
Invention of modern electric motor
During a demonstration at an industrial exposition in ViennaVienna
Vienna is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Austria and one of the nine states of Austria. Vienna is Austria's primary city, with a population of about 1.723 million , and is by far the largest city in Austria, as well as its cultural, economic, and political centre...
in 1873, Gramme accidentally discovered that this device, if supplied with a constant-voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
power supply, will act as an electric motor
Electric motor
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.Most electric motors operate through the interaction of magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors to generate force...
. Gramme's partner, Hippolyte Fontaine
Hippolyte Fontaine
Hippolyte Fontaine was a French engineer and electrician who worked with Zénobe Gramme on the development of the Gramme machine , and whose contributions were essential to the creation of the dynamo...
, carelessly connected the terminals of a Gramme machine to another dynamo which was producing electricity, and its shaft began to spin."Hippolyte Fontaine." Encyclopædia Britannica. 2010. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. 11 Jan. 2010
Electrical generator
In electricity generation, an electric generator is a device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy. A generator forces electric charge to flow through an external electrical circuit. It is analogous to a water pump, which causes water to flow...
s and helped usher in development of large-scale electrical devices.
Earlier designs of electric motors were notoriously inefficient because they had large, or very large, air gaps throughout much of the rotation of their rotors. Long air gaps create weak forces, resulting in low torque. A device called the St. Louis motor (still available from scientific supply houses), although not intended to, clearly demonstrates this great inefficiency, and seriously misleads students as to how real motors work. These early inefficient designs apparently were based on observing how magnets attracted ferromagnetic materials (such as iron and steel) from some distance away. It took a number of decades in the 19th century for electrical engineers to learn the importance of small air gaps. The Gramme ring, however, has a comparatively small air gap, which enhances its efficiency. (In the illustration, the large hoop-like piece is probably the permanent magnet; the Gramme ring is rather hard to see.)
Principle of Operation
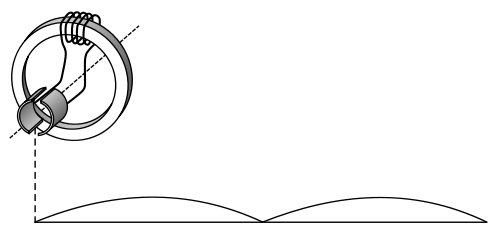
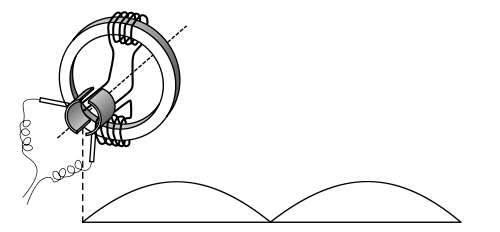

Phase (waves)
Phase in waves is the fraction of a wave cycle which has elapsed relative to an arbitrary point.-Formula:The phase of an oscillation or wave refers to a sinusoidal function such as the following:...
with each other. When coils A and A' are at maximum output, coils B and B' are at zero output.
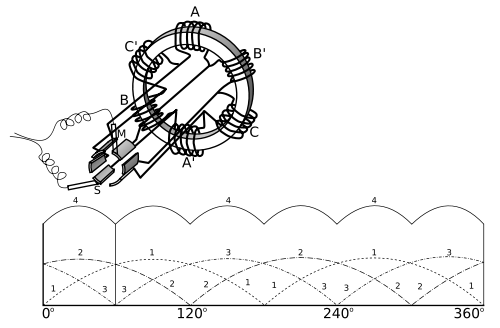
Modern Form of the Gramme Ring
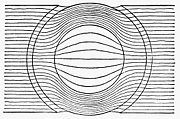
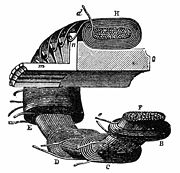
Initial attempts to insert a stationary field coil within the center of the ring to help the lines penetrate into the center proved too complex to engineer.


In small armatures a solid drum is often used simply for ease of construction, since the core can be easily formed from a stack of stamped metal disks keyed to lock into a slot on the shaft.
See also
- Electric generator
- Electric motorElectric motorAn electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.Most electric motors operate through the interaction of magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors to generate force...
- DynamoDynamo- Engineering :* Dynamo, a magnetic device originally used as an electric generator* Dynamo theory, a theory relating to magnetic fields of celestial bodies* Solar dynamo, the physical process that generates the Sun's magnetic field- Software :...
- AlternatorAlternatorAn alternator is an electromechanical device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current.Most alternators use a rotating magnetic field but linear alternators are occasionally used...
- Rotary converterRotary converterA rotary converter is a type of electrical machine which acts as a mechanical rectifier or inverter. It was used to convert AC to DC or DC to AC power before the advent of chemical or solid state power rectification...
- Excitation (magnetic)Excitation (magnetic)An electric generator or electric motor consists of a rotor spinning in a magnetic field. The magnetic field may be produced by permanent magnets or by field coils. In the case of a machine with field coils, a current must flow in the coils to generate the field, otherwise no power is transferred...
- Field coilField coilA field coil is a component of an electro-magnetic machine, typically a rotating electrical machine such as a motor or generator. A current-carrying coil is used to generate a magnetic field....
- StatorStatorThe stator is the stationary part of a rotor system, found in an electric generator, electric motor and biological rotors.Depending on the configuration of a spinning electromotive device the stator may act as the field magnet, interacting with the armature to create motion, or it may act as the...

