Combes quinoline synthesis
Encyclopedia
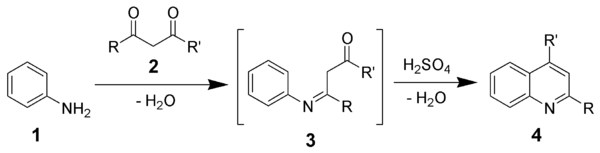
The Combes quinoline synthesis is a chemical reaction
involving the condensation
of unsubstituted aniline
s (1) with β-diketone
s (2) to form substituted quinoline
s (4) after an acid
-catalyzed ring closure of an intermediate Schiff base
(3).
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
involving the condensation
Condensation reaction
A condensation reaction is a chemical reaction in which two molecules or moieties combine to form one single molecule, together with the loss of a small molecule. When this small molecule is water, it is known as a dehydration reaction; other possible small molecules lost are hydrogen chloride,...
of unsubstituted aniline
Aniline
Aniline, phenylamine or aminobenzene is an organic compound with the formula C6H5NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the prototypical aromatic amine. Being a precursor to many industrial chemicals, its main use is in the manufacture of precursors to polyurethane...
s (1) with β-diketone
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure RCR', where R and R' can be a variety of atoms and groups of atoms. It features a carbonyl group bonded to two other carbon atoms. Many ketones are known and many are of great importance in industry and in biology...
s (2) to form substituted quinoline
Quinoline
Quinoline is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound. It has the formula C9H7N and is a colourless hygroscopic liquid with a strong odour. Aged samples, if exposed to light, become yellow and later brown...
s (4) after an acid
Acid
An acid is a substance which reacts with a base. Commonly, acids can be identified as tasting sour, reacting with metals such as calcium, and bases like sodium carbonate. Aqueous acids have a pH of less than 7, where an acid of lower pH is typically stronger, and turn blue litmus paper red...
-catalyzed ring closure of an intermediate Schiff base
Schiff base
A Schiff base, named after Hugo Schiff, is a compound with a functional group that contains a carbon-nitrogen double bond with the nitrogen atom connected to an aryl or alkyl group, not hydrogen....
(3).

See also
- Conrad-Limpach reaction
- Doebner reactionDoebner reactionThe Doebner reaction is the chemical reaction of an aniline with an aldehyde and pyruvic acid to form quinoline-4-carboxylic acids....
- Doebner-Miller reactionDoebner-Miller reactionThe Doebner-Miller reaction is the organic reaction of an aniline with α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds to form quinolines.This reaction is also known as the Skraup-Doebner-Von Miller quinoline synthesis, and is named after the Czech chemist Zdenko Hans Skraup , and the Germans Oscar Döbner and...

