.gif)
Caustic (mathematics)
Encyclopedia
Envelope (mathematics)
In geometry, an envelope of a family of curves in the plane is a curve that is tangent to each member of the family at some point. Classically, a point on the envelope can be thought of as the intersection of two "adjacent" curves, meaning the limit of intersections of nearby curves...
of rays either reflected
Reflection (mathematics)
In mathematics, a reflection is a mapping from a Euclidean space to itself that is an isometry with a hyperplane as set of fixed points; this set is called the axis or plane of reflection. The image of a figure by a reflection is its mirror image in the axis or plane of reflection...
or refracted by a manifold
Manifold
In mathematics , a manifold is a topological space that on a small enough scale resembles the Euclidean space of a specific dimension, called the dimension of the manifold....
. It is related to the optical concept of caustics
Caustic (optics)
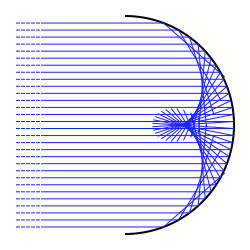
In optics, a caustic or caustic network is the envelope of light rays reflected or refracted by a curved surface or object, or the projection of that envelope of rays on another surface. The caustic is a curve or surface to which each of the light rays is tangent, defining a boundary of an...
. The ray's source may be a point (called the radiant) or infinity, in which case a direction vector must be specified.
More generally, especially as applied to symplectic geometry and singularity theory
Singularity theory
-The notion of singularity:In mathematics, singularity theory is the study of the failure of manifold structure. A loop of string can serve as an example of a one-dimensional manifold, if one neglects its width. What is meant by a singularity can be seen by dropping it on the floor...
, a caustic is the critical value set
Critical value
-Differential topology:In differential topology, a critical value of a differentiable function between differentiable manifolds is the image ƒ in N of a critical point x in M.The basic result on critical values is Sard's lemma...
of a Lagrangian mapping where is a Lagrangian immersion of a Lagrangian submanifold L into a symplectic manifold
Symplectic manifold
In mathematics, a symplectic manifold is a smooth manifold, M, equipped with a closed nondegenerate differential 2-form, ω, called the symplectic form. The study of symplectic manifolds is called symplectic geometry or symplectic topology...
M, and is a Lagrangian fibration of the symplectic manifold M. The caustic is a subset
Subset
In mathematics, especially in set theory, a set A is a subset of a set B if A is "contained" inside B. A and B may coincide. The relationship of one set being a subset of another is called inclusion or sometimes containment...
of the Lagrangian fibration's base space B.
Catacaustic
A catacaustic is the reflective case.With a radiant, it is the evolute
Evolute
In the differential geometry of curves, the evolute of a curve is the locus of all its centers of curvature. Equivalently, it is the envelope of the normals to a curve....
of the orthotomic of the radiant.
The planar, parallel-source-rays case: suppose the direction vector is
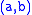 and the mirror curve is parametrised as
and the mirror curve is parametrised as 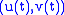 . The normal vector at a point is
. The normal vector at a point is 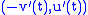 ; the reflection of the direction vector is (normal needs special normalization)
; the reflection of the direction vector is (normal needs special normalization)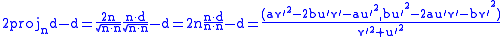
Having components of found reflected vector treat it as a tangent
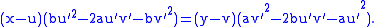
Using the simplest envelope
Envelope (mathematics)
In geometry, an envelope of a family of curves in the plane is a curve that is tangent to each member of the family at some point. Classically, a point on the envelope can be thought of as the intersection of two "adjacent" curves, meaning the limit of intersections of nearby curves...
form
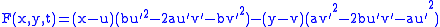
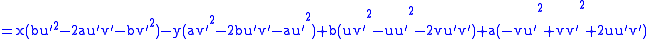
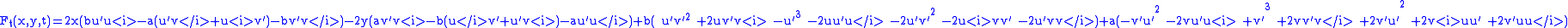
which may be unaesthetic, but
 gives a linear system
gives a linear systemLinear system
A linear system is a mathematical model of a system based on the use of a linear operator.Linear systems typically exhibit features and properties that are much simpler than the general, nonlinear case....
in
 and so it is elementary to obtain a parametrisation of the catacaustic. Cramer's rule
and so it is elementary to obtain a parametrisation of the catacaustic. Cramer's ruleCramer's rule
In linear algebra, Cramer's rule is a theorem, which gives an expression for the solution of a system of linear equations with as many equations as unknowns, valid in those cases where there is a unique solution...
would serve.
Example
Let the direction vector be (0,1) and the mirror be
Then
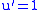
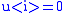

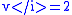
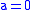

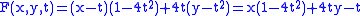

and
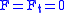 has solution
has solution 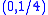 ; i.e., light entering a parabolic
; i.e., light entering a parabolicParabola
In mathematics, the parabola is a conic section, the intersection of a right circular conical surface and a plane parallel to a generating straight line of that surface...
mirror parallel to its axis is reflected through the focus.

