
Delta neutral
Encyclopedia
In finance
, delta neutral describes a portfolio of related financial securities, in which the portfolio value remains unchanged due to small changes in the value of the underlying security. Such a portfolio
typically contains options
and their corresponding underlying securities such that positive and negative delta components offset, resulting in the portfolio's value being relatively insensitive to changes in the value of the underlying security.
A related term, delta hedging is the process of setting or keeping the delta of a portfolio
as close to zero as possible. In practice, maintaining a zero delta is very complex because there are risks associated with re-hedging on large movements in the underlying stock's price, and research indicates portfolios tend to have lower cash flows if re-hedged too frequently.
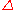 The sensitivity of an option's value to a change in the underlying stock's price.
The sensitivity of an option's value to a change in the underlying stock's price.
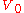 The initial value of the option.
The initial value of the option.
 The current value of the option.
The current value of the option.
 The initial value of the underlying stock.
The initial value of the underlying stock.
Mathematically, delta is represented as partial derivative
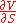
of the option's fair value
with respect to the price of the underlying security
.
Delta is clearly a function of S, however Delta is also a function of Strike Price
and time to expiry.
Therefore, if a position is delta neutral (or, instantaneously delta-hedged) its instantaneous change in value, for an infinitesimal
change in the value of the underlying security, will be zero; see Hedge (finance)
. Since delta measures the exposure of a derivative
to changes in the value of the underlying, a portfolio that is delta neutral is effectively hedged
. That is, its overall value will not change for small changes in the price of its underlying instrument.
Options market makers, or others, may form a delta neutral portfolio using related options instead of the underlying. The portfolio's delta (assuming the same underlier) is then the sum of all the individual options' deltas. This method can also be used when the underlier is difficult to trade, for instance when an underlying stock
is hard to borrow and therefore cannot be sold short
.
One example of delta neutral strategy is buying a deep in the money call and buying a deep in the money put option. Deep in the money call will have delta of 1 and deep in the money put will have delta of -1. Hence their deltas will cancel each other to some extent of stock price movement.
From the Taylor expansion of the value of an option, we get the change in the value of an option,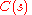 , for a change in the value of the underlier
, for a change in the value of the underlier  :
:
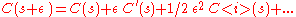
where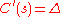 (delta) and
(delta) and 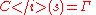 (gamma). (see The Greeks)
(gamma). (see The Greeks)
For any small change in the underlier, we can ignore the second-order term and use the quantity to determine how much of the underlier to buy or sell to create a hedged portfolio.
to determine how much of the underlier to buy or sell to create a hedged portfolio.
When the change in the value of the underlier is not small, the second-order term, , cannot be ignored. In practice, maintaining a delta neutral portfolio requires continual recalculation of the position's Greeks and rebalancing of the underlier's position. Typically, this rebalancing is performed daily or weekly.
, cannot be ignored. In practice, maintaining a delta neutral portfolio requires continual recalculation of the position's Greeks and rebalancing of the underlier's position. Typically, this rebalancing is performed daily or weekly.
Finance
"Finance" is often defined simply as the management of money or “funds” management Modern finance, however, is a family of business activity that includes the origination, marketing, and management of cash and money surrogates through a variety of capital accounts, instruments, and markets created...
, delta neutral describes a portfolio of related financial securities, in which the portfolio value remains unchanged due to small changes in the value of the underlying security. Such a portfolio
Portfolio (finance)
Portfolio is a financial term denoting a collection of investments held by an investment company, hedge fund, financial institution or individual.-Definition:The term portfolio refers to any collection of financial assets such as stocks, bonds and cash...
typically contains options
Option (finance)
In finance, an option is a derivative financial instrument that specifies a contract between two parties for a future transaction on an asset at a reference price. The buyer of the option gains the right, but not the obligation, to engage in that transaction, while the seller incurs the...
and their corresponding underlying securities such that positive and negative delta components offset, resulting in the portfolio's value being relatively insensitive to changes in the value of the underlying security.
A related term, delta hedging is the process of setting or keeping the delta of a portfolio
Portfolio (finance)
Portfolio is a financial term denoting a collection of investments held by an investment company, hedge fund, financial institution or individual.-Definition:The term portfolio refers to any collection of financial assets such as stocks, bonds and cash...
as close to zero as possible. In practice, maintaining a zero delta is very complex because there are risks associated with re-hedging on large movements in the underlying stock's price, and research indicates portfolios tend to have lower cash flows if re-hedged too frequently.
Nomenclature
 The sensitivity of an option's value to a change in the underlying stock's price.
The sensitivity of an option's value to a change in the underlying stock's price.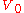 The initial value of the option.
The initial value of the option. The current value of the option.
The current value of the option. The initial value of the underlying stock.
The initial value of the underlying stock.Mathematical interpretation
Delta measures the sensitivity of the value of an option to changes in the price of the underlying stock assuming all other variables remain unchanged.Mathematically, delta is represented as partial derivative
Partial derivative
In mathematics, a partial derivative of a function of several variables is its derivative with respect to one of those variables, with the others held constant...
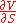
of the option's fair value
Fair value
Fair value, also called fair price , is a concept used in accounting and economics, defined as a rational and unbiased estimate of the potential market price of a good, service, or asset, taking into account such objective factors as:* acquisition/production/distribution costs, replacement costs,...
with respect to the price of the underlying security
Underlying
In finance, the underlying of a derivative is an asset, basket of assets, index, or even another derivative, such that the cash flows of the derivative depend on the value of this underlying...
.
Delta is clearly a function of S, however Delta is also a function of Strike Price
Strike price
In options, the strike price is a key variable in a derivatives contract between two parties. Where the contract requires delivery of the underlying instrument, the trade will be at the strike price, regardless of the spot price of the underlying instrument at that time.Formally, the strike...
and time to expiry.
Therefore, if a position is delta neutral (or, instantaneously delta-hedged) its instantaneous change in value, for an infinitesimal
Infinitesimal
Infinitesimals have been used to express the idea of objects so small that there is no way to see them or to measure them. The word infinitesimal comes from a 17th century Modern Latin coinage infinitesimus, which originally referred to the "infinite-th" item in a series.In common speech, an...
change in the value of the underlying security, will be zero; see Hedge (finance)
Hedge (finance)
A hedge is an investment position intended to offset potential losses that may be incurred by a companion investment.A hedge can be constructed from many types of financial instruments, including stocks, exchange-traded funds, insurance, forward contracts, swaps, options, many types of...
. Since delta measures the exposure of a derivative
Derivative (finance)
A derivative instrument is a contract between two parties that specifies conditions—in particular, dates and the resulting values of the underlying variables—under which payments, or payoffs, are to be made between the parties.Under U.S...
to changes in the value of the underlying, a portfolio that is delta neutral is effectively hedged
Hedge (finance)
A hedge is an investment position intended to offset potential losses that may be incurred by a companion investment.A hedge can be constructed from many types of financial instruments, including stocks, exchange-traded funds, insurance, forward contracts, swaps, options, many types of...
. That is, its overall value will not change for small changes in the price of its underlying instrument.
Creating the position
Delta hedging - i.e. establishing the required hedge - may be accomplished by buying or selling an amount of the underlier that corresponds to the delta of the portfolio. By adjusting the amount bought or sold on new positions, the portfolio delta can be made to sum to zero, and the portfolio is then delta neutral.Options market makers, or others, may form a delta neutral portfolio using related options instead of the underlying. The portfolio's delta (assuming the same underlier) is then the sum of all the individual options' deltas. This method can also be used when the underlier is difficult to trade, for instance when an underlying stock
Stock
The capital stock of a business entity represents the original capital paid into or invested in the business by its founders. It serves as a security for the creditors of a business since it cannot be withdrawn to the detriment of the creditors...
is hard to borrow and therefore cannot be sold short
Short selling
In finance, short selling is the practice of selling assets, usually securities, that have been borrowed from a third party with the intention of buying identical assets back at a later date to return to that third party...
.
One example of delta neutral strategy is buying a deep in the money call and buying a deep in the money put option. Deep in the money call will have delta of 1 and deep in the money put will have delta of -1. Hence their deltas will cancel each other to some extent of stock price movement.
Theory
The existence of a delta neutral portfolio was shown as part of the original proof of the Black–Scholes model, the first comprehensive model to produce correct prices for some classes of options.From the Taylor expansion of the value of an option, we get the change in the value of an option,
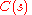 , for a change in the value of the underlier
, for a change in the value of the underlier  :
: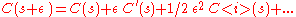
where
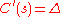 (delta) and
(delta) and 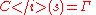 (gamma). (see The Greeks)
(gamma). (see The Greeks)For any small change in the underlier, we can ignore the second-order term and use the quantity
 to determine how much of the underlier to buy or sell to create a hedged portfolio.
to determine how much of the underlier to buy or sell to create a hedged portfolio.When the change in the value of the underlier is not small, the second-order term,
 , cannot be ignored. In practice, maintaining a delta neutral portfolio requires continual recalculation of the position's Greeks and rebalancing of the underlier's position. Typically, this rebalancing is performed daily or weekly.
, cannot be ignored. In practice, maintaining a delta neutral portfolio requires continual recalculation of the position's Greeks and rebalancing of the underlier's position. Typically, this rebalancing is performed daily or weekly.
