
Comparison of computer form factors
Encyclopedia
- For computers form factors both larger and smaller than desktop personal computers, see list of computer size categories.
In computing
Computing
Computing is usually defined as the activity of using and improving computer hardware and software. It is the computer-specific part of information technology...
, a form factor specifies the physical dimensions of major system components. Specifically, in the IBM PC compatible
IBM PC compatible
IBM PC compatible computers are those generally similar to the original IBM PC, XT, and AT. Such computers used to be referred to as PC clones, or IBM clones since they almost exactly duplicated all the significant features of the PC architecture, facilitated by various manufacturers' ability to...
industry, standard form factors ensure that parts are interchangeable across competing vendors and generations of technology, while in enterprise computing, form factors ensure that server modules fit into existing rackmount systems. Traditionally, the most significant specification is for that of the motherboard, which generally dictates the overall size of the case
Computer case
A computer case is the enclosure that contains most of the components of a computer...
. Small form factor
Small form factor
A small form factor is a computer form factor designed to minimize the volume of a desktop computer. For comparison purposes, the size of an SFF case is usually measured in litres. SFFs are available in a variety of sizes and shapes, including shoeboxes, cubes, and book-sized PCs...
s have been developed and implemented, but further reduction in overall size is hampered by current power supply technology.
Overview of form factors
Printed circuit board
A printed circuit board, or PCB, is used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks or signal traces etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. It is also referred to as printed wiring board or etched wiring...
within a typical desktop computer
Desktop computer
A desktop computer is a personal computer in a form intended for regular use at a single location, as opposed to a mobile laptop or portable computer. Early desktop computers are designed to lay flat on the desk, while modern towers stand upright...
, laptop
Laptop
A laptop, also called a notebook, is a personal computer for mobile use. A laptop integrates most of the typical components of a desktop computer, including a display, a keyboard, a pointing device and speakers into a single unit...
or server
Server (computing)
In the context of client-server architecture, a server is a computer program running to serve the requests of other programs, the "clients". Thus, the "server" performs some computational task on behalf of "clients"...
. Its main functions are as follows:
- to serve as a central backbone to which all other modular parts such as CPU, RAMRam-Animals:*Ram, an uncastrated male sheep*Ram cichlid, a species of freshwater fish endemic to Colombia and Venezuela-Military:*Battering ram*Ramming, a military tactic in which one vehicle runs into another...
, and hard drives can be attached as required to create a modern computer; - to accept (on many motherboards) different components (in particular CPU and expansion cardExpansion cardThe expansion card in computing is a printed circuit board that can be inserted into an expansion slot of a computer motherboard or backplane to add functionality to a computer system via the expansion bus.One edge of the expansion card holds the contacts that fit exactly into the slot...
s) for the purposes of customization; - to distribute powerPower supply unit (computer)A power supply unit converts mains AC to low-voltage regulated DC power for the internal components of the computer. Modern personal computers universally use a switched-mode power supply...
to PC components; - to electronically co-ordinate and interface the operation of the components.
As new generations of components have been developed, the standards of motherboards have changed too; for example, with AGP being introduced, and more recently PCI Express
PCI Express
PCI Express , officially abbreviated as PCIe, is a computer expansion card standard designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X, and AGP bus standards...
. However, the standardized size and layout of motherboard have changed much more slowly, and are controlled by their own standards. The list of components a motherboard must include changes far more slowly than the components themselves. For example, north bridge
Northbridge (computing)
The northbridge has historically been one of the two chips in the core logic chipset on a PC motherboard, the other being the southbridge. Increasingly these functions have migrated to the CPU chip itself, beginning with memory and graphics controllers. For Intel Sandy Bridge and AMD Fusion...
controllers have changed many times since their introduction, with many manufacturers bringing out their own versions, but in terms of form factor standards, the requirement to allow for a north bridge has remained fairly static for many years.
Although it is a slower process, form factors do evolve regularly in response to changing demands. The original PC standard (AT) was superseded in 1995 by the current industry standard ATX
ATX
ATX is a motherboard form factor specification developed by Intel in 1995 to improve on previous de facto standards like the AT form factor. It was the first big change in computer case, motherboard, and power supply design in many years, improving standardization and interchangeability of parts...
, which still dictates the size and design of the motherboard in most modern PCs. The latest update to the ATX standard was released in 2007. A divergent standard by chipset
Chipset
A chipset, PC chipset, or chip set refers to a group of integrated circuits, or chips, that are designed to work together. They are usually marketed as a single product.- Computers :...
manufacturer VIA
VIA Technologies
VIA Technologies is a Taiwanese manufacturer of integrated circuits, mainly motherboard chipsets, CPUs, and memory, and is part of the Formosa Plastics Group. It is the world's largest independent manufacturer of motherboard chipsets...
called EPIA
EPIA
VIA EPIA is a series of mini-ITX, nano-ITX and pico-ITX motherboards with integrated VIA processors...
(also known as ITX, and not to be confused with EPIC) is based upon smaller form factors and its own standards.
Differences between form factors are most apparent in terms of their intended market sector, and involve variations in size, design compromises and typical features. Most modern computers have very similar requirements, so form factor differences tend to be based upon subsets and supersets of these. For example, a desktop computer may require more sockets for maximal flexibility and many optional connectors and other features on-board, whereas a computer to be used in a multimedia
Multimedia
Multimedia is media and content that uses a combination of different content forms. The term can be used as a noun or as an adjective describing a medium as having multiple content forms. The term is used in contrast to media which use only rudimentary computer display such as text-only, or...
system may need to be optimized for heat and size, with additional plug-in cards being less common. The smallest motherboards may sacrifice CPU flexibility in favor of a fixed manufacturer's choice.
Tabular information
| Form factor | Originated | Max. size | Typical feature-set (compared to ATX) |
Typical CPU flexibility |
Power handling | Notes (typical usage, Market adoption, etc.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XT IBM Personal Computer XT The IBM Personal Computer XT, often shortened to the IBM XT, PC XT, or simply XT, was IBM's successor to the original IBM PC. It was released as IBM Machine Type number 5160 on March 8, 1983, and came standard with a hard drive... |
IBM IBM International Business Machines Corporation or IBM is an American multinational technology and consulting corporation headquartered in Armonk, New York, United States. IBM manufactures and sells computer hardware and software, and it offers infrastructure, hosting and consulting services in areas... 1983 |
8.5 × 11 in 216 × 279 mm |
Obsolete, see Industry Standard Architecture Industry Standard Architecture Industry Standard Architecture is a computer bus standard for IBM PC compatible computers introduced with the IBM Personal Computer to support its Intel 8088 microprocessor's 8-bit external data bus and extended to 16 bits for the IBM Personal Computer/AT's Intel 80286 processor... . The IBM Personal Computer XT IBM Personal Computer XT The IBM Personal Computer XT, often shortened to the IBM XT, PC XT, or simply XT, was IBM's successor to the original IBM PC. It was released as IBM Machine Type number 5160 on March 8, 1983, and came standard with a hard drive... was the successor to the original IBM PC IBM PC The IBM Personal Computer, commonly known as the IBM PC, is the original version and progenitor of the IBM PC compatible hardware platform. It is IBM model number 5150, and was introduced on August 12, 1981... , its first home computer. As the specifications were open, many clone Clone (computer science) In computing, a clone is a hardware or software system that is designed to mimic another system. Compatibility with the original system is usually the explicit purpose of cloning hardware or low-level software such as operating systems... motherboards were produced and it became a de facto De facto De facto is a Latin expression that means "concerning fact." In law, it often means "in practice but not necessarily ordained by law" or "in practice or actuality, but not officially established." It is commonly used in contrast to de jure when referring to matters of law, governance, or... standard. |
|||
| AT AT form factor In the area of IBM compatible personal computers, the AT form factor referred to the dimensions and layout of the motherboard for the IBM AT. Like the IBM PC and IBM XT models before it, many third-party manufacturers produced motherboards compatible with the IBM AT form factor, allowing end users... (Advanced Technology) |
IBM IBM International Business Machines Corporation or IBM is an American multinational technology and consulting corporation headquartered in Armonk, New York, United States. IBM manufactures and sells computer hardware and software, and it offers infrastructure, hosting and consulting services in areas... 1984 |
12 × 11–13 in 305 × 279–330 mm |
Obsolete, see Industry Standard Architecture Industry Standard Architecture Industry Standard Architecture is a computer bus standard for IBM PC compatible computers introduced with the IBM Personal Computer to support its Intel 8088 microprocessor's 8-bit external data bus and extended to 16 bits for the IBM Personal Computer/AT's Intel 80286 processor... . Created by IBM for the IBM Personal Computer/AT IBM Personal Computer/AT The IBM Personal Computer AT, more commonly known as the IBM AT and also sometimes called the PC AT or PC/AT, was IBM's second-generation PC, designed around the 6 MHz Intel 80286 microprocessor and released in 1984 as machine type 5170... , an Intel 80286 Intel 80286 The Intel 80286 , introduced on 1 February 1982, was a 16-bit x86 microprocessor with 134,000 transistors. Like its contemporary simpler cousin, the 80186, it could correctly execute most software written for the earlier Intel 8086 and 8088... machine. Also known as Full AT, it was popular during the era of the Intel 80386 Intel 80386 The Intel 80386, also known as the i386, or just 386, was a 32-bit microprocessor introduced by Intel in 1985. The first versions had 275,000 transistors and were used as the central processing unit of many workstations and high-end personal computers of the time... microprocessor. Superseded by ATX. |
|||
| Baby-AT | IBM IBM International Business Machines Corporation or IBM is an American multinational technology and consulting corporation headquartered in Armonk, New York, United States. IBM manufactures and sells computer hardware and software, and it offers infrastructure, hosting and consulting services in areas... 1985 |
8.5 × 10–13 in 216 × 254–330 mm |
IBM's 1985 successor to the AT motherboard. Functionally equivalent to the AT, it became popular due to its significantly smaller size. | |||
| ATX ATX ATX is a motherboard form factor specification developed by Intel in 1995 to improve on previous de facto standards like the AT form factor. It was the first big change in computer case, motherboard, and power supply design in many years, improving standardization and interchangeability of parts... |
Intel 1996 | 12 × 9.6 in 305 × 244 mm |
Created by Intel in 1995. , it is the most popular form factor for commodity motherboards. Typical size is 9.6 × 12 in although some companies extend that to 10 × 12 in. | |||
| SSI CEB SSI CEB The Compact Electronics Bay Specification as well as EEB, MEB and are standard form factors for dual or multi processor motherboards defined by the Server System Infrastructure forum... |
SSI SSI CEB The Compact Electronics Bay Specification as well as EEB, MEB and are standard form factors for dual or multi processor motherboards defined by the Server System Infrastructure forum... |
12 × 10.5 in 305 × 267 mm |
Created by the Server System Infrastructure SSI CEB The Compact Electronics Bay Specification as well as EEB, MEB and are standard form factors for dual or multi processor motherboards defined by the Server System Infrastructure forum... (SSI) forum. Derived from the EEB and ATX specifications. This means that SSI CEB motherboards have the same mounting holes and the same IO connector area as ATX motherboards. |
|||
| SSI EEB SSI CEB The Compact Electronics Bay Specification as well as EEB, MEB and are standard form factors for dual or multi processor motherboards defined by the Server System Infrastructure forum... |
SSI SSI CEB The Compact Electronics Bay Specification as well as EEB, MEB and are standard form factors for dual or multi processor motherboards defined by the Server System Infrastructure forum... |
12 × 13 in 305 × 330 mm |
Created by the Server System Infrastructure SSI CEB The Compact Electronics Bay Specification as well as EEB, MEB and are standard form factors for dual or multi processor motherboards defined by the Server System Infrastructure forum... (SSI) forum. Derived from the EEB and ATX specifications. This means that SSI CEB motherboards have the same mounting holes and the same IO connector area as ATX motherboards. |
|||
| SSI MEB SSI CEB The Compact Electronics Bay Specification as well as EEB, MEB and are standard form factors for dual or multi processor motherboards defined by the Server System Infrastructure forum... |
SSI SSI CEB The Compact Electronics Bay Specification as well as EEB, MEB and are standard form factors for dual or multi processor motherboards defined by the Server System Infrastructure forum... |
16.2 × 13 in 411 × 330 mm |
Created by the Server System Infrastructure SSI CEB The Compact Electronics Bay Specification as well as EEB, MEB and are standard form factors for dual or multi processor motherboards defined by the Server System Infrastructure forum... (SSI) forum. Derived from the EEB and ATX specifications. This means that SSI CEB motherboards have the same mounting holes and the same IO connector area as ATX motherboards. |
|||
| microATX MicroATX microATX, also known as µATX is a standard for motherboards that was introduced in December 1997. The maximum size of a microATX motherboard is 244 mm × 244 mm , but some microATX boards can be as small as 171.45 mm × 171.45 mm... |
1996 | 9.6 × 9.6 in 244 × 244 mm |
A smaller variant of the ATX form factor (about 25% shorter). Compatible with most ATX cases, but has fewer slots than ATX, for a smaller power supply Power supply A power supply is a device that supplies electrical energy to one or more electric loads. The term is most commonly applied to devices that convert one form of electrical energy to another, though it may also refer to devices that convert another form of energy to electrical energy... unit. Very popular for desktop and small form factor Small form factor A small form factor is a computer form factor designed to minimize the volume of a desktop computer. For comparison purposes, the size of an SFF case is usually measured in litres. SFFs are available in a variety of sizes and shapes, including shoeboxes, cubes, and book-sized PCs... computers . |
|||
| Mini-ATX Mini ATX Mini-ATX is a 15 x 15 cm motherboard form factor developed by AOpen Inc. Mini-ATX is slightly smaller than Mini-ITX... |
AOpen AOpen AOpen is a major electronics manufacturer from Taiwan that makes computers and parts for computers. AOpen used to be the Open System Business Unit of Acer Computer Inc. which designed, manufactured and sold computer components. It incorporated in December 1996 as a subsidiary of Acer Group with an... 2005 |
5.9 × 5.9 in 150 × 150 mm |
Mini-ATX is slightly smaller than Micro-ITX. Mini-ATX motherboards were design with MoDT (Mobile on Desktop Technology) which adapt mobile CPU for lower power requirement, less heat generation and better application capability. | |||
| FlexATX FlexATX FlexATX is a motherboard form factor derived from ATX. The specification was released in 1999 by Intel as an addendum to the microATX specification... |
Intel 1999 | 9.0 × 7.5 in 228.6 × 190.5 mm max. |
A subset of microATX developed by Intel in 1999. Allows more flexible motherboard design, component positioning and shape. Can be smaller than regular microATX. | |||
| Mini-ITX Mini-ITX Mini-ITX is a 17 x 17 cm low-power motherboard form factor developed by VIA Technologies in 2001. Mini-ITX is slightly smaller than microATX. Mini-ITX boards can often be passively cooled due to their low power consumption architecture, which makes them useful for home theater PC systems,... |
VIA VIA Technologies VIA Technologies is a Taiwanese manufacturer of integrated circuits, mainly motherboard chipsets, CPUs, and memory, and is part of the Formosa Plastics Group. It is the world's largest independent manufacturer of motherboard chipsets... 2001 |
6.7 × 6.7 in 170 × 170 mm max. |
A small, highly-integrated form factor, designed for small devices such as thin client Thin client A thin client is a computer or a computer program which depends heavily on some other computer to fulfill its traditional computational roles. This stands in contrast to the traditional fat client, a computer designed to take on these roles by itself... s and set-top box Set-top box A set-top box or set-top unit is an information appliance device that generally contains a tuner and connects to a television set and an external source of signal, turning the signal into content which is then displayed on the television screen or other display device.-History:Before the... es. |
|||
| Nano-ITX Nano-ITX Nano-ITX is a computer motherboard form factor first proposed by VIA Technologies at CeBIT in March 2003 , and implemented in late 2005. Nano-ITX boards measure 120 × 120 mm , and are fully integrated, very low power consumption motherboards with many uses, but targeted at smart digital... |
VIA VIA Technologies VIA Technologies is a Taiwanese manufacturer of integrated circuits, mainly motherboard chipsets, CPUs, and memory, and is part of the Formosa Plastics Group. It is the world's largest independent manufacturer of motherboard chipsets... 2003 |
4.7 × 4.7 in 120 × 120 mm |
Targeted at smart digital entertainment devices such as PVRs, set-top box Set-top box A set-top box or set-top unit is an information appliance device that generally contains a tuner and connects to a television set and an external source of signal, turning the signal into content which is then displayed on the television screen or other display device.-History:Before the... es, media centers Home theater PC A Home Theater PC or Media Center appliance is a convergence device that combines some or all the capabilities of a personal computer with a software application that supports video, photo, music playback, and sometimes video recording functionality... and Car PCs, and thin devices. |
|||
| Pico-ITX Pico-ITX Pico-ITX is a PC motherboard form factor announced by VIA Technologies in January 2007 and demonstrated later the same year at CeBIT. The formfactor was transferred over to SFF-SIG in 2008. The Pico-ITX form factor specifications call for the board to be 10 × 7.2 cm , which is half the area... |
VIA VIA Technologies VIA Technologies is a Taiwanese manufacturer of integrated circuits, mainly motherboard chipsets, CPUs, and memory, and is part of the Formosa Plastics Group. It is the world's largest independent manufacturer of motherboard chipsets... 2007 |
100 × 72 mm max. | ||||
| Mobile-ITX Mobile-ITX Mobile-ITX is the smallest x86 compliant motherboard form factor presented by VIA Technologies in December, 2009. The motherboard size is 60mm × 60mm. There are no computer ports on the CPU module and it is necessary to use an I/O carrier board. The design is intended for medical, transportation... |
VIA VIA Technologies VIA Technologies is a Taiwanese manufacturer of integrated circuits, mainly motherboard chipsets, CPUs, and memory, and is part of the Formosa Plastics Group. It is the world's largest independent manufacturer of motherboard chipsets... 2007 |
2.953 × 1.772 in 75 × 45 mm |
||||
| BTX BTX (form factor) BTX is a form factor for motherboards, originally intended to be the replacement for the aging ATX motherboard form factor in late 2004 and early 2005... (Balanced Technology Extended) |
Intel 2004 | 12.8 × 10.5 in 325 × 267 mm max. |
A standard proposed by Intel as a successor to ATX in the early 2000s, according to Intel the layout has better cooling. BTX Boards are flipped in comparison to ATX Boards, so a BTX or MicroBTX Board needs a BTX case, while an ATX style board fits in an ATX case. The RAM slots and the PCI slots are parallel to each other. Processor is placed closest to the fan. May contain a CNR board. |
|||
| MicroBTX MicroBTX MicroBTX is a computer motherboard form factor.a microBTX is 10.4x10.5" and it supports up to four expansion slots... (or uBTX MicroBTX MicroBTX is a computer motherboard form factor.a microBTX is 10.4x10.5" and it supports up to four expansion slots... ) |
Intel 2004 | 10.4 × 10.5 in 264 × 267 mm max. |
||||
| PicoBTX | Intel 2004 | 8.0 × 10.5 in 203 × 267 mm max. |
||||
| DTX DTX (form factor) The DTX form factor is a variation of ATX specification designed especially for small form factor PCs with dimensions of 8.0 by 9.6 inches An industry standard intended to enable interchangeability for systems similar to Shuttle's original "SFF" designs, AMD announced its development on January... |
AMD 2007 | 200 × 244 mm max. | ||||
| Mini-DTX | AMD 2007 | 200 × 170 mm max. | ||||
| smartModule | Digital-Logic | 66 × 85 mm | Used in embedded system Embedded system An embedded system is a computer system designed for specific control functions within a larger system. often with real-time computing constraints. It is embedded as part of a complete device often including hardware and mechanical parts. By contrast, a general-purpose computer, such as a personal... s and single board computers. Requires a baseboard. |
|||
| ETX ETX (form factor) ETX, standing for Embedded Technology eXtended, is a highly integrated and compact computer-on-module form factor that can be used in a design application much like an integrated circuit component... |
Kontron Kontron Kontron AG is a German-based multinational company which designs and manufactures embedded computer modules, boards and systems.Kontron AG serves OEMs, system integrators and application providers of different market segments... |
95 × 114 mm | Used in embedded system Embedded system An embedded system is a computer system designed for specific control functions within a larger system. often with real-time computing constraints. It is embedded as part of a complete device often including hardware and mechanical parts. By contrast, a general-purpose computer, such as a personal... s and single board computers. Requires a baseboard. |
|||
| COM Express Basic | PICMG PICMG The PCI Industrial Computer Manufacturers Group is a consortium of over 227 companies. The group, founded in 1994, was originally formed to adapt PCI technology for use in high-performance telecommunications, military and industrial computing applications but its work has now grown to include... |
95 × 125 mm | Used in embedded system Embedded system An embedded system is a computer system designed for specific control functions within a larger system. often with real-time computing constraints. It is embedded as part of a complete device often including hardware and mechanical parts. By contrast, a general-purpose computer, such as a personal... s and single board computers. Requires a carrier board. |
|||
| COM Express Compact | PICMG PICMG The PCI Industrial Computer Manufacturers Group is a consortium of over 227 companies. The group, founded in 1994, was originally formed to adapt PCI technology for use in high-performance telecommunications, military and industrial computing applications but its work has now grown to include... |
95 × 95 mm | Used in embedded system Embedded system An embedded system is a computer system designed for specific control functions within a larger system. often with real-time computing constraints. It is embedded as part of a complete device often including hardware and mechanical parts. By contrast, a general-purpose computer, such as a personal... s and single board computers. Requires a carrier board. |
|||
| nanoETXexpress | Kontron Kontron Kontron AG is a German-based multinational company which designs and manufactures embedded computer modules, boards and systems.Kontron AG serves OEMs, system integrators and application providers of different market segments... |
55 × 84 mm | Used in embedded system Embedded system An embedded system is a computer system designed for specific control functions within a larger system. often with real-time computing constraints. It is embedded as part of a complete device often including hardware and mechanical parts. By contrast, a general-purpose computer, such as a personal... s and single board computers. Requires a carrier board. Also known as COM Express Ultra and adheres to pin-outs Type 1 or Type 10 |
|||
| CoreExpress CoreExpress CoreExpress modules are complete computer-on-module highly integrated, small and compact PCs that can be used in an embedded computer board design, much like an integrated circuit component. COMs integrate CPU, memory, graphics, and BIOS, and common IO interfaces... |
SFF-SIG SFF-SIG In the computer hardware world, the Small Form Factor Special Interest Group or SFF-SIG is an international non-profit standards body focused on the advancement of modular technologies used in embedded and small form factor computers and controllers... |
58 × 65 mm | Used in embedded system Embedded system An embedded system is a computer system designed for specific control functions within a larger system. often with real-time computing constraints. It is embedded as part of a complete device often including hardware and mechanical parts. By contrast, a general-purpose computer, such as a personal... s and single board computers. Requires a carrier board. |
|||
| Extended ATX (EATX) | 12 × 13 in 305 × 330 mm |
Used in rackmount server systems. Typically used for server-class type motherboards with dual processors and too much circuitry for a standard ATX motherboard. The mounting hole pattern for the upper portion of the board matches ATX. | ||||
| LPX LPX form factor LPX , originally developed by Western Digital, was a loosely defined motherboard format widely used in the 1990s.... |
9 × 11–13 in 229 × 279–330 mm |
Based on a design by Western Digital Western Digital Western Digital Corporation is one of the largest computer hard disk drive manufacturers in the world. It has a long history in the electronics industry as an integrated circuit maker and a storage products company. Western Digital was founded on April 23, 1970 by Alvin B... , it allowed smaller cases than the AT standard, by putting the expansion card slots on a Riser card Riser card A riser card is a printed circuit board that picks up a multitude of signal lines via a single connector on a mainboard and distributes them via dedicated connectors on the card.... . Used in slimline retail PCs. LPX was never standardized and generally only used by large OEMs Original Equipment Manufacturer An original equipment manufacturer, or OEM, manufactures products or components that are purchased by a company and retailed under that purchasing company's brand name. OEM refers to the company that originally manufactured the product. When referring to automotive parts, OEM designates a... . |
||||
| Mini-LPX | 8–9 × 10–11 in 203–229 × 254–279 mm |
Used in slimline retail PCs. | ||||
| PC/104™ | PC/104 Consortium PC/104 Consortium The PC/104 Consortium was established in February of 1992 by 12 companies with a common vision of adapting desktop computer technology for embedded applications. The consortium has since had a tremendous, positive effect on the embedded computer marketplace and now includes over 50 member companies... 1992 |
3.8 × 3.6 in | Used in embedded systems. AT Bus (ISA) architecture adapted to vibration-tolerant header connectors. | |||
| PC/104-Plus™ | PC/104 Consortium PC/104 Consortium The PC/104 Consortium was established in February of 1992 by 12 companies with a common vision of adapting desktop computer technology for embedded applications. The consortium has since had a tremendous, positive effect on the embedded computer marketplace and now includes over 50 member companies... 1997 |
3.8 × 3.6 in | Used in embedded systems. PCI Bus architecture adapted to vibration-tolerant header connectors. | |||
| PCI/104-Express™ PCI/104-Express The PCI/104-Express™ specification establishes a standard to use the high-speed PCI Express bus in embedded applications. It was developed by the PC/104 Consortium and adopted by member vote in March of 2008. PCI Express was chosen because of its market adoption, performance, scalability, and... |
PC/104 Consortium PC/104 Consortium The PC/104 Consortium was established in February of 1992 by 12 companies with a common vision of adapting desktop computer technology for embedded applications. The consortium has since had a tremendous, positive effect on the embedded computer marketplace and now includes over 50 member companies... 2008 |
3.8 × 3.6 in | Used in embedded systems. PCI Express architecture adapted to vibration-tolerant header connectors. |
|||
| PCIe/104™ | PC/104 Consortium PC/104 Consortium The PC/104 Consortium was established in February of 1992 by 12 companies with a common vision of adapting desktop computer technology for embedded applications. The consortium has since had a tremendous, positive effect on the embedded computer marketplace and now includes over 50 member companies... 2008 |
3.8 × 3.6 in | Used in embedded systems. PCI/104-Express without the legacy PCI bus. |
|||
| NLX | Intel 1999 | 8–9 × 10–13.6 in 203–229 × 254–345 mm |
A low-profile design released in 1997. It also incorporated a riser Riser card A riser card is a printed circuit board that picks up a multitude of signal lines via a single connector on a mainboard and distributes them via dedicated connectors on the card.... for expansion cards, and never became popular. |
|||
| UTX | TQ-Components 2001 | 88 × 108 mm | Used in embedded system Embedded system An embedded system is a computer system designed for specific control functions within a larger system. often with real-time computing constraints. It is embedded as part of a complete device often including hardware and mechanical parts. By contrast, a general-purpose computer, such as a personal... s and IPCs. Requires a baseboard. |
|||
| WTX | Intel 1998 | 14 × 16.75 in 355.6 × 425.4 mm |
A large design for servers and high-end workstations featuring multiple CPUs and hard drives. | |||
| HPTX | EVGA EVGA Corporation EVGA Corporation is a company that produces NVIDIA based consumer computer hardware, as well as Intel based motherboards. Founded in July 1999, its current headquarters is in Brea, California.- Products :... 2008 |
13.6 × 15 in 345.44 × 381 mm |
A large design by EVGA, it has dual-CPU (Intel Xeon 55xx and 56xx) support, Four-Way nVIDIA SLI or ATi Crossfire support, up to 8 3.5in HDD support, and supports 48GB of RAM. Cases need to have at least 9 expansion slots and the required dimensions to be compatible. | |||
| XTX XTX XTX is a computer-on-module standard for x86-based embedded devices. XTX adds PCI-Express, SATA, and LPC capabilities. The standard was promulgated by Advantech, , and congatec.-External links:* *... |
2005 | 95 × 114 mm | Used in embedded systems. Requires a baseboard. |
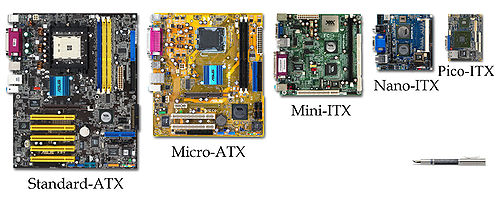
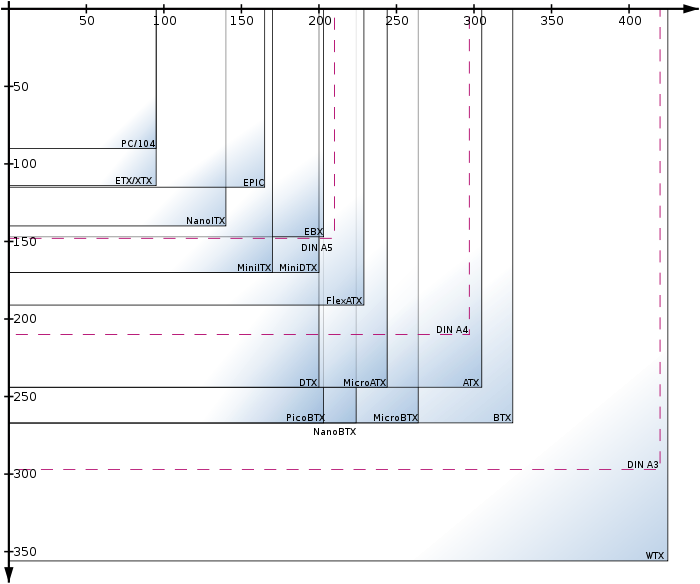
Graphical comparison of physical sizes
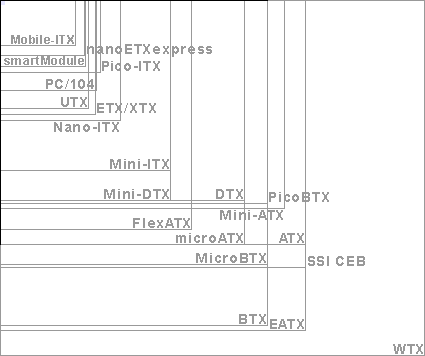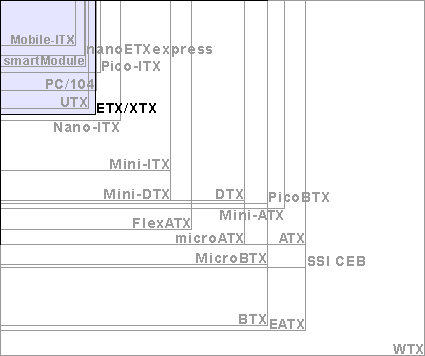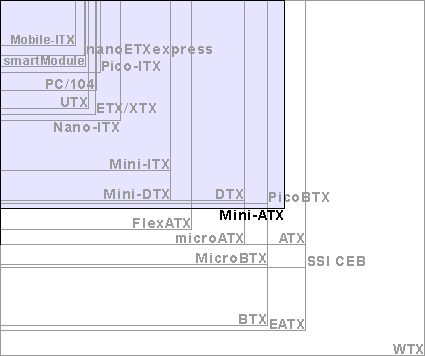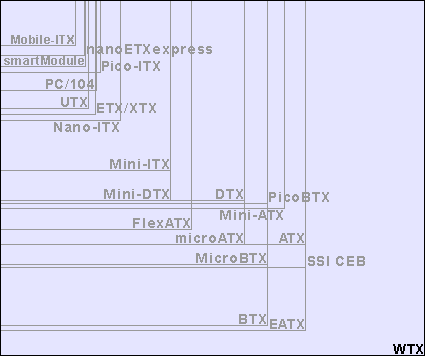
Maximum number of PCI/AGP/PCI-e slots
ATX case compatible:| Specification | Number |
|---|---|
| HPTX | 9 |
| ATX ATX ATX is a motherboard form factor specification developed by Intel in 1995 to improve on previous de facto standards like the AT form factor. It was the first big change in computer case, motherboard, and power supply design in many years, improving standardization and interchangeability of parts... |
7 |
| MicroATX MicroATX microATX, also known as µATX is a standard for motherboards that was introduced in December 1997. The maximum size of a microATX motherboard is 244 mm × 244 mm , but some microATX boards can be as small as 171.45 mm × 171.45 mm... |
4 |
| FlexATX FlexATX FlexATX is a motherboard form factor derived from ATX. The specification was released in 1999 by Intel as an addendum to the microATX specification... |
3 |
| DTX DTX (form factor) The DTX form factor is a variation of ATX specification designed especially for small form factor PCs with dimensions of 8.0 by 9.6 inches An industry standard intended to enable interchangeability for systems similar to Shuttle's original "SFF" designs, AMD announced its development on January... |
2 |
| Mini-DTX/DTX DTX (form factor) The DTX form factor is a variation of ATX specification designed especially for small form factor PCs with dimensions of 8.0 by 9.6 inches An industry standard intended to enable interchangeability for systems similar to Shuttle's original "SFF" designs, AMD announced its development on January... |
2 |
| Mini-ITX Mini-ITX Mini-ITX is a 17 x 17 cm low-power motherboard form factor developed by VIA Technologies in 2001. Mini-ITX is slightly smaller than microATX. Mini-ITX boards can often be passively cooled due to their low power consumption architecture, which makes them useful for home theater PC systems,... |
1 |
PC/104 and EBX
PC/104PC/104
PC/104 is an embedded computer standard controlled by the which defines both a form factor and computer bus. PC/104 is intended for specialized embedded computing environments where applications depend on reliable data acquisition despite an often extreme environment...
is an embedded computer standard which defines both a form factor and computer bus. PC/104 is intended for embedded computing environments. Single board computers built to this form factor are often sold by COTS
Commercial off-the-shelf
In the United States, Commercially available Off-The-Shelf is a Federal Acquisition Regulation term defining a nondevelopmental item of supply that is both commercial and sold in substantial quantities in the commercial marketplace, and that can be procured or utilized under government contract...
vendors, which benefits users who want a customized rugged system, without months of design and paper work.
The PC/104 form factor was standardized by the PC/104 Consortium in 1992.[3] An IEEE standard corresponding to PC/104 was drafted as IEEE P996.1, but never ratified.
The 5.75 × 8.0 in Embedded Board eXpandable
Embedded Board eXpandable
Embedded Board eXpandable is a standardized computer form factor.This format was created for embedded computer systems by a consortium including Motorola and . EBX systems typically were embedded PowerPC or PowerQUICC based....
(EBX) specification, which was derived from Ampro's proprietary Little Board form-factor, resulted from a collaboration between Ampro and Motorola Computer Group.
As compared with PC/104 modules, these larger (but still reasonably embeddable) SBCs tend to have everything of a full PC on them, including application oriented interfaces like audio, analog, or digital I/O in many cases. Also it's much easier to fit Pentium CPUs, whereas it's a tight squeeze (or expensive) to do so on a PC/104 SBC. Typically, EBX SBCs contain: the CPU; upgradeable RAM subassemblies (e.g., DIMM); Flash memory for solid state disk; multiple USB, serial, and parallel ports; onboard expansion via a PC/104 module stack; off-board expansion via ISA and/or PCI buses (from the PC/104 connectors); networking interface (typically Ethernet); and video (typically CRT, LCD, and TV).
Mini PC
Mini PCMini PC
Mini PC is short for “minimized personal computer” and is also called small form factor PC."Mini PC", referring to traditional desktop PC's, refers to the Mini-ITX form factor, which is a 17 x 17 cm motherboard...
is a PC
Personal computer
A personal computer is any general-purpose computer whose size, capabilities, and original sales price make it useful for individuals, and which is intended to be operated directly by an end-user with no intervening computer operator...
form factor very close in size to an external CD or DVD
DVD
A DVD is an optical disc storage media format, invented and developed by Philips, Sony, Toshiba, and Panasonic in 1995. DVDs offer higher storage capacity than Compact Discs while having the same dimensions....
drive.
See also
- Small form factorSmall form factorA small form factor is a computer form factor designed to minimize the volume of a desktop computer. For comparison purposes, the size of an SFF case is usually measured in litres. SFFs are available in a variety of sizes and shapes, including shoeboxes, cubes, and book-sized PCs...
- Hard-disk-drive form factors

