
Elisabeth Church (Marburg)
Encyclopedia

Marburg
Marburg is a city in the state of Hesse, Germany, on the River Lahn. It is the main town of the Marburg-Biedenkopf district and its population, as of March 2010, was 79,911.- Founding and early history :...
, Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
, built by the Order of the Teutonic Knights
Teutonic Knights
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem , commonly the Teutonic Order , is a German medieval military order, in modern times a purely religious Catholic order...
in honour of Elisabeth of Hungary
Elisabeth of Hungary
Elizabeth of Hungary, T.O.S.F., was a princess of the Kingdom of Hungary, Countess of Thuringia, Germany and a greatly-venerated Catholic saint. Elizabeth was married at the age of 14, and widowed at 20. She then became one of the first members of the newly-founded Third Order of St. Francis,...
. Her tomb made the church an important pilgrimage
Pilgrimage
A pilgrimage is a journey or search of great moral or spiritual significance. Typically, it is a journey to a shrine or other location of importance to a person's beliefs and faith...
destination in the late Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
.
Architecture
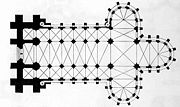

Gothic architecture
Gothic architecture is a style of architecture that flourished during the high and late medieval period. It evolved from Romanesque architecture and was succeeded by Renaissance architecture....
churches in German
German language
German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
-speaking areas, and is held to be a model for the architecture of Cologne Cathedral
Cologne Cathedral
Cologne Cathedral is a Roman Catholic church in Cologne, Germany. It is the seat of the Archbishop of Cologne and the administration of the Archdiocese of Cologne. It is renowned monument of German Catholicism and Gothic architecture and is a World Heritage Site...
. It is built from sandstone
Sandstone
Sandstone is a sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized minerals or rock grains.Most sandstone is composed of quartz and/or feldspar because these are the most common minerals in the Earth's crust. Like sand, sandstone may be any colour, but the most common colours are tan, brown, yellow,...
in a cruciform layout. The nave
Nave
In Romanesque and Gothic Christian abbey, cathedral basilica and church architecture, the nave is the central approach to the high altar, the main body of the church. "Nave" was probably suggested by the keel shape of its vaulting...
and its flanking aisle
Aisle
An aisle is, in general, a space for walking with rows of seats on both sides or with rows of seats on one side and a wall on the other...
s have a vault
Vault (architecture)
A Vault is an architectural term for an arched form used to provide a space with a ceiling or roof. The parts of a vault exert lateral thrust that require a counter resistance. When vaults are built underground, the ground gives all the resistance required...
ed ceiling more than 20 m (66 ft) high. The triple quire consists of the Elisabeth quire, the High quire and the Landgrave quire. The crossing
Crossing (architecture)
A crossing, in ecclesiastical architecture, is the junction of the four arms of a cruciform church.In a typically oriented church , the crossing gives access to the nave on the west, the transept arms on the north and south, and the choir on the east.The crossing is sometimes surmounted by a tower...
is separated from the nave by a stone rood screen
Rood screen
The rood screen is a common feature in late medieval church architecture. It is typically an ornate partition between the chancel and nave, of more or less open tracery constructed of wood, stone, or wrought iron...
. In earlier times, the front part of the church had been reserved for the Knights of the Order. The Elisabeth Church has two towers with an approximate height of 80 m (263 ft). The northern one is crowned by a star, the southern one by a knight. The Elisabeth Church served as an inspiration for St. Paul's Church of Strasbourg
St. Paul's Church (Strasbourg)
The Lutheran St. Paul's Church of Strasbourg is a major Gothic Revival architecture building and one of the landmarks of the city of Strasbourg, in Alsace, France....
.
The Gothic shrine of Saint Elisabeth is the most important treasure of the church, but other pieces of sacral art are also exhibited.
History

Canonization
Canonization is the act by which a Christian church declares a deceased person to be a saint, upon which declaration the person is included in the canon, or list, of recognized saints. Originally, individuals were recognized as saints without any formal process...
. The church was consecrated
Consecration
Consecration is the solemn dedication to a special purpose or service, usually religious. The word "consecration" literally means "to associate with the sacred". Persons, places, or things can be consecrated, and the term is used in various ways by different groups...
in 1283. However, the towers were not finished until 1340. The church was property of the Order of the Teutonic Knights; some buildings of the Order still exist near the church, among them the Deutschhausgut, which now houses the mineral
Mineral
A mineral is a naturally occurring solid chemical substance formed through biogeochemical processes, having characteristic chemical composition, highly ordered atomic structure, and specific physical properties. By comparison, a rock is an aggregate of minerals and/or mineraloids and does not...
collection and the department of geography of the Philipps University of Marburg
Philipps University of Marburg
The Philipp University of Marburg , was founded in 1527 by Landgrave Philip I of Hesse as the world's oldest university dating back to a Protestant foundation...
.
Until the 16th century, the Landgraves
Graf
Graf is a historical German noble title equal in rank to a count or a British earl...
of Hesse
Hesse
Hesse or Hessia is both a cultural region of Germany and the name of an individual German state.* The cultural region of Hesse includes both the State of Hesse and the area known as Rhenish Hesse in the neighbouring Rhineland-Palatinate state...
were buried in the church. In the context of the Reformation
Protestant Reformation
The Protestant Reformation was a 16th-century split within Western Christianity initiated by Martin Luther, John Calvin and other early Protestants. The efforts of the self-described "reformers", who objected to the doctrines, rituals and ecclesiastical structure of the Roman Catholic Church, led...
, Philip I, Landgrave of Hesse
Philip I, Landgrave of Hesse
Philip I of Hesse, , nicknamed der Großmütige was a leading champion of the Protestant Reformation and one of the most important of the early Protestant rulers in Germany....
had the remains of Saint Elisabeth removed, in order to oust the pilgrims from the Protestant city of Marburg. Today, relic
Relic
In religion, a relic is a part of the body of a saint or a venerated person, or else another type of ancient religious object, carefully preserved for purposes of veneration or as a tangible memorial...
s of Elisabeth can be found in the Elisabeth convent in Vienna
Vienna
Vienna is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Austria and one of the nine states of Austria. Vienna is Austria's primary city, with a population of about 1.723 million , and is by far the largest city in Austria, as well as its cultural, economic, and political centre...
, in the City Museum in Stockholm
Stockholm
Stockholm is the capital and the largest city of Sweden and constitutes the most populated urban area in Scandinavia. Stockholm is the most populous city in Sweden, with a population of 851,155 in the municipality , 1.37 million in the urban area , and around 2.1 million in the metropolitan area...
and in Košice
Košice
Košice is a city in eastern Slovakia. It is situated on the river Hornád at the eastern reaches of the Slovak Ore Mountains, near the border with Hungary...
.
Most of the monks converted to Protestantism
Protestantism
Protestantism is one of the three major groupings within Christianity. It is a movement that began in Germany in the early 16th century as a reaction against medieval Roman Catholic doctrines and practices, especially in regards to salvation, justification, and ecclesiology.The doctrines of the...
during the 16th century, and the church was used for Protestant services. For a short time at the beginning of the 19th century, both Catholic
Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the world's largest Christian church, with over a billion members. Led by the Pope, it defines its mission as spreading the gospel of Jesus Christ, administering the sacraments and exercising charity...
mass
Mass (liturgy)
"Mass" is one of the names by which the sacrament of the Eucharist is called in the Roman Catholic Church: others are "Eucharist", the "Lord's Supper", the "Breaking of Bread", the "Eucharistic assembly ", the "memorial of the Lord's Passion and Resurrection", the "Holy Sacrifice", the "Holy and...
and Protestant communion
Eucharist
The Eucharist , also called Holy Communion, the Sacrament of the Altar, the Blessed Sacrament, the Lord's Supper, and other names, is a Christian sacrament or ordinance...
were celebrated in separate parts of the church.
After World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, former German president Paul von Hindenburg
Paul von Hindenburg
Paul Ludwig Hans Anton von Beneckendorff und von Hindenburg , known universally as Paul von Hindenburg was a Prussian-German field marshal, statesman, and politician, and served as the second President of Germany from 1925 to 1934....
and his wife were buried in the Elisabeth church, after the evacuation of their remains from the Tannenberg memorial
Tannenberg Memorial
The Tannenberg Memorial commemorated fallen German soldiers of the second Battle of Tannenberg in 1914, which was named after the medieval Battle of Tannenberg...
in former East Prussia
East Prussia
East Prussia is the main part of the region of Prussia along the southeastern Baltic Coast from the 13th century to the end of World War II in May 1945. From 1772–1829 and 1878–1945, the Province of East Prussia was part of the German state of Prussia. The capital city was Königsberg.East Prussia...
.
Current developments
In order to start a long-needed renovation of the church and the remodeling of its immediate neighborhood, the Stiftung Heilige Elisabeth foundationFoundation (charity)
A foundation is a legal categorization of nonprofit organizations that will typically either donate funds and support to other organizations, or provide the source of funding for its own charitable purposes....
was established in 2004 and supports the city of Marburg and the Protestant Church of Hesse-Kassel and Waldeck in the financing of the repair measures.

