
Expander cycle (rocket)
Encyclopedia
Engine
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert energy into useful mechanical motion. Heat engines, including internal combustion engines and external combustion engines burn a fuel to create heat which is then used to create motion...
meant to improve the efficiency of fuel delivery.
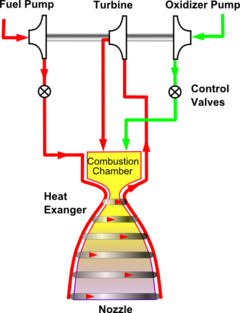
In an expander cycle, the fuel is heated before it is combusted, usually with waste heat from the main combustion chamber. As the liquid fuel passes through coolant passages in the walls of the combustion chamber, it undergoes a phase change into a gaseous state. The fuel in the gaseous state expands through a turbine using the pressure differential from the supply pressure to the ambient exhaust pressure to initiate turbopump rotation. This can provide a bootstrap starting capability as is used on the Pratt & Whitney
Pratt & Whitney
Pratt & Whitney is a U.S.-based aerospace manufacturer with global service operations. It is a subsidiary of United Technologies Corporation . Pratt & Whitney's aircraft engines are widely used in both civil aviation and military aviation. Its headquarters are in East Hartford, Connecticut, USA...
RL10 engine. This bootstrap power is used to drive turbine
Turbine
A turbine is a rotary engine that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work.The simplest turbines have one moving part, a rotor assembly, which is a shaft or drum with blades attached. Moving fluid acts on the blades, or the blades react to the flow, so that they move and...
s that drive the fuel and oxidizer pumps increasing the propellant pressures and flows to the rocket engine
Rocket engine
A rocket engine, or simply "rocket", is a jet engineRocket Propulsion Elements; 7th edition- chapter 1 that uses only propellant mass for forming its high speed propulsive jet. Rocket engines are reaction engines and obtain thrust in accordance with Newton's third law...
thrust chamber. After leaving the turbine(s), the fuel is then injected with the oxidizer into the combustion chamber and burned to produce thrust
Thrust
Thrust is a reaction force described quantitatively by Newton's second and third laws. When a system expels or accelerates mass in one direction the accelerated mass will cause a force of equal magnitude but opposite direction on that system....
for the vehicle.
Because of the necessary phase change, the expander cycle is thrust limited by the square-cube rule
Square-cube law
The square-cube law is a principle, drawn from the mathematics of proportion, that is applied in engineering and biomechanics. It was first demonstrated in 1638 in Galileo's Two New Sciences...
. As the size of a bell-shaped nozzle increases with increasing thrust, the nozzle surface area (from which heat can be extracted to expand the fuel) increases as the square of the radius. However, the volume of fuel that must be heated increases as the cube of the radius. Thus there exists a maximum engine size of approximately 300 kN of thrust beyond which there is no longer enough nozzle area to heat enough fuel to drive the turbines and hence the fuel pumps. Higher thrust levels can be achieved using a bypass expander cycle where a portion of the fuel bypasses the turbine and or thrust chamber cooling passages and goes directly to the main chamber injector. Aerospike
Aerospike engine
The aerospike engine is a type of rocket engine that maintains its aerodynamic efficiency across a wide range of altitudes through the use of an aerospike nozzle. It is a member of the class of altitude compensating nozzle engines. A vehicle with an aerospike engine uses 25–30% less fuel at low...
engines do not suffer from the same limitations because the linear shape of the engine is not subject to the square-cube law. As the width of the engine increases, both the volume of fuel to be heated and the available thermal energy increase linearly, allowing arbitrarily wide engines to be constructed. All expander cycle engines need to use a cryogenic fuel
Cryogenic fuel
Cryogenic fuels are fuels that require storage at extremely low temperatures in order to maintain them in a liquid state. Cryogenic fuels most often constitute liquefied gases such as liquid hydrogen....
such as hydrogen, methane, or propane that easily reach their boiling points
Boiling Points
Boiling Points is a prank reality television show, much like the format used on Candid Camera. It is broadcast on MTV in the United States. In each half-hour episode, annoying situations are set up and deliberately inflicted on one or more young adults who are unaware that they are being tested...
.
Some expander cycle engine may use a gas generator
Gas generator
A gas generator usually refers to a device, often similar to a solid rocket or a liquid rocket that burns to produce large volumes of relatively cool gas, instead of maximizing the temperature and specific impulse. The low temperature allows the gas to be put to use more easily in many...
of some kind to start the turbine and run the engine until the heat input from the thrust chamber and nozzle skirt increases as the chamber pressure builds up.
In an open cycle, or "bleed" expander cycle, only some of the fuel is heated to drive the turbines, which is then vented to atmosphere to increase turbine efficiency. While this increases power output, the dumped fuel leads to a decrease in propellant efficiency (lower engine specific impulse). A closed cycle expander engine sends the turbine exhaust to the combustion chamber (see image at right.)
Expander Bleed Cycle (Open Cycle)
This operational cycle is a modification of the traditional expander cycle. In the bleed (or open) cycle, instead of routing heated propellant through the turbine and sending it back to be combusted, only a small portion of the propellant is heated and used to drive the turbine and is then bled off, being vented overboard without going through the combustion chamber. Bleeding off the turbine exhaust allows for a higher turbopump output by decreasing backpressure and maximizing the pressure drop through the turbine. Compared with a standard expander cycle, this leads to higher engine thrust at the cost of sacrificing some efficiency due to essentially wasting the bled propellant by not combusting it. However, in some cases, such as the Japanese LE-5A/BLE-5
The LE-5 liquid rocket engine and its derivative models were developed in Japan to meet the need for an upper stage propulsion system for the H-I and H-II series of launch vehicles. It is a bipropellant design, using LH2 and LOX. Primary design and production work was carried out by Mitsubishi...
, the thrust performance gains can take precedence over absolute efficiency.
Advantages
The expander cycle has a number of advantages over other designs:- Low temperature. The advantage is that after they have turned gaseous, the fuels are usually near room temperature, and do very little or no damage to the turbine, allowing the engine to be reusable. In contrast Gas-generatorGas-generator cycle (rocket)The gas generator cycle is a power cycle of a bipropellant rocket engine. Some of the propellant is burned in a gas-generator and the resulting hot gas is used to power the engine's pumps. The gas is then exhausted...
or Staged combustionStaged combustion cycle (rocket)The staged combustion cycle, also called topping cycle or pre-burner cycle, is a thermodynamic cycle of bipropellant rocket engines. Some of the propellant is burned in a pre-burner and the resulting hot gas is used to power the engine's turbines and pumps...
engines operate their turbines at high temperature.
- Tolerance. During the development of the RL10 engineers were worried that insulation foam mounted on the inside of the tank might break off and damage the engine. They tested this by putting loose foam in a fuel tank and running it through the engine. The RL10 chewed it up without problems or noticeable degradation in performance. Conventional gas-generators are in practice miniature rocket engines, with all the complexity that implies. Blocking even a small part of a gas generator can lead to a hot spot, which can cause violent loss of the engine. Using the engine bell as a 'gas generator' also makes it very tolerant of fuel contamination because of the wider fuel flow channels used.
- Inherent safety. Because a bell-type expander-cycle engine is thrust limited, it can easily be designed to withstand its maximum thrust conditions. In other engine types, a stuck fuel valve or similar problem can lead to engine thrust spiraling out of control due to unintended feedback systems. Other engine types require complex mechanical or electronic controllers to ensure this does not happen. Expander cycles are by design incapable of malfunctioning that way.
Some examples of an expander cycle engine are the Pratt & Whitney
Pratt & Whitney
Pratt & Whitney is a U.S.-based aerospace manufacturer with global service operations. It is a subsidiary of United Technologies Corporation . Pratt & Whitney's aircraft engines are widely used in both civil aviation and military aviation. Its headquarters are in East Hartford, Connecticut, USA...
RL10 and RL60
RL60
The RL60 is a rocket engine under development by Pratt and Whitney. The design is a high energy LH2/LOX expander cycle, capable of multiple restarts in space.-External links:***...
and the Vinci engine
Vinci (rocket engine)
Vinci is a European Space Agency cryogenic rocket engine currently under development. It is designed to power the new upper stage of Ariane 5, ESC-B, and will be the first European re-ignitable cryogenic upper stage engine, raising the launcher's GTO performances to 12 t.-Overview:Vinci is an...
for the future Ariane 5
Ariane 5
Ariane 5 is, as a part of Ariane rocket family, an expendable launch system used to deliver payloads into geostationary transfer orbit or low Earth orbit . Ariane 5 rockets are manufactured under the authority of the European Space Agency and the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales...
ME http://esamultimedia.esa.int/docs/MinisterialCouncil/MC-ARIANE5_1811.pdf.
Usage
Expander cycle engines include the following:- Pratt & WhitneyPratt & WhitneyPratt & Whitney is a U.S.-based aerospace manufacturer with global service operations. It is a subsidiary of United Technologies Corporation . Pratt & Whitney's aircraft engines are widely used in both civil aviation and military aviation. Its headquarters are in East Hartford, Connecticut, USA...
RL10 - Pratt & Whitney RL60RL60The RL60 is a rocket engine under development by Pratt and Whitney. The design is a high energy LH2/LOX expander cycle, capable of multiple restarts in space.-External links:***...
- Vinci
Expander Bleed cycle engines include the following:
- LE-5A / 5BLE-5The LE-5 liquid rocket engine and its derivative models were developed in Japan to meet the need for an upper stage propulsion system for the H-I and H-II series of launch vehicles. It is a bipropellant design, using LH2 and LOX. Primary design and production work was carried out by Mitsubishi...
Expander cycle engines have been used in:
- Centaur upper stage
- DC-X planned to be the first Single Stage to Orbit Technology demonstration rocket. completed 12 test flights before destruction of the only flight vehicle in an accident.
- Ariane 5Ariane 5Ariane 5 is, as a part of Ariane rocket family, an expendable launch system used to deliver payloads into geostationary transfer orbit or low Earth orbit . Ariane 5 rockets are manufactured under the authority of the European Space Agency and the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales...
upper stage - Saturn ISaturn IThe Saturn I was the United States' first heavy-lift dedicated space launcher, a rocket designed specifically to launch large payloads into low Earth orbit. Most of the rocket's power came from a clustered lower stage consisting of tanks taken from older rocket designs and strapped together to make...
Expander Bleed cycle engines have been used in:
- H-IIH-IIThe H-II rocket was a Japanese satellite launch system, which flew seven times between 1994 and 1999, with five successes. It was developed by NASDA in order to give Japan a capability to launch larger satellites in the 1990s. It was the first two-stage liquid-fuelled rocket Japan made using only...
Second stage - H-IIAH-IIAH-IIA is an active expendable launch system operated by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries for the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency . The liquid-fueled H-IIA rockets have been used to launch satellites into geostationary orbit, to launch a lunar orbiting spacecraft, and to launch an interplanetary...
Second stage - H-IIBH-IIBH-IIB is an expendable launch system used to launch H-II Transfer Vehicles towards the International Space Station. H-IIB rockets are liquid-fuelled with solid-fuel strap-on boosters and are launched from the Tanegashima Space Center in Japan...
Second stage
See also
- Gas-generator cycleGas-generator cycle (rocket)The gas generator cycle is a power cycle of a bipropellant rocket engine. Some of the propellant is burned in a gas-generator and the resulting hot gas is used to power the engine's pumps. The gas is then exhausted...
- Staged combustion cycleStaged combustion cycle (rocket)The staged combustion cycle, also called topping cycle or pre-burner cycle, is a thermodynamic cycle of bipropellant rocket engines. Some of the propellant is burned in a pre-burner and the resulting hot gas is used to power the engine's turbines and pumps...
- Pressure-fed cyclePressure-fed cycle (rocket)The pressure-fed cycle is a class of rocket engine designs. A separate gas supply, usually helium, pressurizes the propellant tanks to force fuel and oxidizer to the combustion chamber. To maintain adequate flow, the tank pressures must exceed the combustion chamber pressure.Pressure fed engines...

