
Archimedes number
Encyclopedia
An Archimedes number 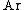 named after the ancient Greek scientist Archimedes
named after the ancient Greek scientist Archimedes
—used to determine the motion of fluid
s due to density
differences—is a dimensionless number in the form:
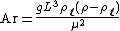
where:
When analyzing potentially mixed convection
of a liquid, the Archimedes number parametrizes the relative strength of free and forced convection
by representing the ratio of Grashof number and the square of Reynolds number. This represents the ratio of buoyancy and inertial forces, which stands in for the contribution of natural convection. When Ar >> 1, natural convection dominates and when Ar << 1, forced convection dominates.
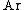 named after the ancient Greek scientist Archimedes
named after the ancient Greek scientist ArchimedesArchimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse was a Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, inventor, and astronomer. Although few details of his life are known, he is regarded as one of the leading scientists in classical antiquity. Among his advances in physics are the foundations of hydrostatics, statics and an...
—used to determine the motion of fluid
Fluid
In physics, a fluid is a substance that continually deforms under an applied shear stress. Fluids are a subset of the phases of matter and include liquids, gases, plasmas and, to some extent, plastic solids....
s due to density
Density
The mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
differences—is a dimensionless number in the form:
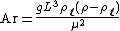
where:
- g = gravitational accelerationGravitational accelerationIn physics, gravitational acceleration is the acceleration on an object caused by gravity. Neglecting friction such as air resistance, all small bodies accelerate in a gravitational field at the same rate relative to the center of mass....
(9.81 m/s²), - ρl = density of the fluid,
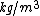
- ρ = density of the body,
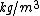
-
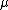 = dynamic viscosity,
= dynamic viscosity, 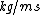
- L = characteristic length of body, m
When analyzing potentially mixed convection
Convection
Convection is the movement of molecules within fluids and rheids. It cannot take place in solids, since neither bulk current flows nor significant diffusion can take place in solids....
of a liquid, the Archimedes number parametrizes the relative strength of free and forced convection
Forced convection
Forced convection is a mechanism, or type of heat transport in which fluid motion is generated by an external source...
by representing the ratio of Grashof number and the square of Reynolds number. This represents the ratio of buoyancy and inertial forces, which stands in for the contribution of natural convection. When Ar >> 1, natural convection dominates and when Ar << 1, forced convection dominates.


