
Strike price
Encyclopedia
In options
, the strike price (or exercise price) is a key variable in a derivatives
contract between two parties. Where the contract requires delivery of the underlying
instrument, the trade will be at the strike price, regardless of the spot price
(market price) of the underlying instrument at that time.
Formally, the strike price can be defined as the fixed price at which the owner of an option can purchase (in the case of a call
), or sell (in the case of a put
), the underlying security or commodity.
For example, an IBM May 50 Call has a strike price of $50 a share. When the option is exercised the owner of the option will buy 100 shares of IBM stock for $50 per share.
is a term describing the relationship between the strike price of an option and the current trading price of its underlying security. Where settlement is financial, the difference between the strike price and the spot price will determine the value, or "moneyness", of the contract.
In options trading, terms such as in-the-money, at-the-money and out-of-the-money describe the moneyness of options.
A call option
is in-the-money if the strike price is below the market price of the underlying stock.
A put option is in-the-money if the strike price is above the market price of the underlying stock.
A call or put option is at-the-money if the stock price and the exercise price are the same (or close).
A call option is out-of-the-money if the strike price is above the market price of the underlying stock.
A put option is out-of-the-money if the strike price is below the market price of the underlying stock.
has positive monetary value at expiration when the underlying has a spot price (S) above the strike price (K). Since the option will not be exercised unless it is in-the-money, the payoff for a call option is
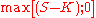
also written as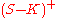
where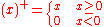
A put option
has positive monetary value at expiration when the underlying has a spot price below the strike price; it is "out-the-money" otherwise, and will not be exercised. The payoff is therefore: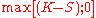
or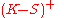
For a digital option payoff is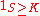 , where
, where 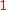 is the indicator function.
is the indicator function.
Option (finance)
In finance, an option is a derivative financial instrument that specifies a contract between two parties for a future transaction on an asset at a reference price. The buyer of the option gains the right, but not the obligation, to engage in that transaction, while the seller incurs the...
, the strike price (or exercise price) is a key variable in a derivatives
Derivative (finance)
A derivative instrument is a contract between two parties that specifies conditions—in particular, dates and the resulting values of the underlying variables—under which payments, or payoffs, are to be made between the parties.Under U.S...
contract between two parties. Where the contract requires delivery of the underlying
Underlying
In finance, the underlying of a derivative is an asset, basket of assets, index, or even another derivative, such that the cash flows of the derivative depend on the value of this underlying...
instrument, the trade will be at the strike price, regardless of the spot price
Spot price
The spot price or spot rate of a commodity, a security or a currency is the price that is quoted for immediate settlement . Spot settlement is normally one or two business days from trade date...
(market price) of the underlying instrument at that time.
Formally, the strike price can be defined as the fixed price at which the owner of an option can purchase (in the case of a call
Call option
A call option, often simply labeled a "call", is a financial contract between two parties, the buyer and the seller of this type of option. The buyer of the call option has the right, but not the obligation to buy an agreed quantity of a particular commodity or financial instrument from the seller...
), or sell (in the case of a put
Put option
A put or put option is a contract between two parties to exchange an asset, the underlying, at a specified price, the strike, by a predetermined date, the expiry or maturity...
), the underlying security or commodity.
For example, an IBM May 50 Call has a strike price of $50 a share. When the option is exercised the owner of the option will buy 100 shares of IBM stock for $50 per share.
Moneyness
MoneynessMoneyness
In finance, moneyness is a measure of the degree to which a derivative is likely to have positive monetary value at its expiration, in the risk-neutral measure. It can be measured in percentage probability, or in standard deviations....
is a term describing the relationship between the strike price of an option and the current trading price of its underlying security. Where settlement is financial, the difference between the strike price and the spot price will determine the value, or "moneyness", of the contract.
In options trading, terms such as in-the-money, at-the-money and out-of-the-money describe the moneyness of options.
A call option
Call option
A call option, often simply labeled a "call", is a financial contract between two parties, the buyer and the seller of this type of option. The buyer of the call option has the right, but not the obligation to buy an agreed quantity of a particular commodity or financial instrument from the seller...
is in-the-money if the strike price is below the market price of the underlying stock.
A put option is in-the-money if the strike price is above the market price of the underlying stock.
A call or put option is at-the-money if the stock price and the exercise price are the same (or close).
A call option is out-of-the-money if the strike price is above the market price of the underlying stock.
A put option is out-of-the-money if the strike price is below the market price of the underlying stock.
Mathematical Formula
A call optionCall option
A call option, often simply labeled a "call", is a financial contract between two parties, the buyer and the seller of this type of option. The buyer of the call option has the right, but not the obligation to buy an agreed quantity of a particular commodity or financial instrument from the seller...
has positive monetary value at expiration when the underlying has a spot price (S) above the strike price (K). Since the option will not be exercised unless it is in-the-money, the payoff for a call option is
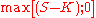
also written as
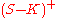
where
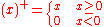
A put option
Put option
A put or put option is a contract between two parties to exchange an asset, the underlying, at a specified price, the strike, by a predetermined date, the expiry or maturity...
has positive monetary value at expiration when the underlying has a spot price below the strike price; it is "out-the-money" otherwise, and will not be exercised. The payoff is therefore:
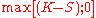
or
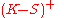
For a digital option payoff is
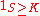 , where
, where 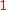 is the indicator function.
is the indicator function.See also
- Option time valueOption time valueIn finance, the time value of an option is the premium a rational investor would pay over its current exercise value , based on its potential to increase in value before expiring. This probability is always greater than zero, thus an option is always worth more than its current exercise value...
- Intrinsic valueIntrinsic value (finance)In finance, intrinsic value refers to the value of a security which is intrinsic to or contained in the security itself. It is also frequently called fundamental value. It is ordinarily calculated by summing the future income generated by the asset, and discounting it to the present value...
- Option screenerOption screenerAn option screener is a tool that evaluates options based on criteria and generates a list of potential trading ideas. Most people who trade options are technical traders. It essentially means they look for patterns in charts. Also they use statistical correlations and deviations and give them...

