
Geysers on Mars
Encyclopedia


Albedo
Albedo , or reflection coefficient, is the diffuse reflectivity or reflecting power of a surface. It is defined as the ratio of reflected radiation from the surface to incident radiation upon it...
), shapes and unusual spider appearance of these features have stimulated a variety of hypotheses about their origin, ranging from differences in frosting reflectance to explanations involving biological processes. However, all current geophysical models assume some sort of geyser
Geyser
A geyser is a spring characterized by intermittent discharge of water ejected turbulently and accompanied by a vapour phase . The word geyser comes from Geysir, the name of an erupting spring at Haukadalur, Iceland; that name, in turn, comes from the Icelandic verb geysa, "to gush", the verb...
-like activity on Mars
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun in the Solar System. The planet is named after the Roman god of war, Mars. It is often described as the "Red Planet", as the iron oxide prevalent on its surface gives it a reddish appearance...
. Their characteristics, and the process of their formation, are still a matter of debate.
These features are unique to the south polar region
Planum Australe
Planum Australe is the southern polar plain on Mars. It extends southward of roughly 75°S and is centered at . The geology of this region was to be explored by the failed NASA mission Mars Polar Lander, which lost contact on entry into the Martian atmosphere.-Ice cap:Planum Australe is partially...
of Mars
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun in the Solar System. The planet is named after the Roman god of war, Mars. It is often described as the "Red Planet", as the iron oxide prevalent on its surface gives it a reddish appearance...
in an area informally called the cryptic region, at latitudes 60° to 80° south and longitudes 150°W to 310°W; this 1 meter deep ice transition area —between the scarps of the thick polar ice layer and the permafrost— is where clusters of the apparent geyser systems are located.
The seasonal frosting and defrosting of ice results in the appearance of a number of features, such dark dune spots with spider-like rille
Rille
Rille is typically used to describe any of the long, narrow depressions in the lunar surface that resemble channels. Typically a rille can be up to several kilometers wide and hundreds of kilometers in length...
s or channels below the ice, where spider-like radial channels are carved between the ground and ice, giving it an appearance of spider webs, then, pressure accumulating in their interior ejects gas and dark basaltic sand or dust, which is deposited on the ice surface and thus, forming dark dune spots. This process is rapid, observed happening in the space of a few days, weeks or months, a growth rate rather unusual in geology – especially for Mars. However, it would seem that multiple years would be required to carve the larger spider-like channels. The current proposed models regarding the possible forces powering the geyser system are discussed below (see: Geyser mechanism models.)
As of November 2008, there is no direct data on these features other than images taken in the visible
Visible spectrum
The visible spectrum is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye. Electromagnetic radiation in this range of wavelengths is called visible light or simply light. A typical human eye will respond to wavelengths from about 390 to 750 nm. In terms of...
and infrared spectra
Electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. The "electromagnetic spectrum" of an object is the characteristic distribution of electromagnetic radiation emitted or absorbed by that particular object....
and no lander
Lander (spacecraft)
A lander is a spacecraft which descends toward and comes to rest on the surface of an astronomical body. For bodies with atmospheres, the landing is called atmospheric reentry and the lander descends as a re-entry vehicle...
is presently planned to visit the geyser-like systems.
History

Mars Global Surveyor
The Mars Global Surveyor was a US spacecraft developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and launched November 1996. It began the United States's return to Mars after a 10-year absence. It completed its primary mission in January 2001 and was in its third extended mission phase when, on 2...
during 1998–1999. At first it was generally thought they were unrelated features because of their appearance, so from 1998 through 2000 they were reported separately on different research publications ( and -respectively), with the first "jet" or "geyser" models starting to be proposed and refined from 2000 onwards.
The name 'spiders' was coined by Malin Space Science Systems
Malin Space Science Systems
Malin Space Science Systems is a San Diego, California company that designs, develops, and operates instruments to fly on unmanned spacecraft. MSSS is headed by chief scientist and CEO Michael C. Malin....
personnel, the developers of the camera. One of the first and most interesting spider photos was found by Greg Orme in October 2000. The unusual shape and appearance of these 'spider webs' and spots caused a lot of speculation about their origin. The first years' surveillance showed that during the following Martian years, 70% of the spots appear at exactly the same place, and a preliminary statistical study obtained between September 1999 and March 2005, indicated that dark dune spots and spiders are related phenomena as functions of the cycle of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
(CO2) ice condensation and sublimation.
It was also initially suggested that the dark spots were simply warm patches of bare ground, but thermal imaging during 2006 revealed that the temperature of these structures is as cold as the ice that covers the area, indicating they were a thin layer of dark material lying on top of the ice and kept chilled by it. However, soon after their first detection, they were discovered to be negative topographical features – i.e. radial troughs or channels of what today are thought to be geyser-like vent systems.
Morphology

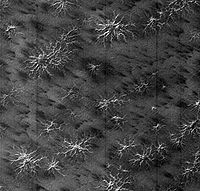
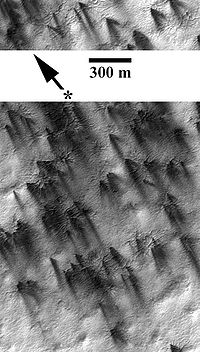
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
(CO2 or 'dry ice'), mainly at the ridges and slopes of the dunes; by the beginning of winter, they disappear. Dark spots' shape is generally round, on the slopes it is usually elongated, sometimes with streams -possibly of water- that accumulate in pools at the bottom of the dunes. Dark dune spots are typically 15 to 46 metres (50 to 150 feet) wide and spaced several hundred feet apart. The size of spots varies, and some are as small as 20 m across, —however, the smaller size seen is limited by imaging resolution— and can grow and coalesce into formations several kilometres wide.
Spider features, when viewed individually, form a round lobed structure reminiscent of a spider web radiating outward in lobes from a central point. Its radial patterns represent shallow channels or ducts in the ice formed by the flow of the sublimation gas toward the vents. The entire spider channel network is typically 160–300 m across, although there are large variations.
Each geyser's characteristic form appears to depend on a combination of such factors as local fluid or gas composition and pressure, ice thickness, underlying gravel type, local climate and meteorological conditions. The geysers' boundary does not seem to correlate with any other properties of the surface such as elevation, geological structure, slope, chemical composition or thermal properties. The geyser-like system produce low albedo
Albedo
Albedo , or reflection coefficient, is the diffuse reflectivity or reflecting power of a surface. It is defined as the ratio of reflected radiation from the surface to incident radiation upon it...
(reflectivity) spots, fans and blotches, with small radial spider-like channel networks most often associated with their location. At first, the spots seem to be grey, but later their centres darken because they gradually get covered with dark ejecta, thought to be mainly basalt
Basalt
Basalt is a common extrusive volcanic rock. It is usually grey to black and fine-grained due to rapid cooling of lava at the surface of a planet. It may be porphyritic containing larger crystals in a fine matrix, or vesicular, or frothy scoria. Unweathered basalt is black or grey...
ic sand. It should be noted that not all dark spots observed in early spring are associated with spider landforms, however, a preponderance of dark spots and streaks on the cryptic terrain are associated with the appearance of spiders later in the season.
Time-lapsed imagery performed by NASA confirms the apparent ejection of dark material following the radial growth of spider channels in the ice. Time-lapsed imaging of a single area of interest also shows that small dark spots generally indicate the position of spider features not yet visible; it also shows that spots expand significantly, including dark fans emanating from some of the spots, which increase in prominence and develop clear directionality indicative of wind action.
Some branching ravines modify, some destroy and others create crust in a dynamic near-surface process that extensively reworks the terrain creating and destroying surface layers. Thus, Mars seems to have a dynamic process of recycling of its near surface crust of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
. Growth process is rapid, happening in the space of a few days, weeks or months, a growth rate rather unusual in geology – especially for Mars. A number of geophysical
Geophysics
Geophysics is the physics of the Earth and its environment in space; also the study of the Earth using quantitative physical methods. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and...
models have been investigated to explain the various colors and shapes' development of these geysers on the southern polar ice cap of Mars.
Geyser mechanism models
The strength of the eruptions is estimated to range from simple upsurges to high-pressure eruptions at speeds of 161 km/h (100 miles/h) or more, carrying dark basaltic sand and dust plumes high aloft. The current proposed models dealing with the possible forces powering the geyser-like system are discussed next.Atmospheric pressure
The surface atmospheric pressure on Mars varies annually around: 6.7–8.8 mbar and 7.5–9.7 mbar; daily around 6.4–6.8 mbar. Because of the pressure changes subsurface gases expand and contract periodically, causing a downward gas flow during increase of and expulsion during decrease of atmospheric pressure. This cycle was first quantified with measurements of the surface pressure, which varies annually with amplitude of 25%.Clathrate hydrate model
This model proposes downward gas flow during increase of and upward flow during decrease of atmospheric pressure. In the defrosting process, ices (clathrate) may partly migrate into the soil and partly may evaporate. These locations can be in connection with the formation of dark dune spots and the arms of spiders as gas travel paths.
Dry venting

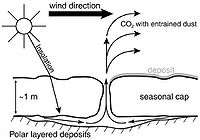
The observation that a few dark spots form before sunrise, with significant spot formation occurring immediately following sunrise, supports the notion that the system is powered by solar energy. Eventually the ice is completely removed and the dark granular material is back on the surface; the cycle repeats many times.
Water-driven erosion
Data obtained by the Mars ExpressMars Express
Mars Express is a space exploration mission being conducted by the European Space Agency . The Mars Express mission is exploring the planet Mars, and is the first planetary mission attempted by the agency. "Express" originally referred to the speed and efficiency with which the spacecraft was...
satellite, made it possible in 2004 to confirm that the southern polar cap has an average of 3 kilometres (1.9 mi) thick slab of CO2 ice with varying contents of frozen water, depending on its latitude: the bright polar cap itself, is a mixture of 85% CO2 ice and 15% water ice. The second part comprises steep slopes known as 'scarps', made almost entirely of water ice, that fall away from the polar cap to the surrounding plains. This transition area between the scarps and the permafrost is the 'cryptic region', where clusters of geysers are located.
This model explores the possibility of active water-driven erosive structures, where soil and water derived from the shallow sub-surface layer is expelled up by CO2 gas through fissures eroding joints to create spider-like radiating tributaries capped with mud-like material and/or ice.
Geothermal
A European team proposes that the features could be a sign that non-solar energy source is responsible of the jets, subsurface heat wave for instance. This model is difficult to reconcile with the evidence collected in the form of thermal emission (infrared) imaging, which shows that the fans, spots and blotches are produced by expulsion of cold fluids or cold gases.Carbon dioxide and water cycling
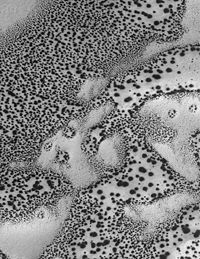
Michael C. Malin
Michael C. Malin is an American astronomer, space-scientist, and CEO of Malin Space Science Systems. His cameras have been important scientific instruments in the Exploration of Mars....
, a planetary scientist and designer of the cameras used by the Mars Global Surveyor
Mars Global Surveyor
The Mars Global Surveyor was a US spacecraft developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and launched November 1996. It began the United States's return to Mars after a 10-year absence. It completed its primary mission in January 2001 and was in its third extended mission phase when, on 2...
that obtained the images, is studying the images acquired of specific areas and he tracks their changes over a period of a few years. On 2000, he modelled the fans and spots' dynamics as a complex process of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
(CO2) and water sublimation and re-precipitation. The typical pattern of defrosting proceeds from the initiation of small, dark spots typically located at the margins of dunes; these spots individually enlarge and eventually all coalesce. The pattern the enlargement follows is distinct and characteristic: a dark nuclear spot enlarges slowly, often with a bright outer zone or 'halo'. As these are progressive, centripetal phenomena, each location of the light zone is overtaken by an expanding dark zone. Although initially developed along dune margins, spot formation quickly spreads onto and between dunes. As spring progresses, fan-shaped tails ('spiders') develop from the central spot. Defrosting occurs as the low albedo polar sand heats beneath an optically thin layer of frost, causing the frost to evaporate. This is the dark nucleus of the spots seen on dunes. As the vapor moves laterally, it encounters cold air and precipitates, forming the bright halo. This precipitated frost is again vaporized as the uncovered zone of sand expands; the cycle repeats many times.
European Space Agency

European Space Agency
The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states...
(ESA) has not yet formulated a theory or model, they have stated that the process of frost sublimation is not compatible with a few important features observed in the images, and that the location and shape of the spots is at odds with a physical explanation, specifically, because the channels appear to radiate downhill as much as they radiate uphill, defying gravity.
Hypothetical biological origin
A team of Hungarian scientists propose that the dark dune spots and channels may be colonies of photosyntheticPhotosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a chemical process that converts carbon dioxide into organic compounds, especially sugars, using the energy from sunlight. Photosynthesis occurs in plants, algae, and many species of bacteria, but not in archaea. Photosynthetic organisms are called photoautotrophs, since they can...
Martian microorganisms, which over-winter beneath the ice cap, and as the sunlight
Sunlight
Sunlight, in the broad sense, is the total frequency spectrum of electromagnetic radiation given off by the Sun. On Earth, sunlight is filtered through the Earth's atmosphere, and solar radiation is obvious as daylight when the Sun is above the horizon.When the direct solar radiation is not blocked...
returns to the pole during early spring, light penetrates the ice, the microorganisms photosynthesise and heat their immediate surroundings. A pocket of liquid water, which would normally evaporate instantly in the thin Martian atmosphere, is trapped around them by the overlying ice. As this ice layer thins, the microorganisms show through grey. When it has completely melted, they rapidly desiccate and turn black surrounded by a grey aureole. The Hungarian scientists believe that even a complex sublimation process is insufficient to explain the formation and evolution of the dark dune spots in space and time. Since their discovery, fiction writer Arthur C. Clarke
Arthur C. Clarke
Sir Arthur Charles Clarke, CBE, FRAS was a British science fiction author, inventor, and futurist, famous for his short stories and novels, among them 2001: A Space Odyssey, and as a host and commentator in the British television series Mysterious World. For many years, Robert A. Heinlein,...
promoted these formations as deserving of study from an astrobiological
Astrobiology
Astrobiology is the study of the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe. This interdisciplinary field encompasses the search for habitable environments in our Solar System and habitable planets outside our Solar System, the search for evidence of prebiotic chemistry,...
perspective.
A multinational European team suggests that if liquid water is present in the spiders' channels during their annual defrost cycle, the structures might provide a niche where certain microscopic life forms could have retreated and adapted while sheltered from UV
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays, in the range 10 nm to 400 nm, and energies from 3 eV to 124 eV...
solar radiation. British and German teams also consider the possibility that organic matter
Organic matter
Organic matter is matter that has come from a once-living organism; is capable of decay, or the product of decay; or is composed of organic compounds...
, microbes, or even simple plants might co-exist with these inorganic formations, especially if the mechanism includes liquid water and a geothermal
Geothermal gradient
Geothermal gradient is the rate of increasing temperature with respect to increasing depth in the Earth's interior. Away from tectonic plate boundaries, it is 25–30°C per km of depth in most of the world. Strictly speaking, geo-thermal necessarily refers to the Earth but the concept may be applied...
energy source. However, they also remark that the majority of geological structures may be accounted for without invoking any organic "life on Mars" hypothesis. (See also: Life on Mars
Life on Mars
Scientists have long speculated about the possibility of life on Mars owing to the planet's proximity and similarity to Earth. Fictional Martians have been a recurring feature of popular entertainment of the 20th and 21st centuries, but it remains an open question whether life currently exists on...
.)
See also
- Arachnoid (astrogeology)Arachnoid (astrogeology)In astrogeology, an arachnoid is a large structure of unknown origin, and they have been found only on the surface of the planet Venus. Arachnoids get their name from their resemblance to spider webs. They appear as concentric ovals surrounded by a complex network of fractures, and can span 200...
- Chaos terrainChaos terrainChaos terrain is an astrogeological term used to denote planetary surface areas where features such as ridges, cracks, and plains appear jumbled and enmeshed with one another. Chaos terrain is a notable feature of the planet Mars and Jupiter's moon Europa...
- Geology of MarsGeology of MarsThe geology of Mars is the scientific study of the surface, crust, and interior of the planet Mars. It emphasizes the composition, structure, history, and physical processes that shape the planet. It is fully analogous to the field of terrestrial geology. In planetary science, the term geology is...
- Planetary geologyPlanetary geologyPlanetary geology, alternatively known as astrogeology or exogeology, is a planetary science discipline concerned with the geology of the celestial bodies such as the planets and their moons, asteroids, comets, and meteorites...
- RilleRilleRille is typically used to describe any of the long, narrow depressions in the lunar surface that resemble channels. Typically a rille can be up to several kilometers wide and hundreds of kilometers in length...
- Swiss cheese featuresSwiss cheese featuresSwiss cheese features are curious pits in the south polar ice cap of Mars named from their similarity to the holes in Swiss cheese. They were first seen in 2000 using Mars Orbiter Camera imagery. They are typically a few hundred meters across and 8 metres deep, with a flat base and steep sides...
External links
- Martian "Spiders" photo repository.
- Arthur C. Clarke on "Martian Spider" features: 1

