
Glossary of project management
Encyclopedia
A glossary of terms relating to Project management
.

Project management
Project management is the discipline of planning, organizing, securing, and managing resources to achieve specific goals. A project is a temporary endeavor with a defined beginning and end , undertaken to meet unique goals and objectives, typically to bring about beneficial change or added value...
.
A
- Agile software developmentAgile software developmentAgile software development is a group of software development methodologies based on iterative and incremental development, where requirements and solutions evolve through collaboration between self-organizing, cross-functional teams...
is a set of fundamental principles about how software should be developed based on an agile way of working in contrast to previous heavy handed software development methodologies.
- Aggregate planningAggregate planningAggregate planning is an operational activity that does an aggregate plan for the production process, in advance of 2 to 18 months, to give an idea to management as to what quantity of materials and other resources are to be procured and when, so that the total cost of operations of the...
is an operational activity which does an aggregate plan for the production process, in advance of 2 to 18 months, to give an idea to management as to what quantity of materials and other resources are to be procured and when, so that the total cost of operations of the organization is kept to the minimum over that period.
- AllocationAllocationAllocation may refer to:* Computers** Delayed allocation** Block allocation map** FAT** IP address allocation** Memory allocation** C++ allocators** No-write allocation ** Register allocation* Economics** Economic system** Asset allocation...
is the assignment of available resources in an economic way.
B
- BudgetBudgetA budget is a financial plan and a list of all planned expenses and revenues. It is a plan for saving, borrowing and spending. A budget is an important concept in microeconomics, which uses a budget line to illustrate the trade-offs between two or more goods...
generally refers to a list of all planned expenses and revenues.
- Budgeted cost of work performedBudgeted cost of work performedBudgeted cost of work performed , or "earned value" , in project management is the budgeted cost of work that has actually been performed in carrying out a scheduled task during a specific time period...
(BCWP) measures the budgeted cost of work that has actually been performed, rather than the cost of work scheduled.
- Budgeted cost of work scheduled (BCWS) the approved budget that has been allocated to complete a scheduled task (or Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) component) during a specific time period.
- Business modelBusiness modelA business model describes the rationale of how an organization creates, delivers, and captures value...
is a term used to describe a profit-producing system that has an important degree of independence from the other systems within an enterprise.
- Business analysisBusiness AnalysisBusiness analysis is the discipline of identifying business needs and determining solutions to business problems. Solutions often include a systems development component, but may also consist of process improvement, organizational change or strategic planning and policy development...
is the set of tasks, knowledge, and techniques required to identify business needs and determine solutions to business problems. Solutions often include a systems development component, but may also consist of process improvement or organizational change.
- Business operationsBusiness operationsBusiness operations are those ongoing recurring activities involved in the running of a business for the purpose of producing value for the stakeholders...
are those ongoing recurring activities involved in the running of a business for the purpose of producing value for the stakeholders. They are contrasted with project management, and consist of business processes.
- Business processBusiness processA business process or business method is a collection of related, structured activities or tasks that produce a specific service or product for a particular customer or customers...
is a collection of related, structured activities or tasks that produce a specific service or product (serve a particular goal) for a particular customer or customers. There are three types of business processes: Management processes, Operational processes, and Supporting processes.
- Business Process ModelingBusiness process modelingBusiness Process Modeling in systems engineering is the activity of representing processes of an enterprise, so that the current process may be analyzed and improved. BPM is typically performed by business analysts and managers who are seeking to improve process efficiency and quality...
(BPM) is the activity of representing processes of an enterprise, so that the current ("as is") process may be analyzed and improved in future ("to be").
C

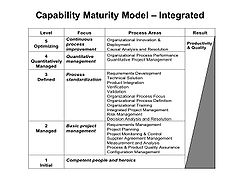
- Capability Maturity ModelCapability Maturity ModelThe Capability Maturity Model is a development model that was created after study of data collected from organizations that contracted with the U.S. Department of Defense, who funded the research. This model became the foundation from which CMU created the Software Engineering Institute...
(CMM) in software engineering is a model of the maturity of the capability of certain business processes. A maturity model can be described as a structured collection of elements that describe certain aspects of maturity in an organization, and aids in the definition and understanding of an organization's processes.
- Change controlChange ControlChange control within Quality management systems and Information Technology systems is a formal process used to ensure that changes to a product or system are introduced in a controlled and coordinated manner...
is a general term describing the procedures used to ensure that changes (normally, but not necessarily, to IT systems) are introduced in a controlled and coordinated manner. Change control is a major aspect of the broader discipline of change management.
- Change managementChange managementChange management is a structured approach to shifting/transitioning individuals, teams, and organizations from a current state to a desired future state. It is an organizational process aimed at helping employees to accept and embrace changes in their current business environment....
is a field of management focused on organizational changes. It aims to ensure that methods and procedures are used for efficient and prompt handling of all changes to controlled IT infrastructure, in order to minimize the number and impact of any related incidents upon service.
- Case studyCase studyA case study is an intensive analysis of an individual unit stressing developmental factors in relation to context. The case study is common in social sciences and life sciences. Case studies may be descriptive or explanatory. The latter type is used to explore causation in order to find...
is a research method which involves an in-depth, longitudinal examination of a single instance or event: a case. They provide a systematic way of looking at events, collecting data, analyzing information, and reporting the results.
- ConstructabilityConstructabilityConstructability is a project management technique to review construction processes from start to finish during pre-construction phase. It is to identify obstacles before a project is actually built to reduce or prevent errors, delays, and cost overruns.The term "constructability" defines the ease...
is a project management technique to review the construction processes from start to finish during pre-construction phrase. It will identify obstacles before a project is actually built to reduce or prevent error, delays, and cost overrun.
- CostCostIn production, research, retail, and accounting, a cost is the value of money that has been used up to produce something, and hence is not available for use anymore. In business, the cost may be one of acquisition, in which case the amount of money expended to acquire it is counted as cost. In this...
s in economics, business, and accounting are the value of money that has been used up to produce something, and hence is not available for use anymore. In business, the cost may be one of acquisition, in which case the amount of money expended to acquire it is counted as cost.
- Cost engineeringCost engineeringCost engineering is an area of engineering practice concerned with the "application of scientific principles and techniques to problems of cost estimating, cost control, business planning and management science, profitability analysis, project management, and planning and scheduling."- Overview...
is the area of engineering practice where engineering judgment and experience are used in the application of scientific principles and techniques to problems of cost estimating, cost control, business planning and management science, profitabilityProfit (accounting)In accounting, profit can be considered to be the difference between the purchase price and the costs of bringing to market whatever it is that is accounted as an enterprise in terms of the component costs of delivered goods and/or services and any operating or other expenses.-Definition:There are...
analysis, project managementProject managementProject management is the discipline of planning, organizing, securing, and managing resources to achieve specific goals. A project is a temporary endeavor with a defined beginning and end , undertaken to meet unique goals and objectives, typically to bring about beneficial change or added value...
, and planning and scheduling."
- ConstructionConstructionIn the fields of architecture and civil engineering, construction is a process that consists of the building or assembling of infrastructure. Far from being a single activity, large scale construction is a feat of human multitasking...
, in the fields of architecture and civil engineering, is a process that consists of the building or assembling of infrastructure. Far from being a single activity, large scale construction is a feat of multitasking. Normally the job is managed by the project manager and supervised by the construction manager, design engineer, construction engineer or project architect.
- Cost overrunCost overrunA cost overrun, also known as a cost increase or budget overrun, is an unexpected cost incurred in excess of a budgeted amount due to an under-estimation of the actual cost during budgeting...
is defined as excess of actual cost over budget.

- Critical path methodCritical path methodThe critical path method is an algorithm for scheduling a set of project activities. It is an important tool for effective project management.-History:...
(CPM) is a mathematically based modeling technique for scheduling a set of project activities, used in project management.
- Critical chain project management (CCPM) is a method of planning and managing projects that puts more emphasis on the resources required to execute project tasks.
D
- DependencyDependency (project management)In a project network, a dependency is a link amongst a project's terminal elements.There are four kinds of dependencies with respect to ordering terminal elements :# Finish to start...
in a project network is a link amongst a project's terminal elements.
- Dynamic Systems Development MethodDynamic Systems Development MethodDynamic systems development method is an agile project delivery framework, primarily used as a software development method. DSDM was originally based upon the rapid application development method. In 2007 DSDM became a generic approach to project management and solution delivery...
(DSDM) is a software development methodology originally based upon the Rapid Application Development methodology. DSDM is an iterative and incremental approach that emphasizes continuous user involvement.
- DurationDuration (project management)Duration of a project's terminal element is the number of calendar periods it takes from the time the execution of element starts to the moment it is completed.Do not confuse duration with work. E.g...
of a project's terminal element is the number of calendar periods it takes from the time the execution of element starts to the moment it is completed.
- DeliverableDeliverableDeliverable is a term used in project management to describe a tangible or intangible object produced as a result of the project that is intended to be delivered to a customer . A deliverable could be a report, a document, a server upgrade or any other building block of an overall project.A...
A contractually required work product, produced and delivered to a required state. A deliverable may be a document, hardware, software or other tangible product.
E
- Earned scheduleEarned ScheduleEarned schedule is an extension to the theory and practice of earned value management . As of 2005, Earned Schedule is designated as an "emerging practice" by the Project Management Institute...
(ES) is an extension to earned value management (EVM), which renames two traditional measures, to indicate clearly they are in units of currency or quantity, not time.
- Earned value managementEarned value managementEarned value management is a project management technique for measuring project performance and progress in an objective manner. EVM has the ability to combine measurements of scope, schedule, and cost in a single integrated system. Earned Value Management is notable for its ability to provide...
(EVM) is a project management technique for measuring project progress in an objective manner, with a combination of measuring scope, schedule, and cost in a single integrated system.
- Effort managementEffort managementIn Project Management, work activities can be measured by effort. This subdiscipline is understood as Effort Management. It is the effective and efficient allocation of time and resources to perform activities. These activities are generally performed in line with a company strategy and/or a project...
is a project management subdiscipline for effective and efficient use of time and resources to perform activities regarding quantity, quality and direction.
- Enterprise modeling is the process of understanding an enterprise business and improving its performance through creation of enterprise models. This includes the modelling of the relevant business domain (usually relatively stable), business processes (usually more volatile), and Information technology
- EstimationEstimation (project management)In project management , accurate estimates are the basis of sound project planning. Many processes have been developed to aid engineers in making accurate estimates, such as*Analogy based estimation...
in project management is the processes of making accurate estimates using the appropriate techniques.

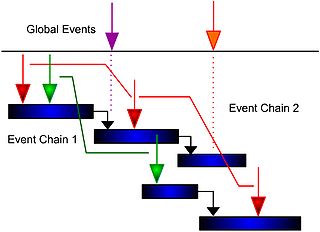
- Event chain diagram : diagram that show the relationships between events and tasks and how the events affect each other.
- Event chain methodologyEvent chain methodologyEvent chain methodology is an uncertainty modeling and schedule network analysis technique that is focused on identifying and managing events and event chains that affect project schedules...
is an uncertainty modeling and schedule network analysis technique that is focused on identifying and managing events and event chains that affect project schedules.
- Extreme project managementExtreme project managementExtreme project management refers to a method of managing very complex and very uncertain projects.Extreme project management differs from traditional project management mainly in its open, elastic and undeterministic approach. The main focus of XPM is on the human side of project management...
(XPM) refers to a method of managing very complex and very uncertain projects.
F
- FloatFloat (project management)In project management, float or slack is the amount of time that a task in a project network can be delayed without causing a delay to:* subsequent tasks * project completion date...
in a project network is the amount of time that a task in a project network can be delayed without causing a delay to subsequent tasks and or the project completion date.
- Focused improvementFocused improvementFocused improvement in Theory of Constraints is the ensemble of activities aimed at elevating the performance of any system, especially a business system, with respect to its goal by eliminating its constraints one by one and by not working on non-constraints.The method to achieve focused...
in Theory of Constraints is the ensemble of activities aimed at elevating the performance of any system, especially a business system, with respect to its goal by eliminating its constraints one by one and by not working on non-constraints.
- FordismFordismFordism, named after Henry Ford, is a modern economic and social system based on industrial mass production. The concept is used in various social theories about production and related socio-economic phenomena. It has varying but related meanings in different fields, as well as for Marxist and...
, named after Henry Ford, refers to various social theories. It has varying but related meanings in different fields, and for Marxist and non-Marxist scholars.
G
- Henry GanttHenry GanttHenry Laurence Gantt, A.B., M.E. was an American mechanical engineer and management consultant who is most famous for developing the Gantt chart in the 1910s....
was an American mechanical engineer and management consultant, who developed the Gantt chart in the 1910s.
- Gantt chartGantt chartA Gantt chart is a type of bar chart that illustrates a project schedule. Gantt charts illustrate the start and finish dates of the terminal elements and summary elements of a project. Terminal elements and summary elements comprise the work breakdown structure of the project. Some Gantt charts...
is a type of bar chart that illustrates a project schedule. It illustrate the start and finish dates of the terminal elements and summary elements of a project. Terminal elements and summary elements comprise the work breakdown structure of the project.
- GoalGoalA goal is an objective, or a projected computation of affairs, that a person or a system plans or intends to achieve.Goal, GOAL or G.O.A.L may also refer to:Sport...
or objective consists of a projected state of affairs which a person or a system plans or intends to achieve or bring about — a personal or organizational desired end-point in some sort of assumed development. Many people endeavor to reach goals within a finite time by setting deadlines
- Goal settingGoal settingGoal setting involves establishing specific, measurable, achievable, realistic and time-targeted goals. Work on the theory of goal-setting suggests that it's an effective tool for making progress by ensuring that participants in a group with a common goal are clearly aware of what is expected from...
involves establishing specific, measurable and time targeted objectives
- Graphical Evaluation and Review TechniqueGraphical Evaluation and Review TechniqueGraphical Evaluation and Review Technique, commonly known as GERT, is a network analysis technique used in project management that allows probabilistic treatment of both network logic and estimation of activity duration. The technique was first described in 1966 by Dr. Alan B...
(GERT), is a network analysis technique that allows probabilistic treatment of both network logic and activity duration estimated.
H
- Hammock activityHammock activityA Hammock activity is a schedule or project planning term for a grouping of subtasks that "hangs" between two end dates it is tied to....
is a schedule (project management) or project planning term for a grouping of subtasks that "hangs" between two end dates it is tied to. (Or the two end-events it is fixed to.)
- HERMES is a Project Management Method developed by the Swiss Government, based on the German V-Modell. The first domain of application was software projects.
I
- Integrated Master PlanIntegrated master planThe Integrated Master Plan is an event-based, top level plan consisting of a hierarchy of Program Events, with each Event being supported by specific Accomplishments, and each Accomplishment associated with specific Criteria to be satisfied for its completion...
(IMP) is an event-based, top level plan, consisting of a hierarchy of Program Events.
- ISO 10006ISO 10006ISO 10006:2003, Quality management systems - Guidelines for quality management in projects, is an international standard developed by the International Organization for Standardization....
is a guidelines for quality management in projects, is an international standard developed by the International Organization for Standardization.
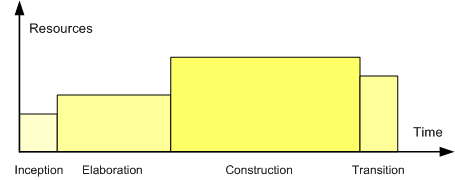
- Iterative and Incremental developmentIterative and incremental developmentIterative and Incremental development is at the liver of a cyclic software development process developed in response to the weaknesses of the waterfall model...
is a cyclic software development process developed in response to the weaknesses of the waterfall modelWaterfall modelThe waterfall model is a sequential design process, often used in software development processes, in which progress is seen as flowing steadily downwards through the phases of Conception, Initiation, Analysis, Design, Construction, Testing, Production/Implementation and Maintenance.The waterfall...
. It starts with an initial planning and ends with deployment with the cyclic interaction in between
K
- Kickoff meetingKickoff meetingThe Kickoff Meeting is the first meeting with the project team and the client of the project. This meeting would follow definition of the base elements for the project and other project planning activities. This meeting introduces the members of the project team and the client and provides the...
is the first meeting with the project team and the client of the project.
L
- Level of EffortLevel of EffortIn project management, level of effort is a support-type project activity that must be done to support other work activities or the entire project effort. It usually consists of short amounts of work that must be repeated periodically...
(LOE) is qualified as a support type activity which doesn't lend itself to measurement of a discrete accomplishment. Examples of such an activity may be project budget accounting, customer liaison, etc.
- Linear scheduling methodLinear scheduling methodLinear Scheduling Method is a graphical scheduling method focusing on continuous resource utilization in repetitive activities. It is believed that it originally adopted the idea of Line-Of-Balance method.-Application:...
(LSM) is a graphical scheduling method focusing on continuous resource utilization in repetitive activities. It is believed that it originally adopted the idea of Line-Of-Balance method.
- Lean manufacturingLean manufacturingLean manufacturing, lean enterprise, or lean production, often simply, "Lean," is a production practice that considers the expenditure of resources for any goal other than the creation of value for the end customer to be wasteful, and thus a target for elimination...
or lean production, which is often known simply as "Lean", is the practice of a theory of production that considers the expenditure of resources for any means other than the creation of value for the presumed customer to be wasteful, and thus a target for elimination. In a more basic term,
M
- ManagementManagementManagement in all business and organizational activities is the act of getting people together to accomplish desired goals and objectives using available resources efficiently and effectively...
in business and human organization activity is simply the act of getting people together to accomplish desired goals. Management comprises planning, organizing, staffing, leading or directing, and controlling an organization (a group of one or more people or entities) or effort for the purpose of accomplishing a goal.
- Management processManagement processManagement process is a process of planning and controlling the performance or execution of any type of activity, such as:* a project or...
is a process of planning and controlling the performance or execution of any type of activity.
- Management science (MS), is the discipline of using mathematical modeling and other analytical methods, to help make better business management decisions.
- MegaprojectMegaprojectA megaproject is an extremely large-scale investment project. Megaprojects are typically defined as costing more than US$1 billion and attracting a lot of public attention because of substantial impacts on communities, environment, and budgets. Megaprojects can also be defined as "initiatives that...
is an extremely large-scale investment project.
- MotivationMotivationMotivation is the driving force by which humans achieve their goals. Motivation is said to be intrinsic or extrinsic. The term is generally used for humans but it can also be used to describe the causes for animal behavior as well. This article refers to human motivation...
is the set of reasons that determines one to engage in a particular behavior.
N
- Nonlinear ManagementNonlinear ManagementLinear management is the application of reductionism to management problems, often relying on the ability to predict, engineer and control outcomes by manipulating the component parts of a business . Business process reengineering is a popular example of linear management at work...
(NLM) is a superset of management techniques and strategies that allows order to emerge by giving organizations the space to self-organize, evolve and adapt, encompassing Agile, Evolutionary and Lean approaches, as well as many others.
O
- Operations managementOperations managementOperations management is an area of management concerned with overseeing, designing, and redesigning business operations in the production of goods and/or services. It involves the responsibility of ensuring that business operations are efficient in terms of using as little resources as needed, and...
is an area of business that is concerned with the production of good quality goods and services, and involves the responsibility of ensuring that business operations are efficient and effective. It is the management of resources, the distribution of goods and services to customers, and the analysis of queue systems.
- Operations, see Business operations
- Operations ResearchOperations researchOperations research is an interdisciplinary mathematical science that focuses on the effective use of technology by organizations...
(OR) is an interdisciplinary branch of applied mathematics and formal science that uses methods such as mathematical modeling, statistics, and algorithms to arrive at optimal or near optimal solutions to complex problems.
- OrganizationOrganizationAn organization is a social group which distributes tasks for a collective goal. The word itself is derived from the Greek word organon, itself derived from the better-known word ergon - as we know `organ` - and it means a compartment for a particular job.There are a variety of legal types of...
is a social arrangement which pursues collective goals, which controls its own performance, and which has a boundary separating it from its environment.
- Organization developmentOrganization developmentOrganization development is a new term which means a conceptual, organization-wide effort to increase an organization's effectiveness and viability...
(OD) is a planned, structured, organization-wide effort to increase the organization's effectiveness and health.
P
- PlanningPlanningPlanning in organizations and public policy is both the organizational process of creating and maintaining a plan; and the psychological process of thinking about the activities required to create a desired goal on some scale. As such, it is a fundamental property of intelligent behavior...
in organizations and public policy is both the organizational process of creating and maintaining a plan; and the psychological process of thinking about the activities required to create a desired goal on some scale.
- PortfolioPortfolio (finance)Portfolio is a financial term denoting a collection of investments held by an investment company, hedge fund, financial institution or individual.-Definition:The term portfolio refers to any collection of financial assets such as stocks, bonds and cash...
in finance is an appropriate mix of or collection of investments held by an institution or a private individual.
- PRINCE2PRINCE2PRojects IN Controlled Environments 2 is a structured project management method endorsed by the UK government as the project management standard for public projects. The methodology encompasses the management, control and organisation of a project...
: PRINCE2 is a project management methodology. The planning, monitoring and control of all aspects of the project and the motivation of all those involved in it to achieve the project objectives on time and to the specified cost, quality and performance.
- Process is an ongoing collection of activities, with an inputs, outputs and the energy required to transform inputs to outputs.
- Process architectureProcess architectureDualistic Petri nets are a process-class variant of Petri nets.Like Petri nets in general and many related formalisms and notations, they are used to describe and analyze process architecture.-Process Modeling with dPNs :...
is the structural design of general process systems and applies to fields such as computers (software, hardware, networks, etc.), business processes (enterprise architecture, policy and procedures, logistics, project management, etc.), and any other process system of varying degrees of complexity.
- Process managementProcess managementProcess management is the ensemble of activities of planning and monitoring the performance of a process. The term usually refers to the management of business processes and manufacturing processes...
is the ensemble of activities of planning and monitoring the performance of a process, especially in the sense of business process, often confused with reengineering.
- Product breakdown structureProduct breakdown structureIn project management, a product breakdown structure is a tool for analysing, documenting and communicating the outcomes of a project, and forms part of the product based planning technique....
(PBS) in project management is an exhaustive, hierarchical tree structure of components that make up an item, arranged in whole-part relationship.
- Product descriptionProduct descriptionA product description in project management is a structured format of presenting information about a project product. Product description is usually created by the project manager and approved by the project board....
in project management is a structured format of presenting information about a project product
- Program ManagementProgram managementProgram management or programme management is the process of managing several related projects, often with the intention of improving an organization's performance...
is the process of managing multiple ongoing inter-dependent projects. An example would be that of designing, manufacturing and providing support infrastructure for an automobile manufacturer.
- ProjectProjectA project in business and science is typically defined as a collaborative enterprise, frequently involving research or design, that is carefully planned to achieve a particular aim. Projects can be further defined as temporary rather than permanent social systems that are constituted by teams...
: A temporary endeavor undertaken to create a unique product, service, or result.
- Project accountingProject accountingProject accounting is the practice of creating financial reports specifically designed to track the financial progress of projects, which can then be used by managers to aid project management....
Is the practice of creating financial reports specifically designed to track the financial progress of projects, which can then be used by managers to aid project management.
- Project Cost ManagementProject cost managementProject cost management is a method which uses technology to measure cost and productivity through the full life cycle of enterprise level projects....
A method of managing a project in real-time from the estimating stage to project control; through the use of technology cost, schedule and productivity is monitored.
- Project managementProject managementProject management is the discipline of planning, organizing, securing, and managing resources to achieve specific goals. A project is a temporary endeavor with a defined beginning and end , undertaken to meet unique goals and objectives, typically to bring about beneficial change or added value...
: The complete set of tasks, techniques, tools applied during project execution'.
- Project Management Body of KnowledgeProject Management Body of KnowledgeA Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge is a book which presents a set of standard terminology and guidelines for project management. The Fourth Edition was recognized by the American National Standards Institute as an American National Standard...
(PMBOK) : The sum of knowledge within the profession of project management that is standardized by ISO.
- Project management office: The Project management office in a business or professional enterprise is the department or group that defines and maintains the standards of process, generally related to project management, within the organization. The PMO strives to standardize and introduce economies of repetition in the execution of projects. The PMO is the source of documentation, guidance and metrics on the practice of project management and execution.
- Project management processProject management processA project management process is the management process of planning and controlling the performance or execution of a project.-Inputs:* Documented need to act* Project plan templates* Lessons learned from previous projects...
is the management process of planning and controlling the performance or execution of a project.
- Project Management ProfessionalProject Management ProfessionalProject Management Professional is a credential offered by the Project Management Institute . , there were 393,413 active PMP certified individuals worldwide...
is a certificated professional in project management.
- Project Management SimulatorProject Management SimulatorProject management simulation is simulation used for project management training and analysis.Project management simulation is often used as training simulation for project managers...
s are computer-based tools used in project managementProject managementProject management is the discipline of planning, organizing, securing, and managing resources to achieve specific goals. A project is a temporary endeavor with a defined beginning and end , undertaken to meet unique goals and objectives, typically to bring about beneficial change or added value...
training programs. Usually, project management simulation is a group exercise. The computer-based simulation is an interactive learning activity.
- Project management softwareProject management softwareProject management software is a term covering many types of software, including estimation and planning, scheduling, cost control and budget management, resource allocation, collaboration software, communication, quality management and documentation or administration systems, which are used to...
is a type of software, including scheduling, cost control and budget management, resource allocation, collaboration software, communication, quality management and documentation or administration systems, which are used to deal with the complexity of large projects.

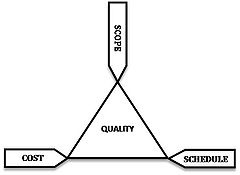
- Project Management TriangleProject management triangleThe Project Management Triangle is a model of the constraints of project management. It is often used to illustrate that project management success is measured by the project team's ability to manage the project, so that the expected results are produced while managing time and cost.- Overview...
is a model of the constraints of project management.
- Project managerProject managerA project manager is a professional in the field of project management. Project managers can have the responsibility of the planning, execution, and closing of any project, typically relating to construction industry, architecture, computer networking, telecommunications or software...
: professional in the field of project management. Project managers can have the responsibility of the planning, execution, and closing of any project, typically relating to construction industry, architecture, computer networking, telecommunications or software development.
- Project networkProject networkA project network is a graph depicting the sequence in which a project's terminal elements are to be completed by showing terminal elements and their dependencies....
is a graph (flow chart) depicting the sequence in which a project's terminal elements are to be completed by showing terminal elements and their dependencies.
- Project planProject planA project plan, according to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, isPRINCE2 defines:In some industries, particularly information technology, the term "project plan" can refer to a Gantt chart or other document that shows project activities along a timeline. While common, this use is inaccurate...
is a formal, approved document used to guide both project execution and project control. The primary uses of the project plan are to document planning assumptions and decisions, facilitate communication among stakeholders, and document approved scope, cost, and schedule baselines. A project plan may be summary or detailed.
- Project planningProject planningProject planning is part of project management, which relates to the use of schedules such as Gantt charts to plan and subsequently report progress within the project environment....
is part of project management, which relates to the use of schedules such as Gantt charts to plan and subsequently report progress within the project environment.
- Project stakeholdersProject stakeholdersProject stakeholders are those entities within or outside an organization which:# sponsor a project, or# have an interest or a gain upon a successful completion of a project;# may have a positive or negative influence in the project completion....
are those entities within or without an organization which sponsor a project or, have an interest or a gain upon a successful completion of a project.
- Project teamProject teamA project team is a team whose members usually belong to different groups, functions and are assigned to activities for the same project. A team can be divided into sub-teams according to need. Usually project teams are only used for a defined period of time. They are disbanded after the project is...
is the management team leading the project, and provide services to the project. Projects often bring together a variety number of problems. Stakeholders have important issues with others.
- Proport refers to the combination of the unique skills of an organisation's members for collective advantage.
Q
- Quality can mean a high degree of excellence (“a quality product”), a degree of excellence or the lack of it (“work of average quality”), or a property of something (“the addictive quality of alcohol”).[1] Distinct from the vernacular, the subject of this article is the business interpretation of quality.
- Quality, Cost, DeliveryQuality, Cost, DeliveryQuality, cost, delivery as used in lean manufacturing measures a businesses activity and develops Key performance indicators. QCD analysis often forms a part of continuous improvement processes....
(QCD) as used in lean manufacturing measures a businesses activity and develops Key performance indicators. QCD analysis often forms a part of continuous improvement programs
R
- ReengineeringReengineeringReengineering can refer to:* Trouble shooting* Business process reengineering* Reengineering * Reengineering * User reengineering...
is radical redesign of an organization's processes, especially its business processes. Rather than organizing a firm into functional specialties (like production, accounting, marketing, etc.) and considering the tasks that each function performs; complete processes from materials acquisition, to production, to marketing and distribution should be considered. The firm should be re-engineered into a series of processes.
- ResourcesResource (project management)In project management terminology, resources are required to carry out the project tasks. They can be people, equipment, facilities, funding, or anything else capable of definition required for the completion of a project activity. The lack of a resource will therefore be a constraint on the...
in project management terminology are required to carry out the project tasks. They can be people, equipment, facilities, funding, or anything else capable of definition (usually other than labour) required for the completion of a project activity.
- RiskRiskRisk is the potential that a chosen action or activity will lead to a loss . The notion implies that a choice having an influence on the outcome exists . Potential losses themselves may also be called "risks"...
is a concept that denotes the precise probability of specific eventualities.
- Risk managementRisk managementRisk management is the identification, assessment, and prioritization of risks followed by coordinated and economical application of resources to minimize, monitor, and control the probability and/or impact of unfortunate events or to maximize the realization of opportunities...
is a management specialism aiming to reduce different risks related to a preselected domain to the level accepted by society. It may refer to numerous types of threats caused by environment, technology, humans, organizations and politics.
- Risk registerRisk registerA Risk Register is a Risk Management tool commonly used in Project Management and organisational risk assessments. It acts as a central repository for all risks identified by the project or organisation and, for each risk, includes information such as risk probability, impact, counter-measures,...
is a tool commonly used in project planning and organizational risk assessments.
S
- ScheduleSchedule (project management)In project management, a schedule consists of a list of a project's terminal elements with intended start and finish dates. Terminal elements are the lowest element in a schedule, which is not further subdivided...
s in project management consists of a list of a project's terminal elements with intended start and finish dates.
- Scientific managementScientific managementScientific management, also called Taylorism, was a theory of management that analyzed and synthesized workflows. Its main objective was improving economic efficiency, especially labor productivity. It was one of the earliest attempts to apply science to the engineering of processes and to management...
is a theory of management that analyzes and synthesizes workflow processes, improving labor productivity.
- ScopeScope (project management)In project management, the term scope has two distinct uses: Project Scope and Product Scope.Project Scope"The work that needs to be accomplished to deliver a product, service, or result with the specified features and functions."Product Scope...
of a project in project management is the sum total of all of its products and their requirements or features.
- Scope creepScope creepScope Creep in project management refers to uncontrolled changes or continuous growth in a project's scope. This phenomenon can occur when the scope of a project is not properly defined, documented, or controlled...
refers to uncontrolled changes in a project's scope. This phenomenon can occur when the scope of a project is not properly defined, documented, or controlled. It is generally considered a negative occurrence that is to be avoided.
- ScrumScrum (development)Scrum is an iterative, incremental framework for project management often seen in agile software development, a type of software engineering....
is an iterative incremental process of software development commonly used with agile software development. Despite the fact that "Scrum" is not an acronym, some companies implementing the process have been known to adhere to an all capital letter expression of the word, i.e. SCRUM.
- Six SigmaSix SigmaSix Sigma is a business management strategy originally developed by Motorola, USA in 1986. , it is widely used in many sectors of industry.Six Sigma seeks to improve the quality of process outputs by identifying and removing the causes of defects and minimizing variability in manufacturing and...
is a business management strategy, originally developed by Motorola, that today enjoys widespread application in many sectors of industry.
- Software engineeringSoftware engineeringSoftware Engineering is the application of a systematic, disciplined, quantifiable approach to the development, operation, and maintenance of software, and the study of these approaches; that is, the application of engineering to software...
is the application of a systematic, disciplined, quantifiable approach to the development, operation, and maintenance of software.
- Systems Development Life CycleSystems Development Life CycleThe systems development life cycle , or software development life cycle in systems engineering, information systems and software engineering, is a process of creating or altering information systems, and the models and methodologies that people use to develop these systems.In software engineering...
(SDLC) is any logical process used by a systems analyst to develop an information system, including requirements, validation, training, and user ownership. An SDLC should result in a high quality system that meets or exceeds customer expectations, within time and cost estimates, works effectively and efficiently in the current and planned Information Technology infrastructure, and is cheap to maintain and cost-effective to enhance.
- Systems engineeringSystems engineeringSystems engineering is an interdisciplinary field of engineering that focuses on how complex engineering projects should be designed and managed over the life cycle of the project. Issues such as logistics, the coordination of different teams, and automatic control of machinery become more...
is an interdisciplinary field of engineering that focuses on how complex engineering projects should be designed and managed.
T
- TaskTask (project management)In project management a task is an activity that needs to be accomplished within a defined period of time. An assignment is a task under the responsibility of an assignee which should have a start and end date defined. One or more assignments on a task puts the task under execution. Completion of...
is part of a set of actions which accomplish a job, problem or assignment.
- TaskTask (project management)In project management a task is an activity that needs to be accomplished within a defined period of time. An assignment is a task under the responsibility of an assignee which should have a start and end date defined. One or more assignments on a task puts the task under execution. Completion of...
s in project management are activity that needs to be accomplished within a defined period of time.
- Task analysisTask analysisTask analysis is the analysis of how a task is accomplished, including a detailed description of both manual and mental activities, task and element durations, task frequency, task allocation, task complexity, environmental conditions, necessary clothing and equipment, and any other unique factors...
is the analysis or a breakdown of exactly how a task is accomplished, such as what sub-tasks are required
- TimelineTimelineA timeline is a way of displaying a list of events in chronological order, sometimes described as a project artifact . It is typically a graphic design showing a long bar labeled with dates alongside itself and events labeled on points where they would have happened.-Uses of timelines:Timelines...
is a graphical representation of a chronological sequence of events, also referred to as a chronology. It can also mean a schedule of activities, such as a timetable.
U

- Unified ProcessUnified ProcessThe Unified Software Development Process or Unified Process is a popular iterative and incremental software development process framework. The best-known and extensively documented refinement of the Unified Process is the Rational Unified Process ....
: The Unified process is a popular iterative and incrementalIterative and incremental developmentIterative and Incremental development is at the liver of a cyclic software development process developed in response to the weaknesses of the waterfall model...
software development processSoftware development processA software development process, also known as a software development life cycle , is a structure imposed on the development of a software product. Similar terms include software life cycle and software process. It is often considered a subset of systems development life cycle...
framework. The best-known and extensively documented refinement of the Unified Process is the Rational Unified ProcessIBM Rational Unified ProcessThe Rational Unified Process is an iterative software development process framework created by the Rational Software Corporation, a division of IBM since 2003...
(RUP).
V
- Value engineeringValue engineeringValue engineering is a systematic method to improve the "value" of goods or products and services by using an examination of function. Value, as defined, is the ratio of function to cost. Value can therefore be increased by either improving the function or reducing the cost...
(VE) is a systematic method to improve the "value" of goods and services by using an examination of function. Value, as defined, is the ratio of function to costCostIn production, research, retail, and accounting, a cost is the value of money that has been used up to produce something, and hence is not available for use anymore. In business, the cost may be one of acquisition, in which case the amount of money expended to acquire it is counted as cost. In this...
. Value can therefore be increased by either improving the function or reducing the costCostIn production, research, retail, and accounting, a cost is the value of money that has been used up to produce something, and hence is not available for use anymore. In business, the cost may be one of acquisition, in which case the amount of money expended to acquire it is counted as cost. In this...
. It is a primary tenet of value engineering that basic functions be preserved and not be reduced as a consequence of pursuing value improvements.
- Vertical sliceVertical sliceA vertical slice, sometimes abbreviated to VS, is a type of milestone, benchmark, or deadline, with emphasis on demonstrating progress across all components of a project...
is a type of milestone, benchmark, or deadline, with emphasis on demonstrating progress across all components of a project.
- Virtual Design and ConstructionVirtual Design and ConstructionVirtual Design and Construction is the management of integrated multi-disciplinary performance models of design-construction projects, including the product , work processes and organization of the design - construction - operation team in order to support explicit and public business objectives...
(VDC) is the use of integrated multi-disciplinary performance models of design-construction projects, including the Product (i.e., facilities), Work Processes and Organization of the design - construction - operation team in order to support explicit and public business objectives.
W
- Wideband DelphiWideband delphiThe Wideband Delphi estimation method is a consensus-based technique for estimating effort. It derives from the Delphi Method which was developed in the 1940s at the RAND Corporation as a forecasting tool...
is a consensus-based estimation technique for estimating effort.
- WorkWork (project management)Work or Work Package in project management is the amount of effort applied to produce a deliverable or to accomplish a task or a group of related tasks defined at the same level in the WBS....
in project management is the amount of effort applied to produce a deliverable or to accomplish a task (a terminal element).

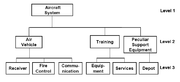
- Work Breakdown StructureWork breakdown structureA work breakdown structure , in project management and systems engineering, is a deliverable oriented decomposition of a project into smaller components. It defines and groups a project's discrete work elements in a way that helps organize and define the total work scope of the project.A work...
(WBS) is a tool that defines a project and groups the project’s discrete work elements in a way that helps organize and define the total work scope of the project. A Work breakdown structure element may be a product, data, a service, or any combination. WBS also provides the necessary framework for detailed cost estimating and control along with providing guidance for schedule development and control.
- Work packageWork packageIn project management, a work package is a subset of a project that can be assigned to a specific part for execution. Because of the similarity, work packages are often misidentified as projects....
is a subset of a project that can be assigned to a specific party for execution. Because of the similarity, work packages are often misidentified as projects.
- Workstream is a set of associated activities, focused around a particular scope that follow a path from initiation to completion.
Related lists
- List of production topics
- List of project management topics
- List of management topics
- List of Theory of Constraints topics
- List of topics in industrial organization
- Timeline of project managementTimeline of project managementTimeline of project management. There is a general understanding that the history of modern project management started around 1950. Until 1900 projects were generally managed by creative architects and engineers themself, among those for example Christopher Wren, Thomas Telford and Isambard Kingdom...

