
Forced convection
Encyclopedia
Forced convection
is a mechanism, or type of heat transport in which fluid motion is generated by an external source (like a pump, fan, suction device, etc.). It should be considered as one of the main methods of useful heat transfer as significant amounts of heat energy can be transported very efficiently and this mechanism is found very commonly in everyday life, including central heating
, air conditioning
, steam turbines and in many other machines. Forced convection is often encountered by engineers designing or analyzing heat exchanger
s, pipe flow, and flow over a plate at a different temperature than the stream (the case of a shuttle wing during re-entry, for example). However, in any forced convection situation, some amount of natural convection is always present whenever there are g-forces present (i.e., unless the system is in free fall). When the natural convection is not negligible, such flows are typically referred to as mixed convection.
When analyzing potentially mixed convection, a parameter called the Archimedes number (Ar) parametrizes the relative strength of free and forced convection. The Archimedes number is the ratio of Grashof number and the square of Reynolds number, which represents the ratio of buoyancy force and inertia force, and which stands in for the contribution of natural convection. When Ar >> 1, natural convection dominates and when Ar << 1, forced convection dominates.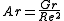
When natural convection isn't a significant factor, mathematical analysis with forced convection theories typically yields accurate results. The parameter of importance in forced convection is the Peclet number
, which is the ratio of advection (movement by currents) and diffusion (movement from high to low concentrations) of heat.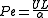
When the Peclet number is much greater than unity (1), advection dominates diffusion. Similarly, much smaller ratios indicate a higher rate of diffusion relative to advection.
Convection
Convection is the movement of molecules within fluids and rheids. It cannot take place in solids, since neither bulk current flows nor significant diffusion can take place in solids....
is a mechanism, or type of heat transport in which fluid motion is generated by an external source (like a pump, fan, suction device, etc.). It should be considered as one of the main methods of useful heat transfer as significant amounts of heat energy can be transported very efficiently and this mechanism is found very commonly in everyday life, including central heating
Central heating
A central heating system provides warmth to the whole interior of a building from one point to multiple rooms. When combined with other systems in order to control the building climate, the whole system may be a HVAC system.Central heating differs from local heating in that the heat generation...
, air conditioning
Air conditioning
An air conditioner is a home appliance, system, or mechanism designed to dehumidify and extract heat from an area. The cooling is done using a simple refrigeration cycle...
, steam turbines and in many other machines. Forced convection is often encountered by engineers designing or analyzing heat exchanger
Heat exchanger
A heat exchanger is a piece of equipment built for efficient heat transfer from one medium to another. The media may be separated by a solid wall, so that they never mix, or they may be in direct contact...
s, pipe flow, and flow over a plate at a different temperature than the stream (the case of a shuttle wing during re-entry, for example). However, in any forced convection situation, some amount of natural convection is always present whenever there are g-forces present (i.e., unless the system is in free fall). When the natural convection is not negligible, such flows are typically referred to as mixed convection.
When analyzing potentially mixed convection, a parameter called the Archimedes number (Ar) parametrizes the relative strength of free and forced convection. The Archimedes number is the ratio of Grashof number and the square of Reynolds number, which represents the ratio of buoyancy force and inertia force, and which stands in for the contribution of natural convection. When Ar >> 1, natural convection dominates and when Ar << 1, forced convection dominates.
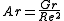
When natural convection isn't a significant factor, mathematical analysis with forced convection theories typically yields accurate results. The parameter of importance in forced convection is the Peclet number
Péclet number
The Péclet number is a dimensionless number relevant in the study of transport phenomena in fluid flows. It is named after the French physicist Jean Claude Eugène Péclet. It is defined to be the ratio of the rate of advection of a physical quantity by the flow to the rate of diffusion of the same...
, which is the ratio of advection (movement by currents) and diffusion (movement from high to low concentrations) of heat.
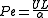
When the Peclet number is much greater than unity (1), advection dominates diffusion. Similarly, much smaller ratios indicate a higher rate of diffusion relative to advection.

