
Complex lamellar vector field
Encyclopedia
In vector calculus, a complex lamellar vector field is a vector field
in three dimensions which is orthogonal
to its own curl. That is,
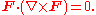
Complex lamellar vector fields are precisely those that are normal to a family of surfaces. A special case are irrotational vector field
s, satisfying
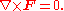
An irrotational vector field is locally the gradient
of a function, and is therefore orthogonal to the family of level surfaces (the equipotential surface
s). Accordingly, the term lamellar vector field is sometimes used as a synonym for an irrotational vector field.
The adjective "lamellar" derives from the noun "lamella", which means a thin layer. The lamellae to which "lamellar flow" refers are the surfaces of constant potential, or in the complex case, the surfaces orthogonal to the vector field.
Vector field
In vector calculus, a vector field is an assignmentof a vector to each point in a subset of Euclidean space. A vector field in the plane for instance can be visualized as an arrow, with a given magnitude and direction, attached to each point in the plane...
in three dimensions which is orthogonal
Orthogonality
Orthogonality occurs when two things can vary independently, they are uncorrelated, or they are perpendicular.-Mathematics:In mathematics, two vectors are orthogonal if they are perpendicular, i.e., they form a right angle...
to its own curl. That is,
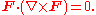
Complex lamellar vector fields are precisely those that are normal to a family of surfaces. A special case are irrotational vector field
Irrotational vector field
In vector calculus a conservative vector field is a vector field which is the gradient of a function, known in this context as a scalar potential. Conservative vector fields have the property that the line integral from one point to another is independent of the choice of path connecting the two...
s, satisfying
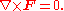
An irrotational vector field is locally the gradient
Gradient
In vector calculus, the gradient of a scalar field is a vector field that points in the direction of the greatest rate of increase of the scalar field, and whose magnitude is the greatest rate of change....
of a function, and is therefore orthogonal to the family of level surfaces (the equipotential surface
Equipotential surface
Equipotential surfaces are surfaces of constant scalar potential. They are used to visualize an -dimensional scalar potential function in dimensional space...
s). Accordingly, the term lamellar vector field is sometimes used as a synonym for an irrotational vector field.
The adjective "lamellar" derives from the noun "lamella", which means a thin layer. The lamellae to which "lamellar flow" refers are the surfaces of constant potential, or in the complex case, the surfaces orthogonal to the vector field.

