
Grad (angle)
Encyclopedia
The gradian is a unit of plane angle
, equivalent to of a turn
. It is also known as gon, grad, or grade (not to be confused with the grade of an inclined surface, i.e. gradient, slope, or pitch, the gradient
in vector calculus, or the radian
unit). One grad equals of a degree
or of a radian
. In continental Europe
, the French term centigrade was in use for one hundredth of a grad, and the term myriograde was in use for one ten-thousandth of a grad. This was one reason for the adoption of the term Celsius
to replace centigrade as the unit of temperature.
as the grade, along with the metric system
. Due to confusion with existing grad(e) units of northern Europe, the name gon was later adopted, first in those regions, later as the international standard. In German
, the unit was formerly also called Neugrad (new degree), and a similar terminology is still used in Danish and Icelandic.
Although attempts at a general introduction were made, the unit was really only adopted in some countries and for specialised areas, like surveying
. The French artillery has used the grad for decades.
The degree, of a circle, or the mathematically more convenient radian, of a circle (used in the SI
system of units) are generally used instead. In the 1970s and 80s most scientific calculator
s offered the grad as well as radians and degrees for their trigonometric functions, but in recent years some offered degrees and radians only.
The international standard symbol for this unit today is "gon" (see ISO 31-1
). Other symbols used in the past include "gr", "grd", and "g", the last sometimes written as a superscript, similarly to a degree sign: 50g = 45°. "Grad" was commonly used on calculators with LCD displays, as "DEG", "GRAD", and "RAD" could all be represented as a subsection of a panel with the letters "DEGRAD".
One advantage of this unit is that right angles are easy to add and subtract in mental arithmetic. If one is traveling on a course of 117 gon (clockwise from due North), say, then the direction from one's left is instantly convertible into 17 gon; while the direction from one's right is 217 gon; and the direction from behind one is 317 gon. A disadvantage is that the common angles of 30° and 60° in geometry must be expressed in fractions (33 gon and 66 gon, respectively). Similarly, in one hour ( day), Earth rotates by 15° or 16 gon.
Originally, 1 gon of arc along the Earth's surface was equal to 100 kilometers of distance at the equator
; therefore 1 centigrad of arc equals 1 kilometer.
Angle
In geometry, an angle is the figure formed by two rays sharing a common endpoint, called the vertex of the angle.Angles are usually presumed to be in a Euclidean plane with the circle taken for standard with regard to direction. In fact, an angle is frequently viewed as a measure of an circular arc...
, equivalent to of a turn
Turn (geometry)
A turn is an angle equal to a 360° or 2 radians or \tau radians. A turn is also referred to as a revolution or complete rotation or full circle or cycle or rev or rot....
. It is also known as gon, grad, or grade (not to be confused with the grade of an inclined surface, i.e. gradient, slope, or pitch, the gradient
Gradient
In vector calculus, the gradient of a scalar field is a vector field that points in the direction of the greatest rate of increase of the scalar field, and whose magnitude is the greatest rate of change....
in vector calculus, or the radian
Radian
Radian is the ratio between the length of an arc and its radius. The radian is the standard unit of angular measure, used in many areas of mathematics. The unit was formerly a SI supplementary unit, but this category was abolished in 1995 and the radian is now considered a SI derived unit...
unit). One grad equals of a degree
Degree (angle)
A degree , usually denoted by ° , is a measurement of plane angle, representing 1⁄360 of a full rotation; one degree is equivalent to π/180 radians...
or of a radian
Radian
Radian is the ratio between the length of an arc and its radius. The radian is the standard unit of angular measure, used in many areas of mathematics. The unit was formerly a SI supplementary unit, but this category was abolished in 1995 and the radian is now considered a SI derived unit...
. In continental Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
, the French term centigrade was in use for one hundredth of a grad, and the term myriograde was in use for one ten-thousandth of a grad. This was one reason for the adoption of the term Celsius
Celsius
Celsius is a scale and unit of measurement for temperature. It is named after the Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius , who developed a similar temperature scale two years before his death...
to replace centigrade as the unit of temperature.
History
The unit originated in FranceFrance
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
as the grade, along with the metric system
Metric system
The metric system is an international decimalised system of measurement. France was first to adopt a metric system, in 1799, and a metric system is now the official system of measurement, used in almost every country in the world...
. Due to confusion with existing grad(e) units of northern Europe, the name gon was later adopted, first in those regions, later as the international standard. In German
German language
German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
, the unit was formerly also called Neugrad (new degree), and a similar terminology is still used in Danish and Icelandic.
Although attempts at a general introduction were made, the unit was really only adopted in some countries and for specialised areas, like surveying
Surveying
See Also: Public Land Survey SystemSurveying or land surveying is the technique, profession, and science of accurately determining the terrestrial or three-dimensional position of points and the distances and angles between them...
. The French artillery has used the grad for decades.
The degree, of a circle, or the mathematically more convenient radian, of a circle (used in the SI
Si
Si, si, or SI may refer to :- Measurement, mathematics and science :* International System of Units , the modern international standard version of the metric system...
system of units) are generally used instead. In the 1970s and 80s most scientific calculator
Scientific calculator
A scientific calculator is a type of electronic calculator, usually but not always handheld, designed to calculate problems in science, engineering, and mathematics...
s offered the grad as well as radians and degrees for their trigonometric functions, but in recent years some offered degrees and radians only.
The international standard symbol for this unit today is "gon" (see ISO 31-1
ISO 31-1
ISO 31-1 is the part of international standard ISO 31 that defines names and symbols for quantities and units related to space and time.Its definitions include:Annex A of ISO 31-1 lists units of space and time based on the foot, pound and second...
). Other symbols used in the past include "gr", "grd", and "g", the last sometimes written as a superscript, similarly to a degree sign: 50g = 45°. "Grad" was commonly used on calculators with LCD displays, as "DEG", "GRAD", and "RAD" could all be represented as a subsection of a panel with the letters "DEGRAD".
Benefits
Each quadrant is assigned a range of 100 gon, which eases recognition of the four quadrants, as well as arithmetic involving perpendicular or opposite angles.| 0° | = | 0 gon |
| 90° | = | 100 gon |
| 180° | = | 200 gon |
| 270° | = | 300 gon |
| 360° | = | 400 gon |
One advantage of this unit is that right angles are easy to add and subtract in mental arithmetic. If one is traveling on a course of 117 gon (clockwise from due North), say, then the direction from one's left is instantly convertible into 17 gon; while the direction from one's right is 217 gon; and the direction from behind one is 317 gon. A disadvantage is that the common angles of 30° and 60° in geometry must be expressed in fractions (33 gon and 66 gon, respectively). Similarly, in one hour ( day), Earth rotates by 15° or 16 gon.
Originally, 1 gon of arc along the Earth's surface was equal to 100 kilometers of distance at the equator
Equator
An equator is the intersection of a sphere's surface with the plane perpendicular to the sphere's axis of rotation and containing the sphere's center of mass....
; therefore 1 centigrad of arc equals 1 kilometer.
Use in surveying
In surveying gradian is the default unit of angles in many parts of the world. Subdivisions of gradian used in surveying are c's (1c=0.01 grad) and cc's (1 cc=0.0001 grad).Conversion of some common angles
| Units | | Values | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turns Turn (geometry) A turn is an angle equal to a 360° or 2 radians or \tau radians. A turn is also referred to as a revolution or complete rotation or full circle or cycle or rev or rot.... |
0 | 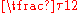 |
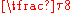 |
 |
 |
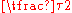 |
 |
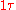 |
| Degrees Degree (angle) A degree , usually denoted by ° , is a measurement of plane angle, representing 1⁄360 of a full rotation; one degree is equivalent to π/180 radians... |
0° | 30° | 45° | 60° | 90° | 180° | 270° | 360° |
| Radian Radian Radian is the ratio between the length of an arc and its radius. The radian is the standard unit of angular measure, used in many areas of mathematics. The unit was formerly a SI supplementary unit, but this category was abolished in 1995 and the radian is now considered a SI derived unit... s |
0 | 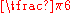 |
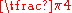 |
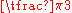 |
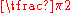 |
 |
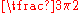 |
2 |
| Grads | 0g | 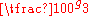 |
50g | 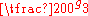 |
100g | 200g | 300g | 400g |
See also
- Angular milAngular milAn angular mil, also mil, is a unit of angle. All versions of the angular mil are approximately the same size as a trigonometric milliradian.-History:The milliradian was first identified in the mid nineteenth Century...
(military measurement) - TrigonometryTrigonometryTrigonometry is a branch of mathematics that studies triangles and the relationships between their sides and the angles between these sides. Trigonometry defines the trigonometric functions, which describe those relationships and have applicability to cyclical phenomena, such as waves...
- Harmonic analysisHarmonic analysisHarmonic analysis is the branch of mathematics that studies the representation of functions or signals as the superposition of basic waves. It investigates and generalizes the notions of Fourier series and Fourier transforms...
- Angular frequencyAngular frequencyIn physics, angular frequency ω is a scalar measure of rotation rate. Angular frequency is the magnitude of the vector quantity angular velocity...
- RadianRadianRadian is the ratio between the length of an arc and its radius. The radian is the standard unit of angular measure, used in many areas of mathematics. The unit was formerly a SI supplementary unit, but this category was abolished in 1995 and the radian is now considered a SI derived unit...
- SteradianSteradianThe steradian is the SI unit of solid angle. It is used to describe two-dimensional angular spans in three-dimensional space, analogous to the way in which the radian describes angles in a plane...
(the "square radian")
External links
- Gradian at MathWorldMathWorldMathWorld is an online mathematics reference work, created and largely written by Eric W. Weisstein. It is sponsored by and licensed to Wolfram Research, Inc. and was partially funded by the National Science Foundation's National Science Digital Library grant to the University of Illinois at...
- Ask Dr Math
- grade
- gon
- centigrade
- Dictionary of Units

