
Degree of ionization
Encyclopedia
Gas
Gas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons...
or aqueous solution, that are ionized into charged particles. A low degree of ionization is sometimes called partially ionized, and a very high degree of ionization as fully ionized.
Ionization refers to the process whereby an atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
or molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
loses an electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
, resulting in two oppositely charged particles, (1) a negatively charged electron and (2) a positively charged ion
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
.
Chemistry usage
The degree of ionization, or α, is a way of representing the strength of an acid, often represented by the Greek letter alpha. It is defined as the ratio between the number of ionized molecules and the number of molecules dissolved in water. It can be represented as a decimal number or as a percentage. One can classify strong acids as having ionization degrees above 50%, weak acids with α below 50%, and the remaining as moderate acids, at a specified molar concentration.Physics usage
In gases and plasmaPlasma (physics)
In physics and chemistry, plasma is a state of matter similar to gas in which a certain portion of the particles are ionized. Heating a gas may ionize its molecules or atoms , thus turning it into a plasma, which contains charged particles: positive ions and negative electrons or ions...
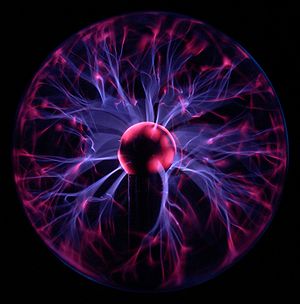
, the degree of ionization refers to the proportion of neutral particles that are ionized into charged particles. For example, when electricity passes through a novelty plasma ball, perhaps 1% of the gases are ionized (sometimes referred to as partially ionized). Our Sun and all stars contain largely hydrogen and helium gases, that are fully ionized into electrons, protons (H+) and helium ions (He++).
A gas may begin to behave like plasma when the degree of ionization is as little as 0.01%.
History
Ionized matter was first identified in a discharge tube (or Crookes tubeCrookes tube
A Crookes tube is an early experimental electrical discharge tube, invented by English physicist William Crookes and others around 1869-1875, in which cathode rays, that is electrons, were discovered....
), and so described by Sir William Crookes in 1879 (he called it "radiant matter"). The nature of the Crookes tube
Crookes tube
A Crookes tube is an early experimental electrical discharge tube, invented by English physicist William Crookes and others around 1869-1875, in which cathode rays, that is electrons, were discovered....
"cathode ray
Cathode ray
Cathode rays are streams of electrons observed in vacuum tubes. If an evacuated glass tube is equipped with two electrodes and a voltage is applied, the glass opposite of the negative electrode is observed to glow, due to electrons emitted from and travelling perpendicular to the cathode Cathode...
" matter was subsequently identified by English physicist Sir J.J. Thomson
J. J. Thomson
Sir Joseph John "J. J." Thomson, OM, FRS was a British physicist and Nobel laureate. He is credited for the discovery of the electron and of isotopes, and the invention of the mass spectrometer...
in 1897, and dubbed "plasma" by Irving Langmuir
Irving Langmuir
Irving Langmuir was an American chemist and physicist. His most noted publication was the famous 1919 article "The Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms and Molecules" in which, building on Gilbert N. Lewis's cubical atom theory and Walther Kossel's chemical bonding theory, he outlined his...
in 1928, perhaps because it reminded him of a blood plasma
Blood plasma
Blood plasma is the straw-colored liquid component of blood in which the blood cells in whole blood are normally suspended. It makes up about 55% of the total blood volume. It is the intravascular fluid part of extracellular fluid...
.

