
Combination tone
Encyclopedia
A combination tone, also called a sum tone or a difference tone (also occasionally resultant tone), can be any of at least three similar psychoacoustic phenomena. When two tones are played simultaneously, a listener can sometimes perceive an additional tone whose frequency
is a sum or difference of the two frequencies. The discovery of some of these phenomena is credited to the violinist Giuseppe Tartini
, and so the tones are also called Tartini tones.
One way a difference tone can be heard is when two tones with fairly complete sets of harmonics make a just fifth. This can be explained as an example of the missing fundamental
phenomenon. If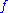 is the missing fundamental frequency
is the missing fundamental frequency
, then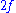 would be the frequency of the lower tone, and its harmonics would be
would be the frequency of the lower tone, and its harmonics would be 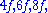 etc. Since a fifth corresponds to a frequency ratio of 2:3, the higher tone and its harmonics would then be
etc. Since a fifth corresponds to a frequency ratio of 2:3, the higher tone and its harmonics would then be 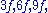 etc. When both tones are sounded, there are components with frequencies of
etc. When both tones are sounded, there are components with frequencies of 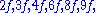 etc. The missing fundamental is heard because so many of these components refer to it.
etc. The missing fundamental is heard because so many of these components refer to it.
The specific phenomenon that Tartini discovered was physical. Sum and difference tones are thought to be caused sometimes by the non-linearity of the inner ear
. This causes intermodulation distortion of the various frequencies which enter the ear. They are combined linearly
, generating relatively faint components with frequencies equal to the sums and differences of whole multiples of the original frequencies. Any components which are heard are usually lower, with the most commonly heard frequency being just the difference tone,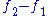 , though this may be a consequence of the other phenomena. Although much less common, the following frequencies may also be heard:
, though this may be a consequence of the other phenomena. Although much less common, the following frequencies may also be heard: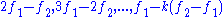
For a time it was thought that the inner ear was solely responsible whenever a sum or difference tone was heard. However, experiments show evidence that even when using headphones
providing a single pure tone
to each ear separately, listeners may still hear a difference tone. Since the peculiar, non-linear physics of the ear doesn't come into play in this case, it is thought that this must be a separate, neural phenomenon. Compare binaural beats
.
Heinz Bohlen proposed what is now known as the Bohlen–Pierce scale on the basis of combination tones.
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
is a sum or difference of the two frequencies. The discovery of some of these phenomena is credited to the violinist Giuseppe Tartini
Giuseppe Tartini
Giuseppe Tartini was an Italian baroque composer and violinist.-Biography:Tartini was born in Piran, a town on the peninsula of Istria, in the Republic of Venice to Gianantonio – native of Florence – and Caterina Zangrando, a descendant of one of the oldest aristocratic Piranian families.It...
, and so the tones are also called Tartini tones.
One way a difference tone can be heard is when two tones with fairly complete sets of harmonics make a just fifth. This can be explained as an example of the missing fundamental
Missing fundamental
A sound is said to have a missing fundamental, suppressed fundamental, or phantom fundamental when its overtones suggest a fundamental frequency but the sound lacks a component at the fundamental frequency itself....
phenomenon. If
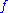 is the missing fundamental frequency
is the missing fundamental frequencyFundamental frequency
The fundamental frequency, often referred to simply as the fundamental and abbreviated f0, is defined as the lowest frequency of a periodic waveform. In terms of a superposition of sinusoids The fundamental frequency, often referred to simply as the fundamental and abbreviated f0, is defined as the...
, then
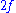 would be the frequency of the lower tone, and its harmonics would be
would be the frequency of the lower tone, and its harmonics would be 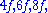 etc. Since a fifth corresponds to a frequency ratio of 2:3, the higher tone and its harmonics would then be
etc. Since a fifth corresponds to a frequency ratio of 2:3, the higher tone and its harmonics would then be 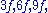 etc. When both tones are sounded, there are components with frequencies of
etc. When both tones are sounded, there are components with frequencies of 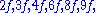 etc. The missing fundamental is heard because so many of these components refer to it.
etc. The missing fundamental is heard because so many of these components refer to it.The specific phenomenon that Tartini discovered was physical. Sum and difference tones are thought to be caused sometimes by the non-linearity of the inner ear
Inner ear
The inner ear is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In mammals, it consists of the bony labyrinth, a hollow cavity in the temporal bone of the skull with a system of passages comprising two main functional parts:...
. This causes intermodulation distortion of the various frequencies which enter the ear. They are combined linearly
Linear combination
In mathematics, a linear combination is an expression constructed from a set of terms by multiplying each term by a constant and adding the results...
, generating relatively faint components with frequencies equal to the sums and differences of whole multiples of the original frequencies. Any components which are heard are usually lower, with the most commonly heard frequency being just the difference tone,
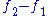 , though this may be a consequence of the other phenomena. Although much less common, the following frequencies may also be heard:
, though this may be a consequence of the other phenomena. Although much less common, the following frequencies may also be heard: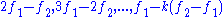
For a time it was thought that the inner ear was solely responsible whenever a sum or difference tone was heard. However, experiments show evidence that even when using headphones
Headphones
Headphones are a pair of small loudspeakers, or less commonly a single speaker, held close to a user's ears and connected to a signal source such as an audio amplifier, radio, CD player or portable Media Player. They are also known as stereophones, headsets or, colloquially, cans. The in-ear...
providing a single pure tone
Pure tone
A pure tone is a tone with a sinusoidal waveshape.A sine wave is characterized by its frequency, the number of cycles per second—or its wavelength, the distance the waveform travels through its medium within a period—and the amplitude, the size of each cycle...
to each ear separately, listeners may still hear a difference tone. Since the peculiar, non-linear physics of the ear doesn't come into play in this case, it is thought that this must be a separate, neural phenomenon. Compare binaural beats
Binaural beats
Binaural beats or binaural tones are auditory processing artifacts, or apparent sounds, the perception of which arises in the brain for specific physical stimuli...
.
Heinz Bohlen proposed what is now known as the Bohlen–Pierce scale on the basis of combination tones.
Further reading
- Adrianus J. M. Houtsma, Julius L. Goldstein, "Percepetion of Musical Intervals: Evidence for the Central Origin of the Pitch of Complex Tones", Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Research Laboratory of Electronics, Technical Report 484, October 1, 1971.
External links
- Sum and Difference Tones
- Titchener Difference Tones Training
- Difference tones on the harmonica
- Pitch Perception Lecture Notes
- Tartini computer program. Uses combination tones for pitch recognition. If certain intervals are played in double-stop, the program can display its Tartini-tone.

