
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale
Encyclopedia
The Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS) intelligence quotient
(IQ) tests are the primary clinical instruments used to measure adult and adolescent intelligence. The original WAIS (Form I) was published in February 1955 by David Wechsler
, as a revision of the Wechsler-Bellevue Intelligence Scale. The fourth edition of the test (WAIS-IV) was released in 2008 by Pearson
.
The Wechsler-Bellevue tests were innovative in the 1930s because they gathered tasks created for nonclinical purposes for administration as a "clinical test battery". Because the Wechsler tests included non-verbal items (known as performance scales) as well as verbal items for all test-takers, and because the 1960 form of Lewis Terman
's Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scales was less carefully developed than previous versions, Form I of the WAIS surpassed the Stanford-Binet tests in popularity by the 1960s.
Wechsler defined intelligence as "... the global capacity of a person to act purposefully, to think rationally, and to deal effectively with his environment."
Intelligence Scale (WBIS), which was a battery of tests published by Wechsler in 1939. The WBIS was composed of subtests that could be found in various other intelligence tests of the time, such as Robert Yerkes
' army testing program and the Binet
-Simon
scale. The WAIS was first released in February 1955 by David Wechsler
.
This revised edition did not provide new validity data, but used the data from the original WAIS; however new norms were provided, carefully stratified.
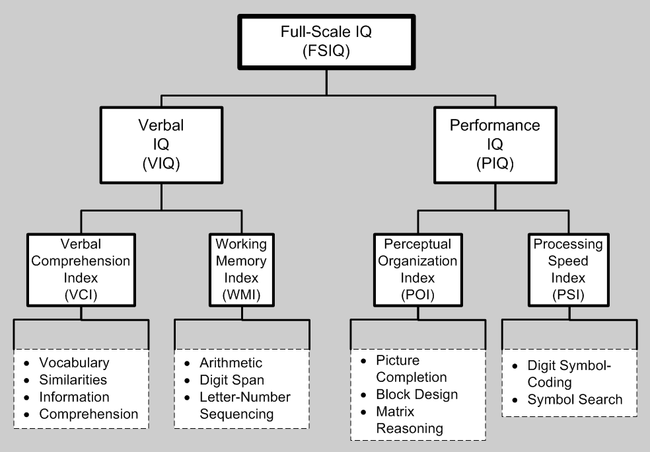 The WAIS-III, a subsequent revision of the WAIS and the WAIS-R, was released in 1997. It provided scores for Verbal IQ, Performance IQ, and Full Scale IQ, along with four secondary indices (Verbal Comprehension, Working Memory, Perceptual Organization, and Processing Speed).
The WAIS-III, a subsequent revision of the WAIS and the WAIS-R, was released in 1997. It provided scores for Verbal IQ, Performance IQ, and Full Scale IQ, along with four secondary indices (Verbal Comprehension, Working Memory, Perceptual Organization, and Processing Speed).
The Verbal comprehension index included the following tests:
The Working memory index included:
Letter-Number Sequencing and Comprehension are not included in these indices, but are used as substitutions for spoiled subtests within the WMI and VCI, respectively
The Perceptual organization index included:
The Processing speed index included:
Two tests; Picture Arrangement and Object Assembly were not included in the indexes. Object Assembly is not included in the PIQ.
Two broad scores are also generated, which can be used to summarize general intellectual abilities:
The Perceptual Reasoning Index comprises five tests
The Working Memory Index is obtained from three tests
The Processing Speed Index includes three tests
Full Scale IQ is centered at 100, with a standard deviation
of 15. In a normal distribution, the IQ range of one standard deviation above and below the mean (i.e., between 85 and 115) is where approximately 68% of all adults would fall.
, 6-16 years) and the Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence (WPPSI
, 2½–7 years, 3 months) are used.
A short, four-subtest version of the WAIS-III battery has been released, allowing clinicians to form a validated estimate of verbal, performance and full scale IQ in a shorter amount of time. The Wechsler Abbreviated Scale of Intelligence (WASI) uses vocabulary, similarities, block design
and matrix reasoning subtests similar to those of the WAIS to provide an estimate of full scale IQ in approximately 30 minutes.
Intelligence tests may also be utilized in populations with psychiatric illness or brain injury, in order to assess level of cognitive functioning, though some regard this use as controversial. Some neuropsychologists use the technique on people suffering brain damage as it leads to links
with which part of the brain has been affected, or use specific subtests in order to get an idea of the extent of the brain damage. For example, digit span may be used to get a sense of attentional difficulties. Others employ the WAIS-R NI (Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-Revised as a Neuropsychological Instrument), another measure published by Harcourt
. Each subtest score is tallied and calculated with respect to non-normal or brain-damaged norms. As the WAIS is developed for the average, non-injured individual, separate norms were developed for appropriate comparison among similar functioning individuals.
Intelligence quotient
An intelligence quotient, or IQ, is a score derived from one of several different standardized tests designed to assess intelligence. When modern IQ tests are constructed, the mean score within an age group is set to 100 and the standard deviation to 15...
(IQ) tests are the primary clinical instruments used to measure adult and adolescent intelligence. The original WAIS (Form I) was published in February 1955 by David Wechsler
David Wechsler
David "Wex" Wechsler was a leading American psychologist. He developed well-known intelligence scales, such as the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale and the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children .-Biography:...
, as a revision of the Wechsler-Bellevue Intelligence Scale. The fourth edition of the test (WAIS-IV) was released in 2008 by Pearson
Pearson PLC
Pearson plc is a global media and education company headquartered in London, United Kingdom. It is both the largest education company and the largest book publisher in the world, with consumer imprints including Penguin, Dorling Kindersley and Ladybird...
.
The Wechsler-Bellevue tests were innovative in the 1930s because they gathered tasks created for nonclinical purposes for administration as a "clinical test battery". Because the Wechsler tests included non-verbal items (known as performance scales) as well as verbal items for all test-takers, and because the 1960 form of Lewis Terman
Lewis Terman
Lewis Madison Terman was an American psychologist, noted as a pioneer in educational psychology in the early 20th century at the Stanford University School of Education. He is best known as the inventor of the Stanford-Binet IQ test...
's Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scales was less carefully developed than previous versions, Form I of the WAIS surpassed the Stanford-Binet tests in popularity by the 1960s.
Wechsler defined intelligence as "... the global capacity of a person to act purposefully, to think rationally, and to deal effectively with his environment."
WAIS
The WAIS was initially created as a revision of the Wechsler-BellevueBellevue Hospital Center
Bellevue Hospital Center, most often referred to as "Bellevue", was founded on March 31, 1736 and is the oldest public hospital in the United States. Located on First Avenue in the Kips Bay neighborhood of Manhattan, New York City, Bellevue is famous from many literary, film and television...
Intelligence Scale (WBIS), which was a battery of tests published by Wechsler in 1939. The WBIS was composed of subtests that could be found in various other intelligence tests of the time, such as Robert Yerkes
Robert Yerkes
Robert Mearns Yerkes was an American psychologist, ethologist, and primatologist best known for his work in intelligence testing and in the field of comparative psychology....
' army testing program and the Binet
Alfred Binet
Alfred Binet was a French psychologist who was the inventor of the first usable intelligence test, known at that time as the Binet test and today referred to as the IQ test. His principal goal was to identify students who needed special help in coping with the school curriculum...
-Simon
Theodore Simon
Théodore Simon was a French psychologist and psychometrician. He co-created the Binet-Simon Intelligence Scale tests with Alfred Binet.- Biography :...
scale. The WAIS was first released in February 1955 by David Wechsler
David Wechsler
David "Wex" Wechsler was a leading American psychologist. He developed well-known intelligence scales, such as the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale and the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children .-Biography:...
.
WAIS-R
The WAIS-R, a revised form of the WAIS, was released in 1981 and consisted of six verbal and five performance subtests. The verbal tests were: Information, Comprehension, Arithmetic, Digit Span, Similarities, and Vocabulary. The Performance subtests were: Picture Arrangement, Picture Completion, Block Design, Object Assembly, and Digit Symbol. A verbal IQ, performance IQ and full scale IQ were obtained.This revised edition did not provide new validity data, but used the data from the original WAIS; however new norms were provided, carefully stratified.
WAIS-III

Verbal IQ (VIQ)
Included seven tests and provided two subindexes; verbal comprehension and working memory.The Verbal comprehension index included the following tests:
- Information
- Similarities
- Vocabulary
The Working memory index included:
- Arithmetic
- Digit Span
Letter-Number Sequencing and Comprehension are not included in these indices, but are used as substitutions for spoiled subtests within the WMI and VCI, respectively
Performance IQ (PIQ)
Included six tests and it also provided two subindexes; perceptual organization and processing speed.The Perceptual organization index included:
- Block DesignBlock design testBlock design is a subtest on many intelligence tests that measures visuospatial and motor skills. The testee is required to take blocks that have all white sides, all red sides, and red and white sides and arrange them according to a pattern...
- Matrix Reasoning
- Picture Completion
The Processing speed index included:
- Digit Symbol-Coding
- Symbol Search
Two tests; Picture Arrangement and Object Assembly were not included in the indexes. Object Assembly is not included in the PIQ.
WAIS-IV
The current version of the test, the WAIS-IV, which was released in 2008, is composed of 10 core subtests and five supplemental subtests, with the 10 core subtests comprising the Full Scale IQ. With the new WAIS-IV, the verbal/performance subscales from previous versions were removed and replaced by the index scores. The General Ability Index (GAI) was included, which consists of the Similarities, Vocabulary and Information subtests from the Verbal Comprehension Index and the Block Design, Matrix Reasoning and Visual Puzzles subtests from the Perceptual Reasoning Index. The GAI is clinically useful because it can be used as a measure of cognitive abilities that are less vulnerable to impairment.Indices and scales
There are four index scores representing major components of intelligence:- Verbal Comprehension Index (VCI)
- Perceptual Reasoning Index (PRI)
- Working Memory Index (WMI)
- Processing Speed Index (PSI)
Two broad scores are also generated, which can be used to summarize general intellectual abilities:
- Full Scale IQ (FSIQ), based on the total combined performance of the VCI, PRI, WMI, and PSI
- General Ability Index (GAI), based only on the six subtests that the VCI and PRI comprise.
Subtests
The Verbal Comprehension Index includes four tests:- Similarities: Abstract verbal reasoning (e.g., "In what way are an apple and a pear alike?")
- Vocabulary: The degree to which one has learned, been able to comprehend and verbally express vocabulary (e.g., "What is a guitar?")
- Information : Degree of general information acquired from cultureCultureCulture is a term that has many different inter-related meanings. For example, in 1952, Alfred Kroeber and Clyde Kluckhohn compiled a list of 164 definitions of "culture" in Culture: A Critical Review of Concepts and Definitions...
(e.g., "Who is the president of Russia?") - Comprehension [Supplemental]: Ability to deal with abstract social conventions, rules and expressions (e.g., "What does Kill 2 birds with 1 stone metaphorically mean?")
The Perceptual Reasoning Index comprises five tests
- Block DesignBlock design testBlock design is a subtest on many intelligence tests that measures visuospatial and motor skills. The testee is required to take blocks that have all white sides, all red sides, and red and white sides and arrange them according to a pattern...
: Spatial perception, visual abstract processing & problem solving - Matrix Reasoning: Nonverbal abstract problem solving, inductive reasoningInductive reasoningInductive reasoning, also known as induction or inductive logic, is a kind of reasoning that constructs or evaluates propositions that are abstractions of observations. It is commonly construed as a form of reasoning that makes generalizations based on individual instances...
, spatial reasoning - Visual Puzzles: non-verbal reasoning
- Picture Completion [Supplemental]: Ability to quickly perceive visual details
- Figure Weights [Supplemental]: quantitative and analogical reasoning
The Working Memory Index is obtained from three tests
- Digit span: attention, concentration, mental control (e.g., Repeat the numbers 1-2-3 in reverse sequence)
- Arithmetic: Concentration while manipulating mental mathematical problems (e.g., "How many 45-cent stamps can you buy for a dollar?")
- Letter-Number Sequencing [Supplemental]: attention and working memory (e.g., Repeat the sequence Q-1-B-3-J-2, but place the numbers in numerical order and then the letters in alphabetical order)
The Processing Speed Index includes three tests
- Symbol Search: Visual perception, speed
- Coding: Visual-motor coordination, motor and mental speed
- Cancellation [Supplemental]: visual-perceptual speed
Standardization
The WAIS-IV was standardized on a sample of 2,200 people in the United States ranging in age from 16 to 90. An extension of the standardization has been conducted with 688 Canadians in the same age range. The medianMedian
In probability theory and statistics, a median is described as the numerical value separating the higher half of a sample, a population, or a probability distribution, from the lower half. The median of a finite list of numbers can be found by arranging all the observations from lowest value to...
Full Scale IQ is centered at 100, with a standard deviation
Standard deviation
Standard deviation is a widely used measure of variability or diversity used in statistics and probability theory. It shows how much variation or "dispersion" there is from the average...
of 15. In a normal distribution, the IQ range of one standard deviation above and below the mean (i.e., between 85 and 115) is where approximately 68% of all adults would fall.
Other test variants and uses
The WAIS-IV measure is appropriate for use with individuals aged 16–90 years. For individuals under 16 years, the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISCWechsler Intelligence Scale for Children
The Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children , developed by Dr. David Wechsler, is an individually administered intelligence test for children between the ages of 6 and 16 inclusive that can be completed without reading or writing...
, 6-16 years) and the Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence (WPPSI
Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence
The Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence is an intelligence test designed for children ages 2 years 6 months to 7 years 3 months developed by David Wechsler in 1967. It is a descendent of the earlier Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale and the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children...
, 2½–7 years, 3 months) are used.
A short, four-subtest version of the WAIS-III battery has been released, allowing clinicians to form a validated estimate of verbal, performance and full scale IQ in a shorter amount of time. The Wechsler Abbreviated Scale of Intelligence (WASI) uses vocabulary, similarities, block design
Block design test
Block design is a subtest on many intelligence tests that measures visuospatial and motor skills. The testee is required to take blocks that have all white sides, all red sides, and red and white sides and arrange them according to a pattern...
and matrix reasoning subtests similar to those of the WAIS to provide an estimate of full scale IQ in approximately 30 minutes.
Intelligence tests may also be utilized in populations with psychiatric illness or brain injury, in order to assess level of cognitive functioning, though some regard this use as controversial. Some neuropsychologists use the technique on people suffering brain damage as it leads to links
Mixed receptive-expressive language disorder
Mixed receptive-expressive language disorder is a communication disorder in which both the receptive and expressive areas of communication may be affected in any degree, from mild to severe....
with which part of the brain has been affected, or use specific subtests in order to get an idea of the extent of the brain damage. For example, digit span may be used to get a sense of attentional difficulties. Others employ the WAIS-R NI (Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-Revised as a Neuropsychological Instrument), another measure published by Harcourt
Harcourt (publisher)
Harcourt was a United States publishing firm with a long history of publishing fiction and nonfiction for children and adults. The company was based in San Diego, California, with an Editorial / Sales / Marketing / Rights offices in New York City and Orlando, Florida.In 2007, the U.S...
. Each subtest score is tallied and calculated with respect to non-normal or brain-damaged norms. As the WAIS is developed for the average, non-injured individual, separate norms were developed for appropriate comparison among similar functioning individuals.

