Process architecture
Encyclopedia
Dualistic Petri nets are a process-class variant of Petri net
s.
Like Petri nets in general and many related formalisms and notations, they are used to describe and analyze process architecture
.
is using the dualistic extension of Petri nets called dualistic Petri nets (dPNs). A Petri net
(PN) is a graphical, bipartite modeling language that intuitively and mathematically represent theoretical relationships of moving objects in a network of interconnected constructs. Classical Place/Transition PNs can represent theoretical processes, where the movement of objects implies their transformation, but is too absolute to be pragmatic in representing real-world processes. The real world is dualistic in nature and process is a dualistic phenomenon, this can not be easily represented using a digital-type modeling system. Instead, dualistic extensions to Place/Transition PNs have been introduced and used successfully in modeling the architecture of computer-based systems and business processes.
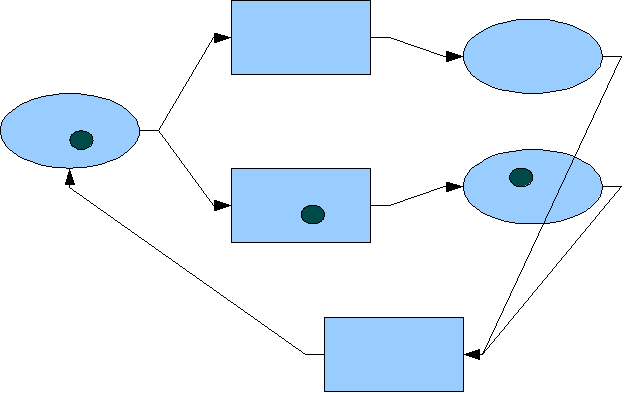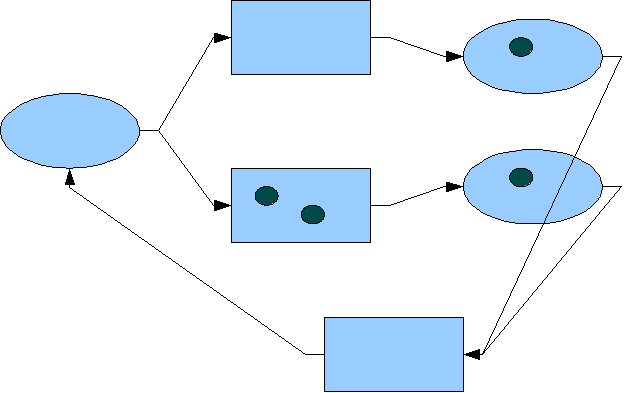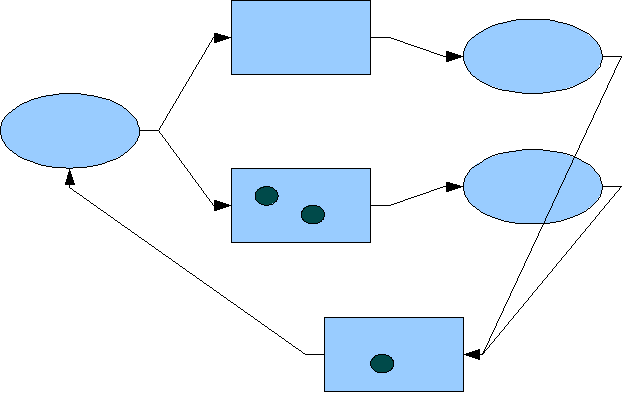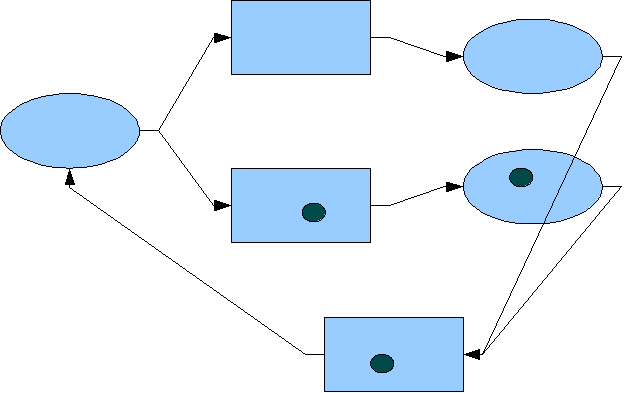
Among the distinctions of dPNs from classical PNs is space and time (due to energy use) in both the place construct and transformation construct. This results in the simulation effect of marked transformations that allow for the explicit representation of parallel processing, multiprocessing, and the implicit representation of deterioration of objects – all unique to dualistic Petri nets.
!
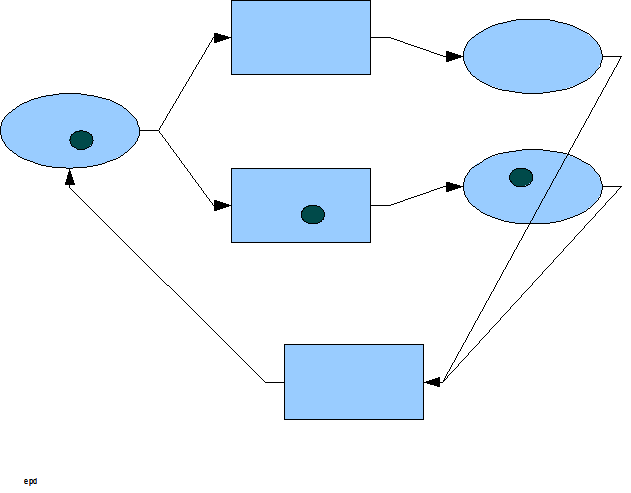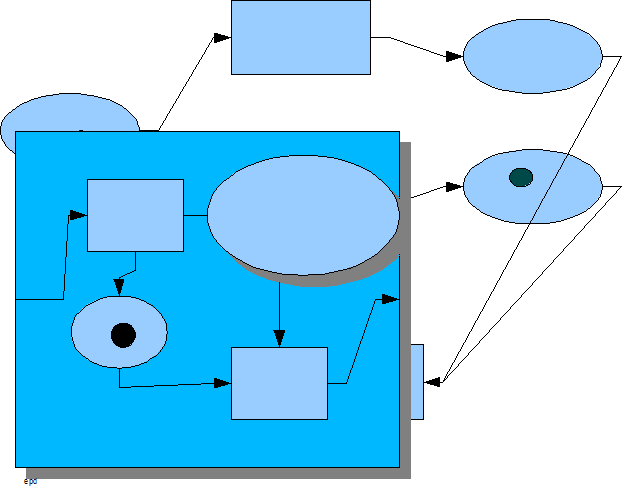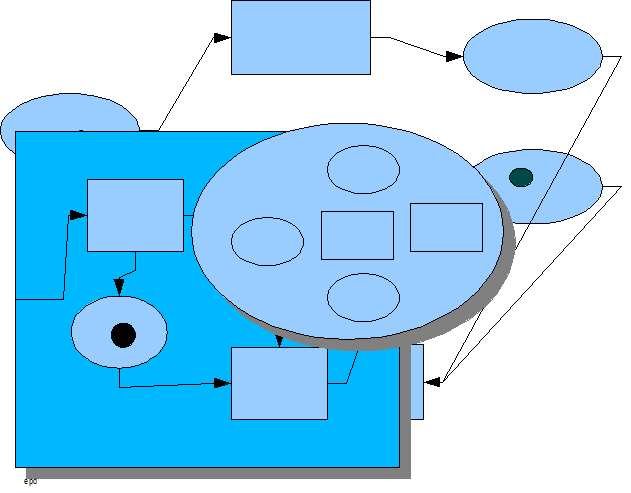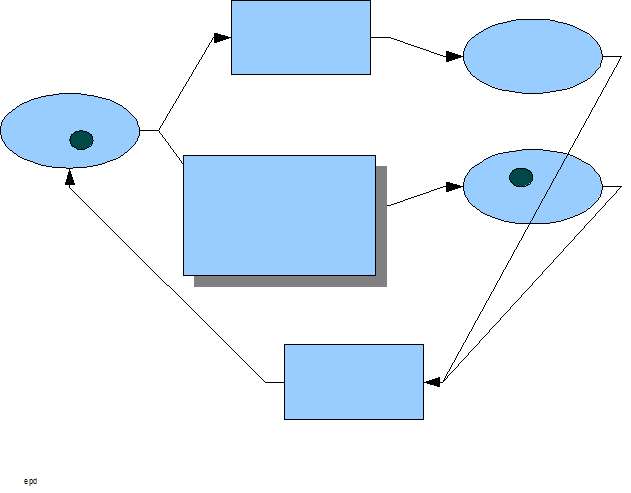
a manifested process, dPNs have a one-to-one correspondence of dPN construct to any manifested process piece, that is, it is isomorphic to the implementation language of the manifested process. For example, several lines of software code could be represented by one dPN transformation construct. Once the manifested process is completely represented by a network of dPNs, small, well-coupled groups of dPN constructs can be lumped together to form higher level dPN constructs – creating a network of dPNs at a higher level of hierarchical abstraction. Each level of abstraction is consistent with its adjacent levels of abstraction and the rules governing them at each level are the exactly the same because PN abstractions are homomorphic. Now the process design can be considered at various levels of abstraction as deemed appropriate by the process architect, allowing for studies in its dynamic behavior and performance.
A typical use of reverse engineering using dPNs in the business world is in the documentation of processes for quality certification against standards like ISO 9000
. In this case, dPNs are used to model pieces of the business process, which are then combined to form an overall enterprise architecture
. The process system can be studied to determine each piece's capability and show where risks occur. Requirements are then reverse-engineered and applied at corresponding dPN constructs. Trouble spot processes can be identified and slated for reengineering
. The overall dPN map not only gives quality entities the necessary information about a business's current process, but it also gives the process architect a blue print from which to manage and improve
said processes. This is a major portion of quality engineering
.
This method for designing a complex process system is reflected in the general software development methodology known as the waterfall model
. Actually, this method is not well-suited for the development of complex software without adjusting it to handle the step-wise decomposition of the process architecture. This decomposition occurs entirely within the domain of dPNs from the problem space context model down to the final mapping of the implementation language.
or the hierarchical structure below the parent dPN.
In complex computer design, requirements are generated
and infrastructures proposed. Chosen infrastructures are then further decomposed by determining the new constructs' requirements and decomposing them further in this iterative fashion until the dPNs are decomposed into the implementation language of software or hardware specification. The final hierarchical dPN map documents the architectural decisions that were accepted and a specification is in place that can be used to maintain the system's future evolution.
In business processes, process requirements are policies that must be fulfilled by acceptable procedures. Complex procedures can be specified by simpler procedures. Since business processes are processes, dPNs are an ideal modeling language for them – especially when considering complex business processes like logistics
.
. If the problem and solution space are business processes, it is known as enterprise architecture
. If the problem and solution space are networked equipment, it is known as network architecture
. What is important to each of these applications and to any other process system of varying complexity is that the hierarchical map of the system's structure created by the network of dPNs allows the process architect to study the behavior and performance of the system, keeps architectural design decisions documented, and organizes process requirements along the architectural structure.
Petri net
A Petri net is one of several mathematical modeling languages for the description of distributed systems. A Petri net is a directed bipartite graph, in which the nodes represent transitions and places...
s.
Like Petri nets in general and many related formalisms and notations, they are used to describe and analyze process architecture
Process architecture
Dualistic Petri nets are a process-class variant of Petri nets.Like Petri nets in general and many related formalisms and notations, they are used to describe and analyze process architecture.-Process Modeling with dPNs :...
.
Process Modeling with dPNs
A simple, yet powerful way to model process architectureProcess architecture
Dualistic Petri nets are a process-class variant of Petri nets.Like Petri nets in general and many related formalisms and notations, they are used to describe and analyze process architecture.-Process Modeling with dPNs :...
is using the dualistic extension of Petri nets called dualistic Petri nets (dPNs). A Petri net
Petri net
A Petri net is one of several mathematical modeling languages for the description of distributed systems. A Petri net is a directed bipartite graph, in which the nodes represent transitions and places...
(PN) is a graphical, bipartite modeling language that intuitively and mathematically represent theoretical relationships of moving objects in a network of interconnected constructs. Classical Place/Transition PNs can represent theoretical processes, where the movement of objects implies their transformation, but is too absolute to be pragmatic in representing real-world processes. The real world is dualistic in nature and process is a dualistic phenomenon, this can not be easily represented using a digital-type modeling system. Instead, dualistic extensions to Place/Transition PNs have been introduced and used successfully in modeling the architecture of computer-based systems and business processes.
Among the distinctions of dPNs from classical PNs is space and time (due to energy use) in both the place construct and transformation construct. This results in the simulation effect of marked transformations that allow for the explicit representation of parallel processing, multiprocessing, and the implicit representation of deterioration of objects – all unique to dualistic Petri nets.
Architecture
Besides a propensity to modeling dualistic real-world behavior, PNs also offer a way to manage complex process systems hierarchically. Using classical PN construction rules, Petri nets of Petri nets can be built and a hierarchical conception of a complex process system can be studied. This structure of hierarchical abstraction is the heart of process architectureProcess architecture
Dualistic Petri nets are a process-class variant of Petri nets.Like Petri nets in general and many related formalisms and notations, they are used to describe and analyze process architecture.-Process Modeling with dPNs :...
!
Bottom-Up: Starting with the manifested process
Dualistic Petri nets are capable of modeling any process system at its manifested level. When reverse engineeringReverse engineering
Reverse engineering is the process of discovering the technological principles of a device, object, or system through analysis of its structure, function, and operation...
a manifested process, dPNs have a one-to-one correspondence of dPN construct to any manifested process piece, that is, it is isomorphic to the implementation language of the manifested process. For example, several lines of software code could be represented by one dPN transformation construct. Once the manifested process is completely represented by a network of dPNs, small, well-coupled groups of dPN constructs can be lumped together to form higher level dPN constructs – creating a network of dPNs at a higher level of hierarchical abstraction. Each level of abstraction is consistent with its adjacent levels of abstraction and the rules governing them at each level are the exactly the same because PN abstractions are homomorphic. Now the process design can be considered at various levels of abstraction as deemed appropriate by the process architect, allowing for studies in its dynamic behavior and performance.
A typical use of reverse engineering using dPNs in the business world is in the documentation of processes for quality certification against standards like ISO 9000
ISO 9000
The ISO 9000 family of standards relates to quality management systems and is designed to help organizations ensure they meet the needs of customers and other stakeholders . The standards are published by ISO, the International Organization for Standardization, and available through National...
. In this case, dPNs are used to model pieces of the business process, which are then combined to form an overall enterprise architecture
Enterprise architecture
An enterprise architecture is a rigorous description of the structure of an enterprise, which comprises enterprise components , the externally visible properties of those components, and the relationships between them...
. The process system can be studied to determine each piece's capability and show where risks occur. Requirements are then reverse-engineered and applied at corresponding dPN constructs. Trouble spot processes can be identified and slated for reengineering
Reengineering
Reengineering can refer to:* Trouble shooting* Business process reengineering* Reengineering * Reengineering * User reengineering...
. The overall dPN map not only gives quality entities the necessary information about a business's current process, but it also gives the process architect a blue print from which to manage and improve
Kaizen
, Japanese for "improvement", or "change for the better" refers to philosophy or practices that focus upon continuous improvement of processes in manufacturing, engineering, game development, and business management. It has been applied in healthcare, psychotherapy, life-coaching, government,...
said processes. This is a major portion of quality engineering
Quality Engineering
Quality Engineering is a quarterly academic journal focusing on quality control and quality assurance management through use of physical technology, standards information, and statistical tools. The journal is co-published between American Society for Quality and Marcel Dekker, Inc....
.
Top-down: From Idea to Implementation
dPN modeling of a new process system starts at a high level of hierarchical abstraction. To design a complex process system, such as a sophisticated hardware component or a major project, the process architect must first define the problem space. Since the problem space is itself a process system, dPNs can be used for its modeling. Abstract dPNs that are yet to be implemented are specified within the context of the problem space. These constructs define the solution space within its context network. It is now up to the process architect to traverse down the hierarchical abstraction dimension, proposing new process designs for the solution space in an iterative manner until specifying the actual implementation in the specific implementation language.This method for designing a complex process system is reflected in the general software development methodology known as the waterfall model
Waterfall model
The waterfall model is a sequential design process, often used in software development processes, in which progress is seen as flowing steadily downwards through the phases of Conception, Initiation, Analysis, Design, Construction, Testing, Production/Implementation and Maintenance.The waterfall...
. Actually, this method is not well-suited for the development of complex software without adjusting it to handle the step-wise decomposition of the process architecture. This decomposition occurs entirely within the domain of dPNs from the problem space context model down to the final mapping of the implementation language.
Process Structure
Whether a dPN hierarchical network map was created from the bottom up or from the top down, it shows the structure of the process system. Complex process systems, such as large software programs, will have several layers of hierarchical abstraction. At the top of the structure is one process represented by a couple of dPN constructs. Each subsequent layer below this process is the decomposition of the dPN constructs made up of more dPNs that are in turn decomposed. The “parent” dPN of a set of decomposed dPNs has associated with it requirements that apply to the decomposed network. These requirements were determined by studying the parent dPN's suprastructure or the hierarchical structure above the construct. The decomposed “children” dPNs form the infrastructureInfrastructure
Infrastructure is basic physical and organizational structures needed for the operation of a society or enterprise, or the services and facilities necessary for an economy to function...
or the hierarchical structure below the parent dPN.
In complex computer design, requirements are generated
Requirements analysis
Requirements analysis in systems engineering and software engineering, encompasses those tasks that go into determining the needs or conditions to meet for a new or altered product, taking account of the possibly conflicting requirements of the various stakeholders, such as beneficiaries or users...
and infrastructures proposed. Chosen infrastructures are then further decomposed by determining the new constructs' requirements and decomposing them further in this iterative fashion until the dPNs are decomposed into the implementation language of software or hardware specification. The final hierarchical dPN map documents the architectural decisions that were accepted and a specification is in place that can be used to maintain the system's future evolution.
In business processes, process requirements are policies that must be fulfilled by acceptable procedures. Complex procedures can be specified by simpler procedures. Since business processes are processes, dPNs are an ideal modeling language for them – especially when considering complex business processes like logistics
Logistics
Logistics is the management of the flow of goods between the point of origin and the point of destination in order to meet the requirements of customers or corporations. Logistics involves the integration of information, transportation, inventory, warehousing, material handling, and packaging, and...
.
Conclusion
The entire network of dualistic Petri nets becomes the architecture specification of the process system. If the problem and solution space are entirely in software, it is known as software architectureSoftware architecture
The software architecture of a system is the set of structures needed to reason about the system, which comprise software elements, relations among them, and properties of both...
. If the problem and solution space are business processes, it is known as enterprise architecture
Enterprise architecture
An enterprise architecture is a rigorous description of the structure of an enterprise, which comprises enterprise components , the externally visible properties of those components, and the relationships between them...
. If the problem and solution space are networked equipment, it is known as network architecture
Network architecture
Network architecture is the design of a communications network. It is a framework for the specification of a network's physical components and their functional organization and configuration, its operational principles and procedures, as well as data formats used in its operation.In...
. What is important to each of these applications and to any other process system of varying complexity is that the hierarchical map of the system's structure created by the network of dPNs allows the process architect to study the behavior and performance of the system, keeps architectural design decisions documented, and organizes process requirements along the architectural structure.
See also
- ArchitectureArchitectureArchitecture is both the process and product of planning, designing and construction. Architectural works, in the material form of buildings, are often perceived as cultural and political symbols and as works of art...
- Complex systemComplex systemA complex system is a system composed of interconnected parts that as a whole exhibit one or more properties not obvious from the properties of the individual parts....
and ComplexityComplexityIn general usage, complexity tends to be used to characterize something with many parts in intricate arrangement. The study of these complex linkages is the main goal of complex systems theory. In science there are at this time a number of approaches to characterizing complexity, many of which are... - Enterprise Information Security ArchitectureEnterprise Information Security ArchitectureEnterprise information security architecture is a part of enterprise architecture focusing on information security throughout the enterprise.- Overview :...
- FlowchartFlowchartA flowchart is a type of diagram that represents an algorithm or process, showing the steps as boxes of various kinds, and their order by connecting these with arrows. This diagrammatic representation can give a step-by-step solution to a given problem. Process operations are represented in these...
- General Systems Theory
- Process architectureProcess architectureDualistic Petri nets are a process-class variant of Petri nets.Like Petri nets in general and many related formalisms and notations, they are used to describe and analyze process architecture.-Process Modeling with dPNs :...
- Process engineeringProcess engineeringProcess engineering focuses on the design, operation, control, and optimization of chemical, physical, and biological processes through the aid of systematic computer-based methods...
- Process managementProcess managementProcess management is the ensemble of activities of planning and monitoring the performance of a process. The term usually refers to the management of business processes and manufacturing processes...
- Process modelingProcess modelingThe term process model is used in various contexts. For example, in business process modeling the enterprise process model is often referred to as the business process model. Process models are core concepts in the discipline of process engineering....
- Process theoryProcess theoryProcess theory is a commonly used form of scientific research study in which events or occurrences are said to be the result of certain input states leading to a certain outcome state, following a set process....
- Systems architectureSystems architectureA system architecture or systems architecture is the conceptual model that defines the structure, behavior, and more views of a system.An architecture description is a formal description and representation of a system, organized in a way that supports reasoning about the structure of the system...
- WorkflowWorkflowA workflow consists of a sequence of connected steps. It is a depiction of a sequence of operations, declared as work of a person, a group of persons, an organization of staff, or one or more simple or complex mechanisms. Workflow may be seen as any abstraction of real work...
External links
- Architecture of Computer-based Systems using Dualistic Petri Nets – IEEE citation and abstract.
- Architecture of an SS7 Protocol Stack on a Broadband Switch Platform using Dualistic Petri Nets – IEEE citation and abstract.