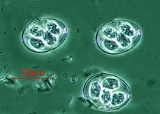
Conoidasida
Encyclopedia
Conoidasida is a class
of protists.
The class was defined in 1988 by Levine and contains two subclasses - the coccidia
and the gregarines. All members of this class have a complete, hollow, truncated conoid
. Gregarines tend to parasitize invertebrate
s with the mature gamonts being extracellular, the coccidia mostly infect vertebrate
s and have intracellular gamonts.
is found in most species and when present forms complete but truncated cone.
Sexual and asexual reproduction are present in lifecycle of all species. Each zygote
normally forms an oocyst wall within which it undergoes meiosis
. This is sometimes followed by mitosis
. This process of sporogony produces mobile vermiform sporozoites.
Mitotic divisions also occur during merogony of the feeding stages (trophozoites) and during gametogony.
Microgametes of some species are flagellated
Locomotion of other gamete
s and any other mobile stages is by gliding or body flexion.
Some species possess pseudopodia but use them only in phagocytosis.
Class (biology)
In biological classification, class is* a taxonomic rank. Other well-known ranks are life, domain, kingdom, phylum, order, family, genus, and species, with class fitting between phylum and order...
of protists.
The class was defined in 1988 by Levine and contains two subclasses - the coccidia
Coccidia
Coccidia is a subclass of microscopic, spore-forming, single-celled obligate parasites belonging to the apicomplexan class Conoidasida. Coccidian parasites infect the intestinal tracts of animals, and are the largest group of apicomplexan protozoa....
and the gregarines. All members of this class have a complete, hollow, truncated conoid
Conoid
In geometry, a conoid is a Catalan surface all of whose rulings intersect a fixed line, called the axis of the conoid. If all its rulings are perpendicular to its axis, then the conoid is called a right conoid....
. Gregarines tend to parasitize invertebrate
Invertebrate
An invertebrate is an animal without a backbone. The group includes 97% of all animal species – all animals except those in the chordate subphylum Vertebrata .Invertebrates form a paraphyletic group...
s with the mature gamonts being extracellular, the coccidia mostly infect vertebrate
Vertebrate
Vertebrates are animals that are members of the subphylum Vertebrata . Vertebrates are the largest group of chordates, with currently about 58,000 species described. Vertebrates include the jawless fishes, bony fishes, sharks and rays, amphibians, reptiles, mammals, and birds...
s and have intracellular gamonts.
Description
A conoidConoid
In geometry, a conoid is a Catalan surface all of whose rulings intersect a fixed line, called the axis of the conoid. If all its rulings are perpendicular to its axis, then the conoid is called a right conoid....
is found in most species and when present forms complete but truncated cone.
Sexual and asexual reproduction are present in lifecycle of all species. Each zygote
Zygote
A zygote , or zygocyte, is the initial cell formed when two gamete cells are joined by means of sexual reproduction. In multicellular organisms, it is the earliest developmental stage of the embryo...
normally forms an oocyst wall within which it undergoes meiosis
Meiosis
Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction. The cells produced by meiosis are gametes or spores. The animals' gametes are called sperm and egg cells....
. This is sometimes followed by mitosis
Mitosis
Mitosis is the process by which a eukaryotic cell separates the chromosomes in its cell nucleus into two identical sets, in two separate nuclei. It is generally followed immediately by cytokinesis, which divides the nuclei, cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two cells containing roughly...
. This process of sporogony produces mobile vermiform sporozoites.
Mitotic divisions also occur during merogony of the feeding stages (trophozoites) and during gametogony.
Microgametes of some species are flagellated
Locomotion of other gamete
Gamete
A gamete is a cell that fuses with another cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually...
s and any other mobile stages is by gliding or body flexion.
Some species possess pseudopodia but use them only in phagocytosis.

