
Cyaxares
Encyclopedia
Cyaxares, Cyaxares the Great or Hvakhshathra ( Uvaxštra, Greek
Κυαξάρης; r. 625–585 BC), the son of King Phraortes
, was the first king of Media
. According to Herodotus
, Cyaxares, grandson of Deioces
, had a far greater military reputation than his father or grandfather, therefore he is often being described as the first official Median King
.
 He was born in the Median capital of Ecbatana
He was born in the Median capital of Ecbatana
, his father Phraortes
was killed in a battle against the Assyrians, led by Ashurbanipal
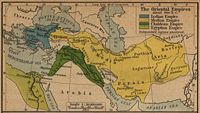
, the king of Neo-Assyria. After his fall the Scythians took over. In his early age Cyaxares was seeking for revenge. He killed the Scythian leaders and proclaimed himself as King of Medes. After throwing of the Scythians, he prepared for war against Assyria. Cyaxares reorganized and modernized the Median Army, then joined with King Nabopolassar
of Babylonia
. This alliance was formalized through the marriage of Cyaxares daughter, Amytis with Nabopolassar
's son, Nebuchadnezzar II, the king who constructed the Hanging Gardens of Babylon
as a present for his Median
wife to help with her homesickness for the mountainous country of her birth. These allies overthrew the Assyrian Empire and destroyed Nineveh
in 612 BC.
, Armenia
and the parts of Asia Minor
east of the Halys
River, which was the border established with Lydia
after a decisive battle between Lydia
and Media
, the Battle of Halys ended with an eclipse on May 28, 585 BC.
The conflict between Lydia
and the Medes
was reported by Herodotus
as follows:
Cyaxares died shortly after the battle and was succeeded by his son, Astyages
, who was the maternal grandfather of Cyrus the Great
through his daughter Mandane of Media
.
. Qyzqapan is today an archaeological site in Silemani (Kurdistan Region).
The construction of the tomb, begun after the death of Cyaxares the Great in 585 BC. The tomb contains Zoroastrian symbols, since the Medes had an ancient religion (a form of pre-Zoroastrian Mazdaism or Mithra worshipping
) with a priesthood named as "Magi
". Later and during the reigns of last Median kings the reforms of Zarathustra spread in northwestern Iran, (mainly the modern Kurdish parts).
Greek language
Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. Native to the southern Balkans, it has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history;...
Κυαξάρης; r. 625–585 BC), the son of King Phraortes
Phraortes
Phraortes , son of Diyako, was the second king of the Median Empire....
, was the first king of Media
Medes
The MedesThe Medes...
. According to Herodotus
Herodotus
Herodotus was an ancient Greek historian who was born in Halicarnassus, Caria and lived in the 5th century BC . He has been called the "Father of History", and was the first historian known to collect his materials systematically, test their accuracy to a certain extent and arrange them in a...
, Cyaxares, grandson of Deioces
Deioces
Deioces, Diyako or Deiokes was the first king of the Medes according to Herodotus. In the late 8th century BC there was a Daiukku or Dayukku who was a Mannaean provincial governor...
, had a far greater military reputation than his father or grandfather, therefore he is often being described as the first official Median King
Medes
The MedesThe Medes...
.
The rise of Cyaxares

Ecbatana
Ecbatana is supposed to be the capital of Astyages , which was taken by the Persian emperor Cyrus the Great in the sixth year of Nabonidus...
, his father Phraortes
Phraortes
Phraortes , son of Diyako, was the second king of the Median Empire....
was killed in a battle against the Assyrians, led by Ashurbanipal
Ashurbanipal
Ashurbanipal |Ashur]] is creator of an heir"; 685 BC – c. 627 BC), also spelled Assurbanipal or Ashshurbanipal, was an Assyrian king, the son of Esarhaddon and the last great king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire...
, the king of Neo-Assyria. After his fall the Scythians took over. In his early age Cyaxares was seeking for revenge. He killed the Scythian leaders and proclaimed himself as King of Medes. After throwing of the Scythians, he prepared for war against Assyria. Cyaxares reorganized and modernized the Median Army, then joined with King Nabopolassar
Nabopolassar
Nabopolassar was the king of the Babylonia and played a key role in the demise of the Assyrian Empire following the death of the last powerful Assyrian king, Ashurbanipal...
of Babylonia
Babylonia
Babylonia was an ancient cultural region in central-southern Mesopotamia , with Babylon as its capital. Babylonia emerged as a major power when Hammurabi Babylonia was an ancient cultural region in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq), with Babylon as its capital. Babylonia emerged as...
. This alliance was formalized through the marriage of Cyaxares daughter, Amytis with Nabopolassar
Nabopolassar
Nabopolassar was the king of the Babylonia and played a key role in the demise of the Assyrian Empire following the death of the last powerful Assyrian king, Ashurbanipal...
's son, Nebuchadnezzar II, the king who constructed the Hanging Gardens of Babylon
Hanging Gardens of Babylon
The Hanging Gardens of Babylon were considered to be one of the greatest Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, and the only one of the Wonders which may in fact have been legendary. They were purportedly built in the ancient city-state of Babylon, near present-day Al Hillah, Babil, in Iraq...
as a present for his Median
Medes
The MedesThe Medes...
wife to help with her homesickness for the mountainous country of her birth. These allies overthrew the Assyrian Empire and destroyed Nineveh
Nineveh
Nineveh was an ancient Assyrian city on the eastern bank of the Tigris River, and capital of the Neo Assyrian Empire. Its ruins are across the river from the modern-day major city of Mosul, in the Ninawa Governorate of Iraq....
in 612 BC.
War against Lydia
After the victory in Assyria, the Medes conquered Northern MesopotamiaMesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a toponym for the area of the Tigris–Euphrates river system, largely corresponding to modern-day Iraq, northeastern Syria, southeastern Turkey and southwestern Iran.Widely considered to be the cradle of civilization, Bronze Age Mesopotamia included Sumer and the...
, Armenia
Armenia
Armenia , officially the Republic of Armenia , is a landlocked mountainous country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia...
and the parts of Asia Minor
Asia Minor
Asia Minor is a geographical location at the westernmost protrusion of Asia, also called Anatolia, and corresponds to the western two thirds of the Asian part of Turkey...
east of the Halys
Halys
Halys may refer to:* The Halys River in Anatolia , Turkish Kızılırmak .* In the Aeneid, Halys is a Trojan who defends Aeneas' camp from a Rutulian attack. He is killed by Turnus....
River, which was the border established with Lydia
Lydia
Lydia was an Iron Age kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the modern Turkish provinces of Manisa and inland İzmir. Its population spoke an Anatolian language known as Lydian....
after a decisive battle between Lydia
Lydia
Lydia was an Iron Age kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the modern Turkish provinces of Manisa and inland İzmir. Its population spoke an Anatolian language known as Lydian....
and Media
Medes
The MedesThe Medes...
, the Battle of Halys ended with an eclipse on May 28, 585 BC.
The conflict between Lydia
Lydia
Lydia was an Iron Age kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the modern Turkish provinces of Manisa and inland İzmir. Its population spoke an Anatolian language known as Lydian....
and the Medes
Medes
The MedesThe Medes...
was reported by Herodotus
Herodotus
Herodotus was an ancient Greek historian who was born in Halicarnassus, Caria and lived in the 5th century BC . He has been called the "Father of History", and was the first historian known to collect his materials systematically, test their accuracy to a certain extent and arrange them in a...
as follows:
- "A horde of the nomad Scythians at feud with the rest withdrew and sought refuge in the land of the Medes: and at this time the ruler of the Medes was Cyaxares the son of Phraortes, the son of Deïokes, who at first dealt well with these Scythians, being suppliants for his protection; and esteeming them very highly he delivered boys to them to learn their speech and the art of shooting with the bow. Then time went by, and the Scythians used to go out continually to the chase and always brought back something; till once it happened that they took nothing, and when they returned with empty hands Cyaxares (being, as he showed on this occasion, not of an eminently good disposition) dealt with them very harshly and used insult towards them. And they, when they had received this treatment from Cyaxares, considering that they had suffered indignity, planned to kill and to cut up one of the boys who were being instructed among them, and having dressed his flesh as they had been wont to dress the wild animals, to bear it to Cyaxares and give it to him, pretending that it was game taken in hunting; and when they had given it, their design was to make their way as quickly as possible to Alyattes the son of Sadyattes at Sardis. This then was done; and Cyaxares with the guests who ate at his table tasted of that meat, and the Scythians having so done became suppliants for the protection of Alyattes.
- After this, since Alyattes would not give up the Scythians when Cyaxares demanded them, there had arisen war between the Lydians and the Medes lasting five years; in which years the Medes often discomfited the Lydians and the Lydians often discomfited the Medes (and among others they fought also a battle by night): and as they still carried on the war with equally balanced fortune, in the sixth year a battle took place in which it happened, when the fight had begun, that suddenly the day became night. And this change of the day Thales the Milesian had foretold to the Ionians laying down as a limit this very year in which the change took place. The Lydians however and the Medes, when they saw that it had become night instead of day, ceased from their fighting and were much more eager both of them that peace should be made between them. And they who brought about the peace between them were Syennesis the Kilikian and Labynetos the Babylonian: these were they who urged also the taking of the oath by them, and they brought about an interchange of marriages; for they decided that Alyattes should give his daughter Aryenis to Astyages the son of Cyaxares, since without the compulsion of a strong tie agreements are apt not to hold strongly together." (Histories
 Histories (Herodotus)The Histories of Herodotus is considered one of the seminal works of history in Western literature. Written from the 450s to the 420s BC in the Ionic dialect of classical Greek, The Histories serves as a record of the ancient traditions, politics, geography, and clashes of various cultures that...
Histories (Herodotus)The Histories of Herodotus is considered one of the seminal works of history in Western literature. Written from the 450s to the 420s BC in the Ionic dialect of classical Greek, The Histories serves as a record of the ancient traditions, politics, geography, and clashes of various cultures that...
, 1.73-74, trans. Macaulay)
Cyaxares died shortly after the battle and was succeeded by his son, Astyages
Astyages
Astyages Astyages Astyages (spelled by Herodotus as Ἀστυάγης - Astyages; by Ctesias as Astyigas; by Diodorus as Aspadas; Akkadian: Ištumegu, was the last king of the Median Empire, r...
, who was the maternal grandfather of Cyrus the Great
Cyrus the Great
Cyrus II of Persia , commonly known as Cyrus the Great, also known as Cyrus the Elder, was the founder of the Achaemenid Empire. Under his rule, the empire embraced all the previous civilized states of the ancient Near East, expanded vastly and eventually conquered most of Southwest Asia and much...
through his daughter Mandane of Media
Mandane of Media
Mandane of Media was a princess of Media and, later, the Queen consort of Cambyses I of Anshan and mother of Cyrus the Great, ruler of the Persia's Achaemenid Dynasty.-Mandane in Herodotus' histories:...
.
Qyzqapan
Qyzqapan is a tomb located in the mountains in Syromedia, and is the last resting place of Cyaxares the Great, according to the Russian historian Igor DiakonovIgor Diakonov
Igor Mikhailovich Diakonov was a Russian historian, linguist, and translator and a renowned expert in the Ancient Near East and its languages....
. Qyzqapan is today an archaeological site in Silemani (Kurdistan Region).
The construction of the tomb, begun after the death of Cyaxares the Great in 585 BC. The tomb contains Zoroastrian symbols, since the Medes had an ancient religion (a form of pre-Zoroastrian Mazdaism or Mithra worshipping
Mithra
Mithra is the Zoroastrian divinity of covenant and oath. In addition to being the divinity of contracts, Mithra is also a judicial figure, an all-seeing protector of Truth, and the guardian of cattle, the harvest and of The Waters....
) with a priesthood named as "Magi
Magi
Magi is a term, used since at least the 4th century BC, to denote a follower of Zoroaster, or rather, a follower of what the Hellenistic world associated Zoroaster with, which...
". Later and during the reigns of last Median kings the reforms of Zarathustra spread in northwestern Iran, (mainly the modern Kurdish parts).
Further reading
- Nos ancêtres de l'Antiquité (1991), Christian SettipaniChristian SettipaniChristian Settipani is the Technical Director of an IT company in Paris and a genealogist and historian.He has a Master of Advanced Studies degree from the Paris-Sorbonne University and is currently preparing his doctoral thesis, while he often gives lectures to students undergraduates at the...
, p. 152
External links
- Livius.org: Cyaxares
- http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nR8fUAkfJRA&feature=channel_video_title
- http://qyzqapan.blogspot.com/2011/08/tomb-of-cyaxares.html

