
Diophantine set
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
, a Diophantine equation
is an equation of the form P(x1, ..., xj, y1, ..., yk)=0 (usually abbreviated P(,)=0 ) where P(,) is a polynomial with integer coefficient
s. A Diophantine set is a subset S of Nj so that for some Diophantine equation
P(,)=0.

That is, a parameter value is in the Diophantine set S if and only if
the associated Diophantine equation is satisfiable under that parameter value. Note that the use of natural numbers both in S and the existential quantification merely reflects the usual applications in computability and model theory. We can equally well speak of Diophantine sets of integers and freely replace quantification over natural numbers with quantification over the integers. Also it is sufficient to assume P is a polynomial over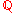 and multiply P by the appropriate denominators to yield integer coefficients. However, whether quantification over rationals can also be substituted for quantification over the integers it is a notoriously hard open problem.
and multiply P by the appropriate denominators to yield integer coefficients. However, whether quantification over rationals can also be substituted for quantification over the integers it is a notoriously hard open problem.
The MRDP theorem states that a set of integers is Diophantine if and only if it is computably enumerable
. A set S is recursively enumerable precisely if there is an algorithm that, when given an integer, eventually halts if that input is a member of S and otherwise runs forever. This means that the concept of general Diophantine set, apparently belonging to number theory
, can be taken rather in logical or recursion-theoretic terms. This is far from obvious, however, and represented the culmination of some decades of work.
Matiyasevich's completion of the MRDP theorem settled Hilbert's tenth problem
. Hilbert's
tenth problem was to find a general algorithm
which can decide whether a given Diophantine equation has a solution among the integers. While Hilbert's tenth problem is not a formal mathematical statement as such the nearly universal acceptance of the (philosophical) identification of a decision algorithm
with a total computable predicate
allows us to use the MRDP theorem to conclude the tenth problem is unsolvable.
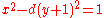
is an example of a Diophantine equation with a parameter. As has long been known, the equation has a solution in the unknowns precisely when the parameter
precisely when the parameter 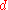 is 0 or not a perfect square
is 0 or not a perfect square
. In the present context, one says that this equation provides a Diophantine definition of the set
consisting of 0 and the natural numbers that are not perfect squares. Other examples of Diophantine definitions are as follows:
A set S of integers is computably enumerable
if there is an algorithm that behaves as follows: When given as input an integer n, if n is a member of S, then the algorithm eventually halts; otherwise it runs forever. That is equivalent to saying there is an algorithm that runs forever and lists the members of S. A set S is Diophantine precisely if there is some polynomial
with integer coefficients f(n, x1, ..., xk)
such that an integer n is in S if and only if there exist some integers
x1, ..., xk
such that f(n, x1, ..., xk) = 0.
It is not hard to see that every Diophantine set is recursively enumerable:
consider a Diophantine equation f(n, x1, ..., xk) = 0.
Now we make an algorithm which simply tries all possible values for
n, x1, ..., xk, in the increasing order of the sum of their absolute values,
and prints n every time f(n, x1, ..., xk) = 0.
This algorithm will obviously run forever and will list exactly the n
for which f(n, x1, ..., xk) = 0 has a solution
in x1, ..., xk.
utilized a method involving Fibonacci number
s in order to show that solutions to Diophantine equations may grow exponentially
. Earlier work by Julia Robinson
, Martin Davis
and Hilary Putnam
had shown that this suffices to show that every computably enumerable set
is Diophantine.
asks for a general algorithm deciding the solvability of Diophantine equations. The conjunction of Matiyasevich's theorem with earlier results known collectively as the MRDP theorem implies that a solution to Hilbert's tenth problem is impossible. The work of the Robinson, Davis and Putnam had proved in the 1960s that there are computably enumerable sets that are non-computable [citation?]. In this context, a set S of integers is called "computable" if there is an algorithm that, when given as input an integer n, returns for every n either a yes-or-no answer to the question of whether n is a member of S. It follows that there are Diophantine equations which cannot be solved by any algorithm.
and differential equation
s are unsolvable.
One can also derive the following stronger form of Gödel's first incompleteness theorem from Matiyasevich's result:
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, a Diophantine equation
Diophantine equation
In mathematics, a Diophantine equation is an indeterminate polynomial equation that allows the variables to be integers only. Diophantine problems have fewer equations than unknown variables and involve finding integers that work correctly for all equations...
is an equation of the form P(x1, ..., xj, y1, ..., yk)=0 (usually abbreviated P(,)=0 ) where P(,) is a polynomial with integer coefficient
Coefficient
In mathematics, a coefficient is a multiplicative factor in some term of an expression ; it is usually a number, but in any case does not involve any variables of the expression...
s. A Diophantine set is a subset S of Nj so that for some Diophantine equation
Diophantine equation
In mathematics, a Diophantine equation is an indeterminate polynomial equation that allows the variables to be integers only. Diophantine problems have fewer equations than unknown variables and involve finding integers that work correctly for all equations...
P(,)=0.

That is, a parameter value is in the Diophantine set S if and only if
If and only if
In logic and related fields such as mathematics and philosophy, if and only if is a biconditional logical connective between statements....
the associated Diophantine equation is satisfiable under that parameter value. Note that the use of natural numbers both in S and the existential quantification merely reflects the usual applications in computability and model theory. We can equally well speak of Diophantine sets of integers and freely replace quantification over natural numbers with quantification over the integers. Also it is sufficient to assume P is a polynomial over
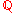 and multiply P by the appropriate denominators to yield integer coefficients. However, whether quantification over rationals can also be substituted for quantification over the integers it is a notoriously hard open problem.
and multiply P by the appropriate denominators to yield integer coefficients. However, whether quantification over rationals can also be substituted for quantification over the integers it is a notoriously hard open problem.The MRDP theorem states that a set of integers is Diophantine if and only if it is computably enumerable
Recursively enumerable set
In computability theory, traditionally called recursion theory, a set S of natural numbers is called recursively enumerable, computably enumerable, semidecidable, provable or Turing-recognizable if:...
. A set S is recursively enumerable precisely if there is an algorithm that, when given an integer, eventually halts if that input is a member of S and otherwise runs forever. This means that the concept of general Diophantine set, apparently belonging to number theory
Number theory
Number theory is a branch of pure mathematics devoted primarily to the study of the integers. Number theorists study prime numbers as well...
, can be taken rather in logical or recursion-theoretic terms. This is far from obvious, however, and represented the culmination of some decades of work.
Matiyasevich's completion of the MRDP theorem settled Hilbert's tenth problem
Hilbert's tenth problem
Hilbert's tenth problem is the tenth on the list of Hilbert's problems of 1900. Its statement is as follows:Given a Diophantine equation with any number of unknown quantities and with rational integral numerical coefficients: To devise a process according to which it can be determined in a finite...
. Hilbert's
David Hilbert
David Hilbert was a German mathematician. He is recognized as one of the most influential and universal mathematicians of the 19th and early 20th centuries. Hilbert discovered and developed a broad range of fundamental ideas in many areas, including invariant theory and the axiomatization of...
tenth problem was to find a general algorithm
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of well-defined instructions for calculating a function. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning...
which can decide whether a given Diophantine equation has a solution among the integers. While Hilbert's tenth problem is not a formal mathematical statement as such the nearly universal acceptance of the (philosophical) identification of a decision algorithm
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of well-defined instructions for calculating a function. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning...
with a total computable predicate
Recursive set
In computability theory, a set of natural numbers is called recursive, computable or decidable if there is an algorithm which terminates after a finite amount of time and correctly decides whether or not a given number belongs to the set....
allows us to use the MRDP theorem to conclude the tenth problem is unsolvable.
Examples
The well known Pell equation
is an example of a Diophantine equation with a parameter. As has long been known, the equation has a solution in the unknowns
 precisely when the parameter
precisely when the parameter 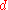 is 0 or not a perfect square
is 0 or not a perfect squareSquare number
In mathematics, a square number, sometimes also called a perfect square, is an integer that is the square of an integer; in other words, it is the product of some integer with itself...
. In the present context, one says that this equation provides a Diophantine definition of the set
- {0,2,3,5,6,7,8,10,...}
consisting of 0 and the natural numbers that are not perfect squares. Other examples of Diophantine definitions are as follows:
- The equation
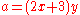 only has solutions in
only has solutions in  when a is not a power of 2.
when a is not a power of 2.
- The equation
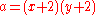 only has solutions in
only has solutions in  when a is greater than 1 and is not a prime numberPrime numberA prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. A natural number greater than 1 that is not a prime number is called a composite number. For example 5 is prime, as only 1 and 5 divide it, whereas 6 is composite, since it has the divisors 2...
when a is greater than 1 and is not a prime numberPrime numberA prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. A natural number greater than 1 that is not a prime number is called a composite number. For example 5 is prime, as only 1 and 5 divide it, whereas 6 is composite, since it has the divisors 2...
.
- The equation
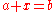 defines the set of pairs
defines the set of pairs 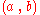 such that
such that 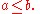
Matiyasevich's theorem
Matiyasevich's theorem says:- Every computably enumerable setRecursively enumerable setIn computability theory, traditionally called recursion theory, a set S of natural numbers is called recursively enumerable, computably enumerable, semidecidable, provable or Turing-recognizable if:...
is Diophantine.
A set S of integers is computably enumerable
Recursively enumerable set
In computability theory, traditionally called recursion theory, a set S of natural numbers is called recursively enumerable, computably enumerable, semidecidable, provable or Turing-recognizable if:...
if there is an algorithm that behaves as follows: When given as input an integer n, if n is a member of S, then the algorithm eventually halts; otherwise it runs forever. That is equivalent to saying there is an algorithm that runs forever and lists the members of S. A set S is Diophantine precisely if there is some polynomial
Polynomial
In mathematics, a polynomial is an expression of finite length constructed from variables and constants, using only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and non-negative integer exponents...
with integer coefficients f(n, x1, ..., xk)
such that an integer n is in S if and only if there exist some integers
x1, ..., xk
such that f(n, x1, ..., xk) = 0.
It is not hard to see that every Diophantine set is recursively enumerable:
consider a Diophantine equation f(n, x1, ..., xk) = 0.
Now we make an algorithm which simply tries all possible values for
n, x1, ..., xk, in the increasing order of the sum of their absolute values,
and prints n every time f(n, x1, ..., xk) = 0.
This algorithm will obviously run forever and will list exactly the n
for which f(n, x1, ..., xk) = 0 has a solution
in x1, ..., xk.
Proof technique
Yuri MatiyasevichYuri Matiyasevich
Yuri Vladimirovich Matiyasevich, is a Russian mathematician and computer scientist. He is best known for his negative solution of Hilbert's tenth problem, presented in his doctoral thesis, at LOMI .- Biography :* In 1962-1963 studied at Saint Petersburg Lyceum 239...
utilized a method involving Fibonacci number
Fibonacci number
In mathematics, the Fibonacci numbers are the numbers in the following integer sequence:0,\;1,\;1,\;2,\;3,\;5,\;8,\;13,\;21,\;34,\;55,\;89,\;144,\; \ldots\; ....
s in order to show that solutions to Diophantine equations may grow exponentially
Exponential growth
Exponential growth occurs when the growth rate of a mathematical function is proportional to the function's current value...
. Earlier work by Julia Robinson
Julia Robinson
Julia Hall Bowman Robinson was an American mathematician best known for her work on decision problems and Hilbert's Tenth Problem.-Background and education:...
, Martin Davis
Martin Davis
Martin David Davis, is an American mathematician, known for his work on Hilbert's tenth problem . He received his Ph.D. from Princeton University in 1950, where his adviser was Alonzo Church . He is Professor Emeritus at New York University. He is the co-inventor of the Davis-Putnam and the DPLL...
and Hilary Putnam
Hilary Putnam
Hilary Whitehall Putnam is an American philosopher, mathematician and computer scientist, who has been a central figure in analytic philosophy since the 1960s, especially in philosophy of mind, philosophy of language, philosophy of mathematics, and philosophy of science...
had shown that this suffices to show that every computably enumerable set
Recursively enumerable set
In computability theory, traditionally called recursion theory, a set S of natural numbers is called recursively enumerable, computably enumerable, semidecidable, provable or Turing-recognizable if:...
is Diophantine.
Application to Hilbert's Tenth problem
Hilbert's tenth problemHilbert's tenth problem
Hilbert's tenth problem is the tenth on the list of Hilbert's problems of 1900. Its statement is as follows:Given a Diophantine equation with any number of unknown quantities and with rational integral numerical coefficients: To devise a process according to which it can be determined in a finite...
asks for a general algorithm deciding the solvability of Diophantine equations. The conjunction of Matiyasevich's theorem with earlier results known collectively as the MRDP theorem implies that a solution to Hilbert's tenth problem is impossible. The work of the Robinson, Davis and Putnam had proved in the 1960s that there are computably enumerable sets that are non-computable [citation?]. In this context, a set S of integers is called "computable" if there is an algorithm that, when given as input an integer n, returns for every n either a yes-or-no answer to the question of whether n is a member of S. It follows that there are Diophantine equations which cannot be solved by any algorithm.
Refinements
Later work has shown that the question of solvability of a Diophantine equation is undecidable even if the equation only has 9 natural number variables (Matiyasevich, 1977) or 11 integer variables (Zhi Wei Sun, 1992).Further applications
Matiyasevich's theorem has since been used to prove that many problems from calculusCalculus
Calculus is a branch of mathematics focused on limits, functions, derivatives, integrals, and infinite series. This subject constitutes a major part of modern mathematics education. It has two major branches, differential calculus and integral calculus, which are related by the fundamental theorem...
and differential equation
Differential equation
A differential equation is a mathematical equation for an unknown function of one or several variables that relates the values of the function itself and its derivatives of various orders...
s are unsolvable.
One can also derive the following stronger form of Gödel's first incompleteness theorem from Matiyasevich's result:
- Corresponding to any given consistent axiomatization of number theory, one can explicitly construct a Diophantine equation which has no solutions, but such that this fact cannot be proved within the given axiomatization.
External links
- Matiyasevich theorem article on ScholarpediaScholarpediaScholarpedia is an English-language online wiki-based encyclopedia that uses the same MediaWiki software as Wikipedia, but has features more commonly associated with open-access online academic journals....
. - Diophantine Set article on PlanetMathPlanetMathPlanetMath is a free, collaborative, online mathematics encyclopedia. The emphasis is on rigour, openness, pedagogy, real-time content, interlinked content, and also community of about 24,000 people with various maths interests. Intended to be comprehensive, the project is hosted by the Digital...
.

