
Dual-band blade antenna
Encyclopedia
Introduction

Monopole antenna
A monopole antenna is a class of radio antenna consisting of a straight rod-shaped conductor, often mounted perpendicularly over some type of conductive surface, called a ground plane. The driving signal from the transmitter is applied, or for receiving antennas the output voltage is taken,...
, pictured to the right, has an omni-directional pattern
Radiation pattern
In the field of antenna design the term radiation pattern most commonly refers to the directional dependence of the strength of the radio waves from the antenna or other source ....
and is limited in its frequency range. Please keep in mind that an omni-directional (see omnidirectional antenna
Omnidirectional antenna
In radio communication, an omnidirectional antenna is an antenna which radiates radio wave power uniformly in all directions in one plane, with the radiated power decreasing with elevation angle above or below the plane, dropping to zero on the antenna's axis. This radiation pattern is often...
) radiation pattern applies to the azimuth patterns and does exhibit a null
Null (radio)
In radio electronics, a null is an area or vector in an antenna's radiation pattern where the signal cancels out almost entirely.This can be an advantage, as nulls in the horizontal plane can be used to protect other transmitters from interference. If not carefully planned however, nulls can...
at zenith
Zenith
The zenith is an imaginary point directly "above" a particular location, on the imaginary celestial sphere. "Above" means in the vertical direction opposite to the apparent gravitational force at that location. The opposite direction, i.e...
.
A monopole antenna can be thought of as a dipole antenna
Dipole antenna
A dipole antenna is a radio antenna that can be made of a simple wire, with a center-fed driven element. It consists of two metal conductors of rod or wire, oriented parallel and collinear with each other , with a small space between them. The radio frequency voltage is applied to the antenna at...
where one end of the dipole antenna now becomes the ground plane for said monopole antenna. By this line of conceptual thinking, one can easily reach the conclusion that the radiation emanating from a monopole antenna exists in half the space of similar dipole antenna. Therefore, the maximum gain is twice that, or an addition 3dB, of the maximum gain of typical dipole. Hence the nominal value of maximum for a monopole antenna is about 5.15dBi.
Stutzman puts is succinctly as follows:
- ... A monopole is a dipole that has been divided in half at its center feed point and fed against a ground plane...
This article covers one type of dual band blade monopoles. This is the slot inside a monopole. Computational Electromagnetic Modeling (CEM) will be used to give some graphics of operations for a more conceptual understanding.
Monopoles
Monopole equations can be arrived by inspection of dipole antennaDipole antenna
A dipole antenna is a radio antenna that can be made of a simple wire, with a center-fed driven element. It consists of two metal conductors of rod or wire, oriented parallel and collinear with each other , with a small space between them. The radio frequency voltage is applied to the antenna at...
derivations with the knowledge that all radiation occurs in half the volume when compared to said dipole antenna. This leads to the following equations:
Directivity
Directivity
In electromagnetics, directivity is a figure of merit for an antenna. It measures the power density the antenna radiates in the direction of its strongest emission, versus the power density radiated by an ideal isotropic radiator radiating the same total power.An antenna's directivity is a...
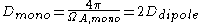
This leads directly to the earlier stated maximum gain relation to a dipole by the definition of gain a
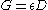 where
where  is the antenna radiation efficiency.
is the antenna radiation efficiency.Impedance
Electrical impedance
Electrical impedance, or simply impedance, is the measure of the opposition that an electrical circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current circuit...
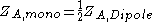
Radiation Resistance
Radiation resistance
Radiation resistance is that part of an antenna's feedpoint resistance that is caused by the radiation of electromagnetic waves from the antenna. The radiation resistance is determined by the geometry of the antenna, not by the materials of which it is made...
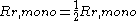
As can be seen in section 1 of the linked radiation resistance
Radiation resistance
Radiation resistance is that part of an antenna's feedpoint resistance that is caused by the radiation of electromagnetic waves from the antenna. The radiation resistance is determined by the geometry of the antenna, not by the materials of which it is made...
article.
Blade Antennas
A blade antenna is an attempt to create a broader band monopole (when compared to a thin wire monopole). Most blade antennas are trapezoidTrapezoid
In Euclidean geometry, a convex quadrilateral with one pair of parallel sides is referred to as a trapezoid in American English and as a trapezium in English outside North America. A trapezoid with vertices ABCD is denoted...
al in shape. Variations have been made on this shape for aerodynamic
Aerodynamics
Aerodynamics is a branch of dynamics concerned with studying the motion of air, particularly when it interacts with a moving object. Aerodynamics is a subfield of fluid dynamics and gas dynamics, with much theory shared between them. Aerodynamics is often used synonymously with gas dynamics, with...
purposes and notches have been introduced in order to achieve a better broad band performance. These type of monopole antennas are generally used in aviation for VHF
Very high frequency
Very high frequency is the radio frequency range from 30 MHz to 300 MHz. Frequencies immediately below VHF are denoted High frequency , and the next higher frequencies are known as Ultra high frequency...
and UHF
Ultra high frequency
Ultra-High Frequency designates the ITU Radio frequency range of electromagnetic waves between 300 MHz and 3 GHz , also known as the decimetre band or decimetre wave as the wavelengths range from one to ten decimetres...
frequency ranges.
For more information see the Antenna Engineering Handbook.
Slot Antennas
A slot antennaSlot antenna
A slot antenna consists of a metal surface, usually a flat plate, with a hole or slot cut out. When the plate is driven as an antenna by a driving frequency, the slot radiates electromagnetic waves in similar way to a dipole antenna. The shape and size of the slot, as well as the driving frequency,...
can be viewed as a dipole with opposite polarization. This is due to the typical feed which sets the orientation of the E-field across the smallest linear dimension of the slot. The following equations can be used to 'translate' a vertical or horizontal slot antenna into its complement (dipole):
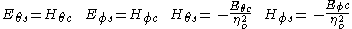
Where the subscript S denotes the opening on the screen and the subscript C denotes its complement (a dipole). In addition,
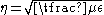 where
where 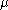 is the complex permeability
is the complex permeabilityPermeability (electromagnetism)
In electromagnetism, permeability is the measure of the ability of a material to support the formation of a magnetic field within itself. In other words, it is the degree of magnetization that a material obtains in response to an applied magnetic field. Magnetic permeability is typically...
and
 is the complex permittivity
is the complex permittivityPermittivity
In electromagnetism, absolute permittivity is the measure of the resistance that is encountered when forming an electric field in a medium. In other words, permittivity is a measure of how an electric field affects, and is affected by, a dielectric medium. The permittivity of a medium describes how...
of the medium into which one is radiating. This assumes an unbounded medium. In addition, all of the slot equations assume a screen thickness much less than a wavelength (
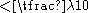 ). If these were not held to be true, fringing and the existence of modes could not be ignored.
). If these were not held to be true, fringing and the existence of modes could not be ignored.This is defined by Babinet's principle
Babinet's principle
In physics, Babinet's principle is a theorem concerning diffraction that states that the diffraction pattern from an opaque body is identical to that from a hole of the same size and shape except for the overall forward beam intensity.-Explanation:...
and Booker's Extension further expands this
principle to include polarization. The simple equations from Babinet's principle are stated on the linked page for which the author has had input.
Dual Band Antennas
Dual band antennas are not a new idea. For years many manufactures have combined multiple elements to create antennas that operate in two separate bands (do not get this confused with so-called frequency independent antennas such as a log-periodic antennaLog-periodic antenna
In telecommunication, a log-periodic antenna is a broadband, multi-element, unidirectional, narrow-beam antenna that has impedance and radiation characteristics that are regularly repetitive as a logarithmic function of the excitation frequency...
).
One way to create a dual band blade antenna is to create a slot in a blade antenna that is less than or on the order of
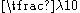 so that the lower frequency does not 'see' the slot (it is a general rule of thumb that the perturbation created by a discontinuity less than
so that the lower frequency does not 'see' the slot (it is a general rule of thumb that the perturbation created by a discontinuity less than 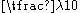 on a structure is negligible).
on a structure is negligible).Computational Electromagnetic Modeling (CEM)
Computational Electromagnetic Modeling (CEM)uses various methods to numerically calculate an antenna pattern.To the untrained eye, this may seem a trivial process. Although, with some research and thought, one will realize that all local structures affect the radiation pattern either by reflection, absorption, refraction, fringing, or being a part of the radiating structure. Some structure which is not local will also cause these items and more including blockage and 're-radiation'. With this in mind, the calculation can become cumbersome.
Multiple algorithms exist in CEM. These include but are not limited to Method of Moments (MoM), Finite Element Method (FEM), and Uniform Theory of Diffraction (UTD). Two examples of software packages that use these methods in free-space are FEKO
FEKO
FEKO is a software product developed by EM Software & Systems - S.A. Ltd. for the simulation of electromagnetic fields. The name is derived from a German acronym which can be translated as "Field Calculations for Bodies with Arbitrary Surface". The software is based on the Method of Moments ...
and WIPL-D. The examples shown here come from WIPL-D. Please keep in mind, these software packages must be used by someone who understands the process and can decide whether the calculated is real or if an error in the model and input data generated false output data (the old adage of garbage in equals garbage out).
Dual Band Blade Antenna Example
This example will use a design for an approximate frequency for Biomedical Telemetry at 460MHz and GPS frequency L1 (1575.42 MHz) in a single package (I hesitate to say a single antenna because there are two radiating elements which would require two baluns for matching). Please keep in mind, these are not match to any transmission line. Therefore the design will not be practical for use. It is only for demonstration purposes.Below you will see the simple used for the simulations. The ground plane is twice the wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
at 460MHz.
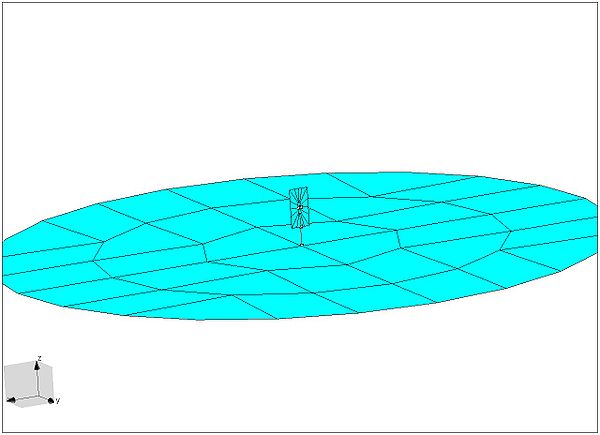
One will also note the polarization of the two elements. As stated before, the polarization of the slot is due to its feed which is generally across the smallest linear dimension. Hence, this slot is Horizontally polarized with respect to the ground plane and the blade is vertically polarized with respect to the ground plane.
Here we are seeing the vertically polarized radiation patters or Vpol for 460MHz.
Whereas presented here we can see the Hpol radiation pattern for both the blade and slot elements.
Conclusion
By the preceding section, it is seen that a dual band blade antenna can be polarity diverse as well as dual band. The bands chosen for this example are relatively close in frequency and give a poor example of the power of such a device, yet it nicely illustrates what can be completed. Given enough real-estate, one can cover two very diverse bands with good coverage and opposite polarization.It also clearly illustrates that the impact of the rectangular slot radiating element is negligible on the radiation pattern of the lower frequency monopole. This is due to the previously mentioned rule of thumb stating it is wise to keep the slot smaller than one-tenth the frequency of operation of the blade. Hence, that frequency does not 'see' the slot.
By combining two elements in this manner, one saves costs in manufacturing and saves real-estate in mounting the antenna. It is noteworthy to mention again that each radiating element must have a different feed structure and most likely a different matching network.

