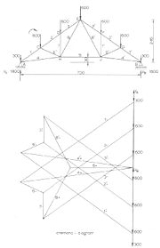
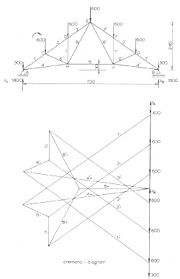
Cremona diagram
Encyclopedia
Statics
Statics is the branch of mechanics concerned with the analysis of loads on physical systems in static equilibrium, that is, in a state where the relative positions of subsystems do not vary over time, or where components and structures are at a constant velocity...
of truss
Truss
In architecture and structural engineering, a truss is a structure comprising one or more triangular units constructed with straight members whose ends are connected at joints referred to as nodes. External forces and reactions to those forces are considered to act only at the nodes and result in...
es to determine the forces in members (graphic statics). The method was created by the Italian mathematician Luigi Cremona
Luigi Cremona
Luigi Cremona was an Italian mathematician. His life was devoted to the study of geometry and reforming advanced mathematical teaching in Italy. His reputation mainly rests on his Introduzione ad una teoria geometrica delle curve piane...
.
In the Cremona method, first the external forces and reactions are drawn (to scale
Scale (ratio)
The scale ratio of some sort of model which represents an original proportionally is the ratio of a linear dimension of the model to the same dimension of the original. Examples include a 3-dimensional scale model of a building or the scale drawings of the elevations or plans of a building. In such...
) forming a vertical line in the lower right side of the picture. This is the sum
Net force
In physics, net force is the total force acting on an object. It is calculated by vector addition of all forces that are actually acting on that object. Net force has the same effect on the translational motion of the object as all actual forces taken together...
of all the force vectors and is equal to zero as there is mechanical equilibrium.
Since the equilibrium holds for the external forces on the entire truss construction, it also holds for the internal forces acting on each joint. For a joint to be at rest the sum of the forces on a joint must also be equal to zero. Starting at joint Aorda, the internal forces can be found by drawing lines in the Cremona diagram representing the forces in the members 1 and 4, going clockwise; VA (going up) load at A (going down), force in member 1 (going down/left), member 4 (going up/right) and closing with VA. As the force in member 1 is towards the joint, the member is under compression, the force in member 4 is away from the joint so the member 4 is under tension. The length of the lines for members 1 and 4 in the diagram, multiplied with the chosen scale factor
Coefficient
In mathematics, a coefficient is a multiplicative factor in some term of an expression ; it is usually a number, but in any case does not involve any variables of the expression...
is the magnitude
Magnitude (mathematics)
The magnitude of an object in mathematics is its size: a property by which it can be compared as larger or smaller than other objects of the same kind; in technical terms, an ordering of the class of objects to which it belongs....
of the force in members 1 and 4.
Now, in the same way the forces in members 2 and 6 can be found for joint C; force in member 1 (going up/right), force in C going down, force in 2 (going down/left), force in 6 (going up/left) and closing with the force in member 1.
The same steps can be taken for joints D, H and E resulting in the complete Cremona diagram where the internal forces in all members are known.
In a next phase the forces caused by wind
Wind
Wind is the flow of gases on a large scale. On Earth, wind consists of the bulk movement of air. In outer space, solar wind is the movement of gases or charged particles from the sun through space, while planetary wind is the outgassing of light chemical elements from a planet's atmosphere into space...
must be considered. Wind will cause pressure on the upwind side of a roof
Roof
A roof is the covering on the uppermost part of a building. A roof protects the building and its contents from the effects of weather. Structures that require roofs range from a letter box to a cathedral or stadium, dwellings being the most numerous....
(and truss) and suction on the downwind side. This will translate to asymmetrical loads but the Cremona method is the same. Wind force may introduce larger forces in the individual truss members than the static vertical loads.

