_sulfide.gif)
Copper(II) sulfide
Encyclopedia
Copper monosulfide is a chemical compound
of copper
and sulfur
. It occurs in nature as the dark indigo blue mineral covellite
. It is a moderate conductor of electricity. A black colloidal precipitate of CuS is formed when hydrogen sulfide
, H2S, is bubbled through solutions of Cu(II) salts. It is one of a number of binary compounds of copper and sulfur (see copper sulfide
for an overview of this subject), and has attracted interest because of its potential uses in catalysis and photovoltaics.
. There is also an amorphous high pressure form which on the basis of the Raman spectrum
has been described as having a distorted covellite structure. An amorphous room temperature semiconducting form produced by the reaction of a Cu(II) ethylenediamine complex with thiourea
has been reported, which transforms to the crystalline covellite form at 30 °C.
The crystal structure of covellite has been reported several times, and whilst these studies are in general agreement on assigning the space group
P63/mmc there are small discrepancies in bond lengths and angles between them. The structure was described as "extraordinary" by Wells and is quite different from copper(II) oxide
, but similar to CuSe (klockmannite). The covellite unit cell contains 6 formula units (12 atoms)in which:
The formulation of copper monosulfide as CuIIS (i.e. containing no sulfur-sulfur bond) is clearly incompatible with the crystal structure, and also at variance with the observed diamagnetism as a Cu(II) compound would have a d9 configuration and be expected to be paramagnetic.
Studies using XPS
indicate that all of the copper atoms have an oxidation state of +1. This contradicts a formulation based on the crystal structure and obeying the octet
rule that is found in many textbooks (e.g. ) describing CuS as containing both CuI and CuII i.e. (Cu+)2Cu2+(S2)2–S2–. An alternative formulation as (Cu+)3(S2–)(S2)– was proposed and supported by calculations.
The formulation should not be interpreted as containing radical anion, but rather that there is a delocalized valence "hole".
Electron paramagnetic resonance
studies on the precipitation of Cu(II) salts indicates that the reduction of Cu(II) to Cu(I) occurs in solution.
Chemical compound
A chemical compound is a pure chemical substance consisting of two or more different chemical elements that can be separated into simpler substances by chemical reactions. Chemical compounds have a unique and defined chemical structure; they consist of a fixed ratio of atoms that are held together...
of copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
and sulfur
Sulfur
Sulfur or sulphur is the chemical element with atomic number 16. In the periodic table it is represented by the symbol S. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow...
. It occurs in nature as the dark indigo blue mineral covellite
Covellite
Covellite is a rare copper sulfide mineral with the formula CuS. This indigo blue mineral is ubiquitous in copper ores, it is found in limited abundance and is not an important ore of copper itself, although it is well known to mineral collectors.The mineral is associated with chalcocite in zones...
. It is a moderate conductor of electricity. A black colloidal precipitate of CuS is formed when hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless, very poisonous, flammable gas with the characteristic foul odor of expired eggs perceptible at concentrations as low as 0.00047 parts per million...
, H2S, is bubbled through solutions of Cu(II) salts. It is one of a number of binary compounds of copper and sulfur (see copper sulfide
Copper sulfide
Copper sulfides describe a family of chemical compounds and minerals with the formula CuxSy. Both minerals and synthetic materials comprise these compounds. Some copper sulfides are economically important ores....
for an overview of this subject), and has attracted interest because of its potential uses in catalysis and photovoltaics.
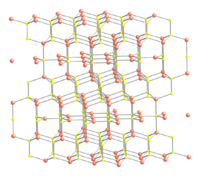
CuS structure and bonding
Copper monosulfide crystallizes in the hexagonal crystal system, and this is the form of the mineral covelliteCovellite
Covellite is a rare copper sulfide mineral with the formula CuS. This indigo blue mineral is ubiquitous in copper ores, it is found in limited abundance and is not an important ore of copper itself, although it is well known to mineral collectors.The mineral is associated with chalcocite in zones...
. There is also an amorphous high pressure form which on the basis of the Raman spectrum
Raman spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy is a spectroscopic technique used to study vibrational, rotational, and other low-frequency modes in a system.It relies on inelastic scattering, or Raman scattering, of monochromatic light, usually from a laser in the visible, near infrared, or near ultraviolet range...
has been described as having a distorted covellite structure. An amorphous room temperature semiconducting form produced by the reaction of a Cu(II) ethylenediamine complex with thiourea
Thiourea
Thiourea is an organosulfur compound of with the formula SC2 . It is structurally similar to urea, except that the oxygen atom is replaced by a sulfur atom, but the properties of urea and thiourea differ significantly. Thiourea is a reagent in organic synthesis. "Thioureas" refers to a broad...
has been reported, which transforms to the crystalline covellite form at 30 °C.
The crystal structure of covellite has been reported several times, and whilst these studies are in general agreement on assigning the space group
Space group
In mathematics and geometry, a space group is a symmetry group, usually for three dimensions, that divides space into discrete repeatable domains.In three dimensions, there are 219 unique types, or counted as 230 if chiral copies are considered distinct...
P63/mmc there are small discrepancies in bond lengths and angles between them. The structure was described as "extraordinary" by Wells and is quite different from copper(II) oxide
Copper(II) oxide
Copper oxide or cupric oxide is the higher oxide of copper. As a mineral, it is known as tenorite.-Chemistry:It is a black solid with an ionic structure which melts above 1200 °C with some loss of oxygen...
, but similar to CuSe (klockmannite). The covellite unit cell contains 6 formula units (12 atoms)in which:
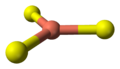
- 4 Cu atoms have tetrahedral coordination (see illustration).
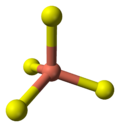
- 2 Cu atoms have trigonal planar coordination (see illustration).
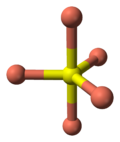
- 2 pairs of S atoms are only 207.1 pm apart indicating the existence of an S-S bond (a disulfide unit).
- the 2 remaining S atoms form trigonal planar triangles around the copper atoms, and are surrounded by five Cu atoms in a pentagonal bipyramid (see illustration).
- The S atoms at each end of a disulfide unit are tetrahedrally coordinated to 3 tetrahedrally coordinated Cu atoms and the other S atom in the disulfide unit (see illustration).
The formulation of copper monosulfide as CuIIS (i.e. containing no sulfur-sulfur bond) is clearly incompatible with the crystal structure, and also at variance with the observed diamagnetism as a Cu(II) compound would have a d9 configuration and be expected to be paramagnetic.
Studies using XPS
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy is a quantitative spectroscopic technique that measures the elemental composition, empirical formula, chemical state and electronic state of the elements that exist within a material...
indicate that all of the copper atoms have an oxidation state of +1. This contradicts a formulation based on the crystal structure and obeying the octet
Octet
-Music:* Octet , ensemble consisting of eight instruments or voices, or composition written for such an ensemble* Octet , 1793 composition by Ludwig van Beethoven* Octet , 1825 composition by Felix Mendelssohn...
rule that is found in many textbooks (e.g. ) describing CuS as containing both CuI and CuII i.e. (Cu+)2Cu2+(S2)2–S2–. An alternative formulation as (Cu+)3(S2–)(S2)– was proposed and supported by calculations.
The formulation should not be interpreted as containing radical anion, but rather that there is a delocalized valence "hole".
Electron paramagnetic resonance
Electron paramagnetic resonance
Electron paramagnetic resonance or electron spin resonance spectroscopyis a technique for studying chemical species that have one or more unpaired electrons, such as organic and inorganic free radicals or inorganic complexes possessing a transition metal ion...
studies on the precipitation of Cu(II) salts indicates that the reduction of Cu(II) to Cu(I) occurs in solution.
 |
 |
 |
 |
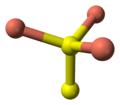 |
Ball-and-stick model In chemistry, the ball-and-stick model is a molecular model of a chemical substance which is to display both the three-dimensional position of the atoms and the bonds between them... of part of the crystal structure of covellite Covellite Covellite is a rare copper sulfide mineral with the formula CuS. This indigo blue mineral is ubiquitous in copper ores, it is found in limited abundance and is not an important ore of copper itself, although it is well known to mineral collectors.The mineral is associated with chalcocite in zones... |
coordination of copper |
coordination of copper |
coordination of sulfur |
coordination of sulfur-note disulfide unit |
See also
- Copper sulfideCopper sulfideCopper sulfides describe a family of chemical compounds and minerals with the formula CuxSy. Both minerals and synthetic materials comprise these compounds. Some copper sulfides are economically important ores....
for an overview of all copper sulfide phases - copper(I) sulfideCopper(I) sulfideCopper sulfide is a copper sulfide, a chemical compound of copper and sulfur. It has the chemical compound Cu2S. It is found in nature as the mineral chalcocite. It has a narrow range of stoichiometry ranging from Cu1.997S to Cu2.000S....
, Cu2S - CovelliteCovelliteCovellite is a rare copper sulfide mineral with the formula CuS. This indigo blue mineral is ubiquitous in copper ores, it is found in limited abundance and is not an important ore of copper itself, although it is well known to mineral collectors.The mineral is associated with chalcocite in zones...

