
French referendum on the European Constitution
Encyclopedia
The French referendum on the Treaty establishing a Constitution for Europe was held on 29 May 2005 to decide whether France should ratify
the proposed Constitution
of the European Union. The result was a victory for the "No" campaign, with 55% of voters rejecting the treaty on a turnout of 69%.
The question put to voters was:
France was the first country to reject the treaty, and the second country to go to the polls in a referendum on ratification, after a Spanish referendum approved the treaty by a wide margin in February 2005. France's rejection of the Constitution left the treaty with an uncertain future, with other EU member states pledging to continue with their own arrangements for ratification.
 President Jacques Chirac
President Jacques Chirac
's decision to hold a referendum was thought in some part to have been influenced in part by the surprise announcement that the United Kingdom was to hold a vote of its own, though it was also widely commented that the expected easy victory would also be an expression of confidence in the President. Moreover, it would do much to cement his legacy as a French statesman. It would also have a divisive effect on the opposition Socialist Party. Although the adoption of a Constitution had initially been played down as a 'tidying-up' exercise with no need for a popular vote, as increasing numbers of EU member states announced their intention to hold a referendum, the French government came under increasing pressure to follow suit.
The date was announced on 4 March 2005. Opinion polling had shown the "Yes" and "No" campaigns in the lead at various times, but in the weeks leading up the referendum the "No" campaign consistently held the lead. This led many, even some on the "Yes" side, to predict openly that France would reject the Constitution.
held a vote among its members to determine the stance it would take. The issue of the Constitution had caused considerable divisions within the party, with many members—although broadly in favour of European integration—opposing the Constitution for reasons including a perceived lack of democratic accountability, and the threat they considered it posed to the European social model. The "Yes" side was led by party leader François Hollande
while the "No" side was led by deputy leader Laurent Fabius
. A former prime minister of France (1984–1986), Laurent Fabius traditionally on the center right of the Socialist Party opted for the No to the Constitution, switching to the left of the party. For many commentators, this paradoxical move was a gamble to get the upper hand within the party before the next presidentical elections, in case of success of the No vote.
Within the Socialist Party, out of 127,027 members eligible to vote, 59% voted "Yes", with a turnout of 79%. Out of 102 Socialist Party regional federations, 26 voted "No".
ruled that the European Constitution could not legally coexist with the current Constitution of France
. For that reason, a vote was taken to amend the Constitution of France in order to make the two documents compatible.
This amendment passed in an extraordinary joint session of deputies and senators at the Palace of Versailles
on 28 February 2005, with 730 votes in favour and 66 votes against, with 96 abstentions. Both the ruling party and the Socialists supported the constitutional amendment. Communist Party members were the only ones to vote against it.
The three major political forces in France (UMP
, PS
and UDF
) supported the proposed Constitution, as did President Chirac. Supporters of the Constitution from the left sought to emphasise that the treaty incorporates a Charter of Fundamental Rights
and thus helped to secure the future of the European social model. Somewhat surprisingly considering his usual political orientation, Jacques Chirac
defended it as a possible barrier against neoliberal economic policies.
Objections to the Constitution in France can be broadly divided into two camps. On the left, many expressed the view that the Constitution would enforce a neoliberal economic model. Among those were some members of the Socialist Party who dissented from the party's stance as decided by its internal referendum, some members of the Green Party (though the party's official policy was also to support ratification), the Communist Party
and other parties of the hard left, such as the Trotskyist
Revolutionary Communist League
and Workers' Struggle
, as well as associations like ATTAC and trade union
s such as the CGT
or SUD
. These critics sought to link the Constitution to the proposed directive on services in the internal market
, which is widely opposed in France.
There were also prominent opponents of the Constitution from the right, notably Nicolas Dupont-Aignan
(a Gaullist
) and Philippe de Villiers
(of the Movement for France
), and from the extreme right, Jean-Marie Le Pen
of the National Front, who opposed the Constitution on the grounds that France should not be part of any institution whose decisions can take precedence over what is decided in France at a national level. Another factor in the defeat of the Constitution may have been the linking of the Constitution in the minds of voters with the possibility of the accession of Turkey to the European Union
, with which most of the French population disagrees.
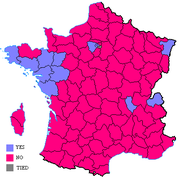
 Most of the départements had a majority of "No" votes. In Brittany and the Pays-de-la-Loire, almost all departments had a majority in favour of ratification, as well in Bas-Rhin
Most of the départements had a majority of "No" votes. In Brittany and the Pays-de-la-Loire, almost all departments had a majority in favour of ratification, as well in Bas-Rhin
, parts of the Île-de-France
, :Haute-Savoie, Rhône
and the DOM
s of Guadeloupe
, French Guiana
, Martinique
and Saint-Pierre and Miquelon
. The département with the most votes in favour was Martinique
, with a 69% "Yes" vote. In metropolitan France, it was Paris
, where 66% of votes were "yes".
, claimed that France's standing in Europe had been considerably weakened.
Pro-EU campaigners for a "No" vote (as opposed to those opposing the EU altogether) argue that the Constitution will be renegotiated. "No" vote campaigners, particularly the prominent socialist Laurent Fabius
, have labelled this option Plan B. Campaigners for a "Yes" vote have stated that there would be no such Plan B and that the 'European project' could be brought to a standstill for at least ten years.
Practically the perspective of a renegotiation quickly appeared illusory after the result of the referendum. First, the challenge of a renegotiation was made all the greater by the diversity of reasons for the rejection of the treaty, ranging from the far left who saw the Constitution as a "capitalists' charter", to the far right who opposed it on nationalistic grounds.
 Prime Minister Jean-Pierre Raffarin
Prime Minister Jean-Pierre Raffarin
was quickly replaced by Dominique de Villepin
. UMP
leader Nicolas Sarkozy
returned to cabinet as Minister of the Interior
.
Although this rejection and the similar no-vote in the Dutch referendum seriously damaged the Constitution, subsequent EU Presidency holders
have vowed to keep it going.
Sarkozy was elected President of the French Republic
in May 2007. Amongst his pledges was a re-negotiation and ratification of a mini-treaty without a referendum. Eventually, the new version of the text, the Lisbon Treaty, was voted by the Parliament.
On the internal political scene, the success of the No did not have the expected effect on the political landscape. Begrudged by the members of the Socialist Party for his divisive role, Laurent Fabius lost the race to the presidential primaries for the 2007 elections, finishing third (18.66%) behind Segolene Royal
(60.65%) and Dominique Strauss-Kahn
(20.83%). The proponents of the Yes eventually got the upper hand in the party, and the lasting division of the far left prevented the apparition of a strong opposition force on left of the Socialist Party by the proponents of the No. On the right of the political spectrum, the far right did not benefit from the success of the No and suffered, for the first time in 15 years a strong decline in the 2007 elections.
Ratification
Ratification is a principal's approval of an act of its agent where the agent lacked authority to legally bind the principal. The term applies to private contract law, international treaties, and constitutionals in federations such as the United States and Canada.- Private law :In contract law, the...
the proposed Constitution
Treaty establishing a Constitution for Europe
The Treaty establishing a Constitution for Europe , , was an unratified international treaty intended to create a consolidated constitution for the European Union...
of the European Union. The result was a victory for the "No" campaign, with 55% of voters rejecting the treaty on a turnout of 69%.
The question put to voters was:
- Approuvez-vous le projet de loi qui autorise la ratification du traité établissant une Constitution pour l'Europe ?
- "Do you approve the bill authorising the ratification of the treaty establishing a Constitution for Europe?"
France was the first country to reject the treaty, and the second country to go to the polls in a referendum on ratification, after a Spanish referendum approved the treaty by a wide margin in February 2005. France's rejection of the Constitution left the treaty with an uncertain future, with other EU member states pledging to continue with their own arrangements for ratification.
Campaign

Jacques Chirac
Jacques René Chirac is a French politician who served as President of France from 1995 to 2007. He previously served as Prime Minister of France from 1974 to 1976 and from 1986 to 1988 , and as Mayor of Paris from 1977 to 1995.After completing his studies of the DEA's degree at the...
's decision to hold a referendum was thought in some part to have been influenced in part by the surprise announcement that the United Kingdom was to hold a vote of its own, though it was also widely commented that the expected easy victory would also be an expression of confidence in the President. Moreover, it would do much to cement his legacy as a French statesman. It would also have a divisive effect on the opposition Socialist Party. Although the adoption of a Constitution had initially been played down as a 'tidying-up' exercise with no need for a popular vote, as increasing numbers of EU member states announced their intention to hold a referendum, the French government came under increasing pressure to follow suit.
The date was announced on 4 March 2005. Opinion polling had shown the "Yes" and "No" campaigns in the lead at various times, but in the weeks leading up the referendum the "No" campaign consistently held the lead. This led many, even some on the "Yes" side, to predict openly that France would reject the Constitution.
Socialist Party vote on stance
On 1 December 2004, the opposition Socialist PartySocialist Party (France)
The Socialist Party is a social-democratic political party in France and the largest party of the French centre-left. It is one of the two major contemporary political parties in France, along with the center-right Union for a Popular Movement...
held a vote among its members to determine the stance it would take. The issue of the Constitution had caused considerable divisions within the party, with many members—although broadly in favour of European integration—opposing the Constitution for reasons including a perceived lack of democratic accountability, and the threat they considered it posed to the European social model. The "Yes" side was led by party leader François Hollande
François Hollande
François Gérard Georges Hollande is a French politician. From 1997 to 2008, he was the First Secretary of the French Socialist Party. He has also served as a Deputy of the National Assembly of France, representing the first constituency of Corrèze, since 1997. He previously represented that seat...
while the "No" side was led by deputy leader Laurent Fabius
Laurent Fabius
Laurent Fabius is a French Socialist politician. He served as Prime Minister from 17 July 1984 to 20 March 1986. He was 37 years old when he was appointed and is, so far, the youngest Prime Minister of the Fifth Republic.-Early life:...
. A former prime minister of France (1984–1986), Laurent Fabius traditionally on the center right of the Socialist Party opted for the No to the Constitution, switching to the left of the party. For many commentators, this paradoxical move was a gamble to get the upper hand within the party before the next presidentical elections, in case of success of the No vote.
Within the Socialist Party, out of 127,027 members eligible to vote, 59% voted "Yes", with a turnout of 79%. Out of 102 Socialist Party regional federations, 26 voted "No".
Amendment to the French Constitution
The Constitutional Council of FranceConstitutional Council of France
The Constitutional Council is the highest constitutional authority in France. It was established by the Constitution of the Fifth Republic on 4 October 1958, and its duty is to ensure that the principles and rules of the constitution are upheld.Its main activity is to rule on whether proposed...
ruled that the European Constitution could not legally coexist with the current Constitution of France
Constitution of France
The current Constitution of France was adopted on 4 October 1958. It is typically called the Constitution of the Fifth Republic, and replaced that of the Fourth Republic dating from 1946. Charles de Gaulle was the main driving force in introducing the new constitution and inaugurating the Fifth...
. For that reason, a vote was taken to amend the Constitution of France in order to make the two documents compatible.
This amendment passed in an extraordinary joint session of deputies and senators at the Palace of Versailles
Palace of Versailles
The Palace of Versailles , or simply Versailles, is a royal château in Versailles in the Île-de-France region of France. In French it is the Château de Versailles....
on 28 February 2005, with 730 votes in favour and 66 votes against, with 96 abstentions. Both the ruling party and the Socialists supported the constitutional amendment. Communist Party members were the only ones to vote against it.
Opinion polls and course of the campaign
Initial opinion polls showed a clear majority in favour of the Constitution, but public opposition grew over time. By May, the "Yes" campaign's lead was smaller than the opinion pollsters' margin of error.The three major political forces in France (UMP
Union for a Popular Movement
The Union for a Popular Movement is a centre-right political party in France, and one of the two major contemporary political parties in the country along with the center-left Socialist Party...
, PS
Socialist Party (France)
The Socialist Party is a social-democratic political party in France and the largest party of the French centre-left. It is one of the two major contemporary political parties in France, along with the center-right Union for a Popular Movement...
and UDF
Union for French Democracy
The Union for French Democracy was a French centrist political party. It was founded in 1978 as an electoral alliance to support President Valéry Giscard d'Estaing in order to counterbalance the Gaullist preponderance over the right. This name was chosen due to the title of Giscard d'Estaing's...
) supported the proposed Constitution, as did President Chirac. Supporters of the Constitution from the left sought to emphasise that the treaty incorporates a Charter of Fundamental Rights
Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union
The Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union enshrines certain political, social, and economic rights for European Union citizens and residents, into EU law. It was drafted by the European Convention and solemnly proclaimed on 7 December 2000 by the European Parliament, the Council of...
and thus helped to secure the future of the European social model. Somewhat surprisingly considering his usual political orientation, Jacques Chirac
Jacques Chirac
Jacques René Chirac is a French politician who served as President of France from 1995 to 2007. He previously served as Prime Minister of France from 1974 to 1976 and from 1986 to 1988 , and as Mayor of Paris from 1977 to 1995.After completing his studies of the DEA's degree at the...
defended it as a possible barrier against neoliberal economic policies.
Objections to the Constitution in France can be broadly divided into two camps. On the left, many expressed the view that the Constitution would enforce a neoliberal economic model. Among those were some members of the Socialist Party who dissented from the party's stance as decided by its internal referendum, some members of the Green Party (though the party's official policy was also to support ratification), the Communist Party
French Communist Party
The French Communist Party is a political party in France which advocates the principles of communism.Although its electoral support has declined in recent decades, the PCF retains a large membership, behind only that of the Union for a Popular Movement , and considerable influence in French...
and other parties of the hard left, such as the Trotskyist
Trotskyism
Trotskyism is the theory of Marxism as advocated by Leon Trotsky. Trotsky considered himself an orthodox Marxist and Bolshevik-Leninist, arguing for the establishment of a vanguard party of the working-class...
Revolutionary Communist League
Revolutionary Communist League (France)
See Revolutionary Communist League for the other Ligue communiste révolutionnaire.The Revolutionary Communist League was a French democratic revolutionary socialist political party. It was the French section of the Fourth International...
and Workers' Struggle
Workers' Struggle
Lutte Ouvrière is the usual name under which the Union Communiste , a French Trotskyist political party, is known, after the name of its weekly paper. Arlette Laguiller has been its spokeswoman since 1973 and has run in each presidential election, but Robert Barcia was its founder and central...
, as well as associations like ATTAC and trade union
Trade union
A trade union, trades union or labor union is an organization of workers that have banded together to achieve common goals such as better working conditions. The trade union, through its leadership, bargains with the employer on behalf of union members and negotiates labour contracts with...
s such as the CGT
Confédération générale du travail
The General Confederation of Labour is a national trade union center, the first of the five major French confederations of trade unions.It is the largest in terms of votes , and second largest in terms of membership numbers.Its membership decreased to 650,000 members in 1995-96 The General...
or SUD
Solidaires Unitaires Démocratiques
The Solidaires or Solidaires Unitaires Démocratiques is a French group of trade unions.-Political position:They tend to favor progressive or even radical views and work with the alter-globalization or anti-globalization movement....
. These critics sought to link the Constitution to the proposed directive on services in the internal market
Directive on services in the internal market
The Directive on services in the internal market is an EU law aiming at establishing a single market for services within the European Union . Drafted under the leadership of the former European Commissioner for the Internal Market Frits Bolkestein, it has been popularly referred to by his name...
, which is widely opposed in France.
There were also prominent opponents of the Constitution from the right, notably Nicolas Dupont-Aignan
Nicolas Dupont-Aignan
Nicolas Dupont-Aignan is a French gaullist and souverainist politician. He has been a MP of the Essonne's 8th constituency since 1997 and a mayor of Yerres, Essonne since 1995....
(a Gaullist
Gaullism
Gaullism is a French political ideology based on the thought and action of Resistance leader then president Charles de Gaulle.-Foreign policy:...
) and Philippe de Villiers
Philippe de Villiers
Viscount Philippe Le Jolis de Villiers de Saintignon, known as Philippe de Villiers, born on 25 March 1949, is a French politician. He was the Mouvement pour la France nominee for the French presidential election of 2007. He received 2.23% of the vote, putting him in sixth place. As only the top...
(of the Movement for France
Movement for France
The Movement for France , abbreviated to MPF, is a French conservative and eurosceptic political party, founded on 20 November 1994, with a marked regional stronghold in the Vendée. It is led by Philippe de Villiers, once communications minister under Jacques Chirac.The party is considered...
), and from the extreme right, Jean-Marie Le Pen
Jean-Marie Le Pen
Jean-Marie Le Pen is a French far right-wing and nationalist politician who is founder and former president of the Front National party. Le Pen has run for the French presidency five times, most notably in 2002, when in a surprise upset he came second, polling more votes in the first round than...
of the National Front, who opposed the Constitution on the grounds that France should not be part of any institution whose decisions can take precedence over what is decided in France at a national level. Another factor in the defeat of the Constitution may have been the linking of the Constitution in the minds of voters with the possibility of the accession of Turkey to the European Union
Accession of Turkey to the European Union
Turkey's application to accede to the European Union was made on 14 April 1987. Turkey has been an associate member of the European Union and its predecessors since 1963...
, with which most of the French population disagrees.
Results

Bas-Rhin
Bas-Rhin is a department of France. The name means "Lower Rhine". It is the more populous and densely populated of the two departments of the Alsace region, with 1,079,013 inhabitants in 2006.- History :...
, parts of the Île-de-France
Île-de-France (région)
Île-de-France is the wealthiest and most populated of the twenty-two administrative regions of France, composed mostly of the Paris metropolitan area....
, :Haute-Savoie, Rhône
Rhône (département)
Rhône is a French department located in the central Eastern region of Rhône-Alpes. It is named after the Rhône River.- History :The Rhône department was created on August 12, 1793 when the former département of Rhône-et-Loire was split into two departments: Rhône and Loire.Originally, the eastern...
and the DOM
Département d'outre-mer
An overseas department is a department of France that is outside metropolitan France. They have the same political status as metropolitan departments. As integral parts of France and the European Union, overseas departments are represented in the National Assembly, Senate, and Economic and Social...
s of Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe is an archipelago located in the Leeward Islands, in the Lesser Antilles, with a land area of 1,628 square kilometres and a population of 400,000. It is the first overseas region of France, consisting of a single overseas department. As with the other overseas departments, Guadeloupe...
, French Guiana
French Guiana
French Guiana is an overseas region of France, consisting of a single overseas department located on the northern Atlantic coast of South America. It has borders with two nations, Brazil to the east and south, and Suriname to the west...
, Martinique
Martinique
Martinique is an island in the eastern Caribbean Sea, with a land area of . Like Guadeloupe, it is an overseas region of France, consisting of a single overseas department. To the northwest lies Dominica, to the south St Lucia, and to the southeast Barbados...
and Saint-Pierre and Miquelon
Saint-Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Pierre and Miquelon is a self-governing territorial overseas collectivity of France. It is the only remnant of the former colonial empire of New France that remains under French control....
. The département with the most votes in favour was Martinique
Martinique
Martinique is an island in the eastern Caribbean Sea, with a land area of . Like Guadeloupe, it is an overseas region of France, consisting of a single overseas department. To the northwest lies Dominica, to the south St Lucia, and to the southeast Barbados...
, with a 69% "Yes" vote. In metropolitan France, it was Paris
Paris
Paris is the capital and largest city in France, situated on the river Seine, in northern France, at the heart of the Île-de-France region...
, where 66% of votes were "yes".
Consequences
The possible consequences of a "No" vote were highly debated in France before the referendum. Proponents of the Constitution, including President ChiracJacques Chirac
Jacques René Chirac is a French politician who served as President of France from 1995 to 2007. He previously served as Prime Minister of France from 1974 to 1976 and from 1986 to 1988 , and as Mayor of Paris from 1977 to 1995.After completing his studies of the DEA's degree at the...
, claimed that France's standing in Europe had been considerably weakened.
Pro-EU campaigners for a "No" vote (as opposed to those opposing the EU altogether) argue that the Constitution will be renegotiated. "No" vote campaigners, particularly the prominent socialist Laurent Fabius
Laurent Fabius
Laurent Fabius is a French Socialist politician. He served as Prime Minister from 17 July 1984 to 20 March 1986. He was 37 years old when he was appointed and is, so far, the youngest Prime Minister of the Fifth Republic.-Early life:...
, have labelled this option Plan B. Campaigners for a "Yes" vote have stated that there would be no such Plan B and that the 'European project' could be brought to a standstill for at least ten years.
Practically the perspective of a renegotiation quickly appeared illusory after the result of the referendum. First, the challenge of a renegotiation was made all the greater by the diversity of reasons for the rejection of the treaty, ranging from the far left who saw the Constitution as a "capitalists' charter", to the far right who opposed it on nationalistic grounds.

Jean-Pierre Raffarin
Jean-Pierre Raffarin is a French conservative politician and senator for Vienne.Jean-Pierre Raffarin served as the Prime Minister of France from 6 May 2002 to 31 May 2005, resigning after France's rejection of the referendum on the European Union draft constitution. However, after Raffarin...
was quickly replaced by Dominique de Villepin
Dominique de Villepin
Dominique Marie François René Galouzeau de Villepin is a French politician who served as the Prime Minister of France from 31 May 2005 to 17 May 2007....
. UMP
Union for a Popular Movement
The Union for a Popular Movement is a centre-right political party in France, and one of the two major contemporary political parties in the country along with the center-left Socialist Party...
leader Nicolas Sarkozy
Nicolas Sarkozy
Nicolas Sarkozy is the 23rd and current President of the French Republic and ex officio Co-Prince of Andorra. He assumed the office on 16 May 2007 after defeating the Socialist Party candidate Ségolène Royal 10 days earlier....
returned to cabinet as Minister of the Interior
Minister of the Interior (France)
The Minister of the Interior in France is one of the most important governmental cabinet positions, responsible for the following:* The general interior security of the country, with respect to criminal acts or natural catastrophes...
.
Although this rejection and the similar no-vote in the Dutch referendum seriously damaged the Constitution, subsequent EU Presidency holders
Presidency of the Council of the European Union
The Presidency of the Council of the European Union is the responsibility for the functioning of the Council of the European Union that rotates between the member states of the European Union every six months. The presidency is not a single president but rather the task is undertaken by a national...
have vowed to keep it going.
Sarkozy was elected President of the French Republic
President of the French Republic
The President of the French Republic colloquially referred to in English as the President of France, is France's elected Head of State....
in May 2007. Amongst his pledges was a re-negotiation and ratification of a mini-treaty without a referendum. Eventually, the new version of the text, the Lisbon Treaty, was voted by the Parliament.
On the internal political scene, the success of the No did not have the expected effect on the political landscape. Begrudged by the members of the Socialist Party for his divisive role, Laurent Fabius lost the race to the presidential primaries for the 2007 elections, finishing third (18.66%) behind Segolene Royal
Ségolène Royal
Marie-Ségolène Royal , known as Ségolène Royal, is a French politician. She is the president of the Poitou-Charentes Regional Council, a former member of the National Assembly, a former government minister, and a prominent member of the French Socialist Party...
(60.65%) and Dominique Strauss-Kahn
Dominique Strauss-Kahn
Dominique Gaston André Strauss-Kahn , often referred to in the media, and by himself, as DSK, is a French economist, lawyer, politician, and member of the French Socialist Party...
(20.83%). The proponents of the Yes eventually got the upper hand in the party, and the lasting division of the far left prevented the apparition of a strong opposition force on left of the Socialist Party by the proponents of the No. On the right of the political spectrum, the far right did not benefit from the success of the No and suffered, for the first time in 15 years a strong decline in the 2007 elections.
External links
- Monitoring report evaluating the fairness of the referendum campaign
- Official results from the Ministry of the Interior
- Proclamation des résultats du référendum du 29 mai 2005 by the Constitutional CouncilConstitutional Council of FranceThe Constitutional Council is the highest constitutional authority in France. It was established by the Constitution of the Fifth Republic on 4 October 1958, and its duty is to ensure that the principles and rules of the constitution are upheld.Its main activity is to rule on whether proposed...
- Results by département from Le MondeLe MondeLe Monde is a French daily evening newspaper owned by La Vie-Le Monde Group and edited in Paris. It is one of two French newspapers of record, and has generally been well respected since its first edition under founder Hubert Beuve-Méry on 19 December 1944...
- :fr:Résultats du référendum français du 29 mai 2005 sur la Constitution européenne: detailed results by département on one page (French Wikipedia)
- Mobilization : French books sold ; web frequenting (fr) ; appeals to court (fr)
- A left perspective on the No campaign by Jim Wolfreys, writing in International SocialismInternational Socialism (journal)International Socialism is a British-based quarterly magazine of socialist theory published by the Socialist Workers Party. It is currently edited by Alex Callinicos, who took over after the death of Chris Harman in November 2009....

