
Electronic throttle control
Encyclopedia
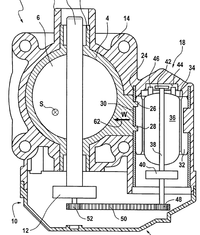
Electronic throttle control (ETC) is an automobile
Automobile
An automobile, autocar, motor car or car is a wheeled motor vehicle used for transporting passengers, which also carries its own engine or motor...
technology which severs the mechanical link between the accelerator pedal and the throttle
Throttle
A throttle is the mechanism by which the flow of a fluid is managed by constriction or obstruction. An engine's power can be increased or decreased by the restriction of inlet gases , but usually decreased. The term throttle has come to refer, informally and incorrectly, to any mechanism by which...
. Most automobiles already use a throttle position sensor
Throttle position sensor
A throttle position sensor is a sensor used to monitor the position of the throttle in an internal combustion engine. The sensor is usually located on the butterfly spindle so that it can directly monitor the position of the throttle valve butterfly....
(TPS) to provide input to traction control
Traction control system
A traction control system , also known as anti-slip regulation , is typically a secondary function of the anti-lock braking system on production motor vehicles, designed to prevent loss of traction of driven road wheels...
, antilock brakes, fuel injection
Fuel injection
Fuel injection is a system for admitting fuel into an internal combustion engine. It has become the primary fuel delivery system used in automotive petrol engines, having almost completely replaced carburetors in the late 1980s....
, and other systems, but use a bowden cable
Bowden cable
A Bowden cable is a type of flexible cable used to transmit mechanical force or energy by the movement of an inner cable relative to a hollow outer cable housing...
to directly connect the pedal with the throttle. An ETC-equipped vehicle has no such cable. Instead, the electronic control unit (ECU) determines the required throttle position by calculations from data measured by other sensors such as an accelerator pedal position sensor, engine speed sensor, vehicle speed sensor etc. The electric motor
Electric motor
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.Most electric motors operate through the interaction of magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors to generate force...
within the ETC is then driven to the required position via a closed-loop control algorithm within the ECU.
The benefits of ETC are largely unnoticed by most drivers because the aim is to make the vehicle power-train characteristics seamlessly consistent irrespective of prevailing conditions, such as engine temperature, altitude, accessory loads etc. However, acceleration response may occasionally be slower than with cable-driven throttle. The ETC is also working 'behind the scenes' to dramatically improve the ease with which the driver can execute gear changes and deal with the dramatic torque changes associated with rapid accelerations and decelerations.
ETC facilitates the integration of features such as cruise control
Cruise control
Cruise control is a system that automatically controls the speed of a motor vehicle. The system takes over the throttle of the car to maintain a steady speed as set by the driver.-History:...
, traction control
Traction control system
A traction control system , also known as anti-slip regulation , is typically a secondary function of the anti-lock braking system on production motor vehicles, designed to prevent loss of traction of driven road wheels...
, stability control, and precrash system
Precrash system
A precrash system is an automobile safety system designed to reduce the severity of an accident. Also known as forward collision warning systems they use radar and sometimes laser sensors to detect an imminent crash...
s and others that require torque management, since the throttle can be moved irrespective of the position of the driver's accelerator pedal. ETC provides only a very limited benefit in areas such as air-fuel ratio control, exhaust emissions and fuel consumption reduction, working in concert with other technologies such as gasoline direct injection
Gasoline direct injection
In internal combustion engines, gasoline direct injection , also known as petrol direct injection or direct petrol injection, is a variant of fuel injection employed in modern two-stroke and four-stroke gasoline engines...
.
A criticism of the very early ETC implementations was that they were "overruling" driver decisions. Nowadays, the vast majority of drivers have no idea how much intervention is happening. Much of the engineering involved with drive-by-wire technologies including ETC deals with failure and fault management. Most ETC systems have sensor and controller redundancy, even as complex as independent microprocessors with independently written software within a control module whose calculations are compared to check for possible errors and faults.
Anti-lock braking (ABS) is a similar safety critical technology, whilst not completely 'by-wire', it has the ability to electronically intervene contrary to the driver's demand. Such technology has recently been extended to other vehicle systems to include features like brake assist
Brake assist
Brake Assist is a generic term for an automobile braking technology that increases braking pressure in an emergency situation. The first application was developed jointly by Daimler-Benz and TRW/LucasVarity...
and electronic steering control, but these systems are much less common, also requiring careful design to ensure appropriate back-up and fail-safe
Fail-safe
A fail-safe or fail-secure device is one that, in the event of failure, responds in a way that will cause no harm, or at least a minimum of harm, to other devices or danger to personnel....
modes.
Failure modes
Before drive by wire technology was introduced, if a throttle stuck open a driver could generally put a toe under the accelerator and lift up. Occasionally after servicing or repair, the wire or cable between the accelerator and throttle would not be correctly reinstalled causing sudden acceleration. However, with the ETC, the movement is all done by electronic controls moving an electric motor. But just moving the throttle by sending a signal to the motor is an open loop condition and leads to poor control. Most if not all current ETC systems have a closed loop system whereby the ECU tells the throttle to open a certain amount according to an algorithm based on the geometry of the throttle. Then, if due to dirt build up in the throttle bore or a damaged TPS a signal is sent from the TPS to the ECU, the ECU can make appropriate adjustments to compensate, though it might result in surging, hesitation or uneven idle.There are two primary types of throttle position sensors: a potentiometer or a Hall Effect sensor
Hall effect sensor
A Hall effect sensor is a transducer that varies its output voltage in response to a magnetic field. Hall effect sensors are used for proximity switching, positioning, speed detection, and current sensing applications....
(magnetic device). The potentiometer is a satisfactory way for non-critical applications such as volume control on a radio, but as it has a wiper contact rubbing against a resistance element, and dirt and wear between the wiper and the resistor can cause erratic readings. The more reliable solution is the magnetic coupling that makes no physical contact, so will never be subject to failing by wear.
This is an insidious failure as it may not provide any symptoms until there is total failure. All cars having a TPS have what is known as a 'limp-home-mode'. When the car goes into the limp-home-mode it is because the accelerator and engine control computer and the throttle are not talking to each other in a way that they can understand. The engine control computer shuts down the signal to the throttle position motor and a set of springs in the throttle set it to a fast idle, fast enough to get the transmission in gear but not so fast that driving may be dangerous.
Recently, ETC was initially suspected by some to be responsible for alleged incidents of unintended acceleration in Toyota and Lexus vehicles. No evidence of this has been demonstrated, and Toyota has been exonerated by the U.S. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration is an agency of the Executive Branch of the U.S. government, part of the Department of Transportation...
(NHTSA).

