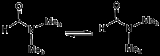
Fluxional
Encyclopedia
Fluxional molecules are molecule
s that undergo dynamics such that some or all of their atom
s interchange between symmetry-equivalent positions. Because virtually all molecules are fluxional in some respects, e.g. bond rotations in most organic compound
s, the term fluxional depends on the context and the method used to assess the dynamics. Often, a molecule is considered fluxional if its spectroscopic signature exhibits line-broadening (beyond that dictated by the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle) due to chemical exchange. In some cases, where the rates are slow, fluxionality is not detected spectroscopically, but by isotopic labeling
.
, which is protonated methane, CH5+. In this unusual species, whose IR spectrum was recently experimentally observed and more recently understood, the barriers to proton exchange are lower than the zero point energy. Thus, even at absolute zero
there is no rigid molecular structure, the H atoms are always in motion. More precisely, the spatial distribution of protons in CH5+ is many times broader than its parent molecule CH4, methane.
.
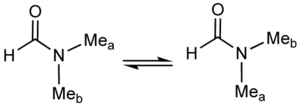 At temperatures near 100 °C, the 500 MHz NMR spectrum of this compound shows only one signal for the methyl groups. Near room temperature however, separate signals are seen for the non-equivalent methyl groups. The rate of exchange can be readily calculated at the temperature where the two signals are just merged. This "coalescence temperature" depends on the measuring field. The relevant equation is:
At temperatures near 100 °C, the 500 MHz NMR spectrum of this compound shows only one signal for the methyl groups. Near room temperature however, separate signals are seen for the non-equivalent methyl groups. The rate of exchange can be readily calculated at the temperature where the two signals are just merged. This "coalescence temperature" depends on the measuring field. The relevant equation is:
where Δνo is the difference in Hz between the frequencies of the exchanging sites. These frequencies are obtained from the limiting low-temperature NMR spectrum. At these lower temperatures, the dynamics continue, of course, but the contribution of the dynamics to line broadening is negligible.
For example, if Δνo = 1ppm @ 500 MHz
Many molecular processes exhibit fluxionality that can be probed on the NMR time scale. Well-known examples include:
in a mixed valence dimer of metal clusters. Application of above equation for coalescence of two signals separated by 10 cm−1 gives the following result:
Clearly, processes that induce line-broadening on the IR time-scale must be extremely rapid.
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
s that undergo dynamics such that some or all of their atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
s interchange between symmetry-equivalent positions. Because virtually all molecules are fluxional in some respects, e.g. bond rotations in most organic compound
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
s, the term fluxional depends on the context and the method used to assess the dynamics. Often, a molecule is considered fluxional if its spectroscopic signature exhibits line-broadening (beyond that dictated by the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle) due to chemical exchange. In some cases, where the rates are slow, fluxionality is not detected spectroscopically, but by isotopic labeling
Isotopic labeling
Isotopic labeling is a technique for tracking the passage of a sample of substance through a system. The substance is 'labeled' by including unusual isotopes in its chemical composition...
.
Carbonium ion
The prototypical fluxional molecule is the carbonium ionCarbonium ion
A carbonium ion is a carbocation of the penta- or tetracoordinated nonclassical type such as an ion of the type R5C+.- Methanium:The parent compound methanium or CH5+ is protonated methane and a superacid. This ion exists as a reactive intermediate in the interstellar medium and can be produced in...
, which is protonated methane, CH5+. In this unusual species, whose IR spectrum was recently experimentally observed and more recently understood, the barriers to proton exchange are lower than the zero point energy. Thus, even at absolute zero
Absolute zero
Absolute zero is the theoretical temperature at which entropy reaches its minimum value. The laws of thermodynamics state that absolute zero cannot be reached using only thermodynamic means....
there is no rigid molecular structure, the H atoms are always in motion. More precisely, the spatial distribution of protons in CH5+ is many times broader than its parent molecule CH4, methane.
NMR spectroscopy
A classic example of a fluxional molecule is dimethylformamideDimethylformamide
Dimethylformamide is an organic compound with the formula 2NCH. Commonly abbreviated as DMF , this colourless liquid is miscible with water and the majority of organic liquids. DMF is a common solvent for chemical reactions...
.
- k = πΔνo/21/2 ~ 2 Δνo
where Δνo is the difference in Hz between the frequencies of the exchanging sites. These frequencies are obtained from the limiting low-temperature NMR spectrum. At these lower temperatures, the dynamics continue, of course, but the contribution of the dynamics to line broadening is negligible.
For example, if Δνo = 1ppm @ 500 MHz
- k ~ 2(500) = 1000 s-1 (ca. 0.5 millisecond half-lifeHalf-lifeHalf-life, abbreviated t½, is the period of time it takes for the amount of a substance undergoing decay to decrease by half. The name was originally used to describe a characteristic of unstable atoms , but it may apply to any quantity which follows a set-rate decay.The original term, dating to...
)
Many molecular processes exhibit fluxionality that can be probed on the NMR time scale. Well-known examples include:
- Cope rearrangementCope rearrangementThe Cope rearrangement is an extensively studied organic reaction involving the [3,3]-sigmatropic rearrangement of 1,5-dienes. It was developed by Arthur C. Cope...
in bullvaleneBullvaleneBullvalene is a hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C10H10 with the unusual property that the chemical bonds making up the molecule are constantly rearranging as in fluxional molecules...
and other 1,5-dienes. - Berry pseudorotation in iron pentacarbonylIron pentacarbonylIron pentacarbonyl, also known as iron carbonyl, is the compound with formula 5. Under standard conditions Fe5 is a free-flowing, straw-colored liquid with a pungent odour. This compound is a common precursor to diverse iron compounds, including many that are useful in organic synthesis. Fe5 is...
and phosphorus pentafluoridePhosphorus pentafluoridePhosphorus pentafluoride, PF5, is a phosphorus halide. It's a colourless gas at room temperature and pressure.-Structure:Single-crystal X-ray studies indicate PF5 molecule has two distinct P−F bonds : P−Fax = 158.0 pm and P−Feq = 152.2 pm...
. - chair inversionCyclohexane conformationA cyclohexane conformation is any of several three-dimensional shapes that a cyclohexane molecule can assume while maintaining the integrity of its chemical bonds....
in cyclohexaneCyclohexaneCyclohexane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula C6H12. Cyclohexane is used as a nonpolar solvent for the chemical industry, and also as a raw material for the industrial production of adipic acid and caprolactam, both of which being intermediates used in the production of nylon...
.
IR spectroscopy
Although less common, some dynamics are also observable on the time-scale of IR spectroscopy. One example is electron transferElectron transfer
Electron transfer is the process by which an electron moves from an atom or a chemical species to another atom or chemical species...
in a mixed valence dimer of metal clusters. Application of above equation for coalescence of two signals separated by 10 cm−1 gives the following result:
- k ~ 2 Δνo ~ 2(10 cm-1)(300 x 108 cm/s) ~ 6 x 1011 s-1
Clearly, processes that induce line-broadening on the IR time-scale must be extremely rapid.

