
Cricosaurus
Encyclopedia
Cricosaurus is an extinct genus
of marine crocodyliform belonging to the family
Metriorhynchidae
. The genus was established by Johann Andreas Wagner
in 1858 for three skulls from the Tithonian
(Late Jurassic
) of Germany
. The name Cricosaurus means "Ring lizard", and is derived from the Greek
Cricos- ("ring") and -sauros ("lizard").
Fossil specimens referrable to Cricosaurus are known from Late Jurassic deposits in England
, France
, Switzerland
, Germany
, Argentina
, Cuba
, and Mexico
.
 Cricosaurus was first named by Wagner in 1858, as a re-classification of a specimen he had previously described in 1852.
Cricosaurus was first named by Wagner in 1858, as a re-classification of a specimen he had previously described in 1852.
Several other species have since been named, including C. suevicus by Fraas in 1901 (originally as a species of Geosaurus. One former species, C. medius (named by Wagner in 1858) has since been reclassified as a junior synonym of Rhacheosaurus gracilis
.
The original three skulls (all assigned to different species) were poorly known, and the genus had been considered a junior synonym of Metriorhynchus
, Geosaurus
or Dakosaurus
by different palaeontologists in the past. Some phylogenetic analysis did not support the monophyly
of Cricosaurus, However, a more comprehensive analysis in 2009 showed that the species contained in Cricosaurus were valid, and furthermore that several long-snouted species formerly classified in the related genera Geosaurus, Enaliosuchus and Metriorhynchus were in fact more closely related to the original specimens of Cricosaurus, and thus were re-classified into this genus.
Cladogram
after Cau & Fanti (2010).
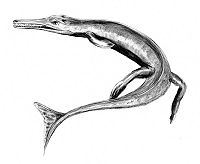 All currently known species would have been three metres or less in length. When compared to living crocodilians, Cricosaurus can be considered moderate to small-sized. Its body was streamlined for greater hydrodynamic efficiency, which along with its finned tail made it a more efficient swimmer than modern crocodilian species.
All currently known species would have been three metres or less in length. When compared to living crocodilians, Cricosaurus can be considered moderate to small-sized. Its body was streamlined for greater hydrodynamic efficiency, which along with its finned tail made it a more efficient swimmer than modern crocodilian species.
s. This means that it would have been able to "drink" salt-water from birth (necessary for a pelagic animal) and eat prey that have the same ionic concentration as the surrounding sea water (i.e. cephalopod
s) without dehydrating
. Adult specimens of Metriorhynchus
also have these well-developed salt glands.
 Several species of metriorhynchids are known from the Mörnsheim Formation (Solnhofen limestone
Several species of metriorhynchids are known from the Mörnsheim Formation (Solnhofen limestone
, early Tithonian) of Bavaria
, Germany: Dakosaurus maximus
, Geosaurus giganteus, Cricosaurus suevicus and Rhacheosaurus gracilis
. It has been hypothesised that niche partitioning
enabled several species of crocodyliforms to co-exist. The top predators of this Formation appear to be Dakosaurus and G. giganteus, which were large, short-snouted species with serrated teeth. The long-snouted Cricosaurus species would have feed mostly on fish, although the more lightly built Rhacheosaurus may have specialised towards feeding on small prey. In addition to these four species of metriorhynchids, a moderate-sized species of Steneosaurus
was also contemporaneous.
From the slightly older Nusplingen
Plattenkalk (late Kimmeridgian) of southern Germany, both C. suevicus and Dakosaurus maximus are contemporaneous. As with Solnhofen, C. suevicus feed upon fish, while D. maximus was the top predator.
Genus
In biology, a genus is a low-level taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms, which is an example of definition by genus and differentia...
of marine crocodyliform belonging to the family
Family (biology)
In biological classification, family is* a taxonomic rank. Other well-known ranks are life, domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, genus, and species, with family fitting between order and genus. As for the other well-known ranks, there is the option of an immediately lower rank, indicated by the...
Metriorhynchidae
Metriorhynchidae
Metriorhynchidae is an extinct family of metriorhynchoid crocodyliforms from the Middle Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous period of Europe, North America and South America. Metriorhynchids are fully aquatic crocodyliforms. Their forelimbs were small and paddle-like, and unlike living crocodilians,...
. The genus was established by Johann Andreas Wagner
Johann Andreas Wagner
Johann Andreas Wagner was a German palaeontologist, zoologist and archaeologist.Wagner was a professor at the University of Munich, and curator of the Zoologische Staatssammlung ....
in 1858 for three skulls from the Tithonian
Tithonian
In the geologic timescale the Tithonian is the latest age of the Late Jurassic epoch or the uppermost stage of the Upper Jurassic series. It spans the time between 150.8 ± 4 Ma and 145.5 ± 4 Ma...
(Late Jurassic
Late Jurassic
The Late Jurassic is the third epoch of the Jurassic Period, and it spans the geologic time from 161.2 ± 4.0 to 145.5 ± 4.0 million years ago , which is preserved in Upper Jurassic strata. In European lithostratigraphy, the name "Malm" indicates rocks of Late Jurassic age...
) of Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
. The name Cricosaurus means "Ring lizard", and is derived from the Greek
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek is the stage of the Greek language in the periods spanning the times c. 9th–6th centuries BC, , c. 5th–4th centuries BC , and the c. 3rd century BC – 6th century AD of ancient Greece and the ancient world; being predated in the 2nd millennium BC by Mycenaean Greek...
Cricos- ("ring") and -sauros ("lizard").
Fossil specimens referrable to Cricosaurus are known from Late Jurassic deposits in England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
, France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, Switzerland
Switzerland
Switzerland name of one of the Swiss cantons. ; ; ; or ), in its full name the Swiss Confederation , is a federal republic consisting of 26 cantons, with Bern as the seat of the federal authorities. The country is situated in Western Europe,Or Central Europe depending on the definition....
, Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
, Argentina
Argentina
Argentina , officially the Argentine Republic , is the second largest country in South America by land area, after Brazil. It is constituted as a federation of 23 provinces and an autonomous city, Buenos Aires...
, Cuba
Cuba
The Republic of Cuba is an island nation in the Caribbean. The nation of Cuba consists of the main island of Cuba, the Isla de la Juventud, and several archipelagos. Havana is the largest city in Cuba and the country's capital. Santiago de Cuba is the second largest city...
, and Mexico
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
.
History and classification

Several other species have since been named, including C. suevicus by Fraas in 1901 (originally as a species of Geosaurus. One former species, C. medius (named by Wagner in 1858) has since been reclassified as a junior synonym of Rhacheosaurus gracilis
Rhacheosaurus
Rhacheosaurus is an extinct genus of marine crocodyliform belonging to the family Metriorhynchidae. The genus was established by von Meyer in 1831 for skeletal remains from the Tithonian of Germany.-History and classification:...
.
The original three skulls (all assigned to different species) were poorly known, and the genus had been considered a junior synonym of Metriorhynchus
Metriorhynchus
Metriorhynchus is an extinct genus of marine crocodyliform that lived in the oceans during the Middle to Late Jurassic. Metriorhynchus was named by the German palaeontologist Christian von Meyer in 1830. Metriorhynchus was a carnivore that spent much, if not all, its life out at sea...
, Geosaurus
Geosaurus
Geosaurus is an extinct genus of marine crocodyliform within the family Metriorhynchidae that lived during the Late Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous. Geosaurus was a carnivore that spent much, if not all, its life out at sea...
or Dakosaurus
Dakosaurus
Dakosaurus is an extinct genus within the family Metriorhynchidae that lived during the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous. It was large, with teeth that were serrated and compressed lateromedially . The genus was established by Friedrich August von Quenstedt in 1856 for an isolated tooth named...
by different palaeontologists in the past. Some phylogenetic analysis did not support the monophyly
Monophyly
In common cladistic usage, a monophyletic group is a taxon which forms a clade, meaning that it contains all the descendants of the possibly hypothetical closest common ancestor of the members of the group. The term is synonymous with the uncommon term holophyly...
of Cricosaurus, However, a more comprehensive analysis in 2009 showed that the species contained in Cricosaurus were valid, and furthermore that several long-snouted species formerly classified in the related genera Geosaurus, Enaliosuchus and Metriorhynchus were in fact more closely related to the original specimens of Cricosaurus, and thus were re-classified into this genus.
Cladogram
Cladogram
A cladogram is a diagram used in cladistics which shows ancestral relations between organisms, to represent the evolutionary tree of life. Although traditionally such cladograms were generated largely on the basis of morphological characters, DNA and RNA sequencing data and computational...
after Cau & Fanti (2010).
Paleobiology

Salt glands
Recent examination of the fossil specimens of Cricosaurus araucanensis have shown that both juveniles and adults of this species had well-developed salt glandSalt gland
The salt gland is an organ for excreting excess salts. It is found in elasmobranchs, seabirds, and some reptiles. In sharks, salt glands are found in the rectum, but in birds and reptiles, they are found in or on the skull, in the area of the eyes, nostrils or mouth. In crocodiles, the salt is...
s. This means that it would have been able to "drink" salt-water from birth (necessary for a pelagic animal) and eat prey that have the same ionic concentration as the surrounding sea water (i.e. cephalopod
Cephalopod
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda . These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head, and a set of arms or tentacles modified from the primitive molluscan foot...
s) without dehydrating
Dehydration
In physiology and medicine, dehydration is defined as the excessive loss of body fluid. It is literally the removal of water from an object; however, in physiological terms, it entails a deficiency of fluid within an organism...
. Adult specimens of Metriorhynchus
Metriorhynchus
Metriorhynchus is an extinct genus of marine crocodyliform that lived in the oceans during the Middle to Late Jurassic. Metriorhynchus was named by the German palaeontologist Christian von Meyer in 1830. Metriorhynchus was a carnivore that spent much, if not all, its life out at sea...
also have these well-developed salt glands.
Niche partitioning

Solnhofen limestone
The Solnhofen Plattenkalk is a Jurassic Konservat-Lagerstätte that preserves a rare assemblage of fossilized organisms, including highly detailed imprints of soft bodied organisms such as sea jellies...
, early Tithonian) of Bavaria
Bavaria
Bavaria, formally the Free State of Bavaria is a state of Germany, located in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the largest state by area, forming almost 20% of the total land area of Germany...
, Germany: Dakosaurus maximus
Dakosaurus
Dakosaurus is an extinct genus within the family Metriorhynchidae that lived during the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous. It was large, with teeth that were serrated and compressed lateromedially . The genus was established by Friedrich August von Quenstedt in 1856 for an isolated tooth named...
, Geosaurus giganteus, Cricosaurus suevicus and Rhacheosaurus gracilis
Rhacheosaurus
Rhacheosaurus is an extinct genus of marine crocodyliform belonging to the family Metriorhynchidae. The genus was established by von Meyer in 1831 for skeletal remains from the Tithonian of Germany.-History and classification:...
. It has been hypothesised that niche partitioning
Niche differentiation
The term niche differentiation , as it applies to the field of ecology, refers to the process by which natural selection drives competing species into different patterns of resource use or different niches...
enabled several species of crocodyliforms to co-exist. The top predators of this Formation appear to be Dakosaurus and G. giganteus, which were large, short-snouted species with serrated teeth. The long-snouted Cricosaurus species would have feed mostly on fish, although the more lightly built Rhacheosaurus may have specialised towards feeding on small prey. In addition to these four species of metriorhynchids, a moderate-sized species of Steneosaurus
Steneosaurus
Steneosaurus is an extinct genus of teleosaurid crocodyliform from the Early Jurassic to Early Cretaceous . Fossil specimens have been found in England, France, Germany, Switzerland and Morocco.-Species:...
was also contemporaneous.
From the slightly older Nusplingen
Nusplingen
Nusplingen is a Swabian town in the Zollernalb district, Baden-Württemberg, Germany.The town is located in the valley of the small river Bära, about 12 miles up-river from where it flows in to the Danube. In the Middle Ages Nusplingen gained the rights of a city...
Plattenkalk (late Kimmeridgian) of southern Germany, both C. suevicus and Dakosaurus maximus are contemporaneous. As with Solnhofen, C. suevicus feed upon fish, while D. maximus was the top predator.

