
Carboxylation
Encyclopedia
Carboxylation in chemistry
is a chemical reaction
in which a carboxylic acid
group is introduced in a substrate
. The opposite reaction is decarboxylation
.
many different protocols exist for carboxylation. One general approach is by reaction of nucleophile
s with dry ice
(solid carbon dioxide
) or formic acid
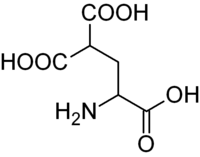
Carboxylation in biochemistry
is a posttranslational modification
of glutamate residues, to γ-carboxyglutamate, in proteins. It occurs primarily in proteins involved in the blood clotting cascade, specifically factors II, VII, IX, and X, protein C, and protein S, and also in some bone proteins. This modification is required for these proteins to function. Carboxylation occurs in the liver
and is performed by γ-glutamyl carboxylase
.
The carboxylase requires vitamin K
as a cofactor and performs the reaction in a processive manner. γ-carboxyglutamate binds calcium, which is essential for its activity. For example, in prothrombin, calcium binding allows the protein to associate with the plasma membrane in platelets, bringing it into close proximity with the proteins that cleave prothrombin to active thrombin
after injury.
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
is a chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
in which a carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acids are organic acids characterized by the presence of at least one carboxyl group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is R-COOH, where R is some monovalent functional group...
group is introduced in a substrate
Substrate (chemistry)
In chemistry, a substrate is the chemical species being observed, which reacts with a reagent. This term is highly context-dependent. In particular, in biochemistry, an enzyme substrate is the material upon which an enzyme acts....
. The opposite reaction is decarboxylation
Decarboxylation
Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction that releases carbon dioxide . Usually, decarboxylation refers to a reaction of carboxylic acids, removing a carbon atom from a carbon chain. The reverse process, which is the first chemical step in photosynthesis, is called carbonation, the addition of CO2 to...
.
Carboxylation in organic chemistry
In organic chemistryOrganic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives...
many different protocols exist for carboxylation. One general approach is by reaction of nucleophile
Nucleophile
A nucleophile is a species that donates an electron-pair to an electrophile to form a chemical bond in a reaction. All molecules or ions with a free pair of electrons can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are by definition Lewis bases.Nucleophilic describes the...
s with dry ice
Dry ice
Dry ice, sometimes referred to as "Cardice" or as "card ice" , is the solid form of carbon dioxide. It is used primarily as a cooling agent. Its advantages include lower temperature than that of water ice and not leaving any residue...
(solid carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
) or formic acid
Formic acid
Formic acid is the simplest carboxylic acid. Its chemical formula is HCOOH or HCO2H. It is an important intermediate in chemical synthesis and occurs naturally, most notably in the venom of bee and ant stings. In fact, its name comes from the Latin word for ant, formica, referring to its early...
Carboxylation in biochemistry

Carboxylation in biochemistry
Biochemistry
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes in living organisms, including, but not limited to, living matter. Biochemistry governs all living organisms and living processes...
is a posttranslational modification
Posttranslational modification
Posttranslational modification is the chemical modification of a protein after its translation. It is one of the later steps in protein biosynthesis, and thus gene expression, for many proteins....
of glutamate residues, to γ-carboxyglutamate, in proteins. It occurs primarily in proteins involved in the blood clotting cascade, specifically factors II, VII, IX, and X, protein C, and protein S, and also in some bone proteins. This modification is required for these proteins to function. Carboxylation occurs in the liver
Liver
The liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
and is performed by γ-glutamyl carboxylase
Gamma-glutamyl carboxylase
Gamma-glutamyl carboxylase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GGCX gene, located on chromosome 2 at 2p12.-Function:Gamma-glutamyl carboxylase is an enzyme that catalyzes the posttranslational modification of vitamin K-dependent proteins...
.
The carboxylase requires vitamin K
Vitamin K
Vitamin K is a group of structurally similar, fat soluble vitamins that are needed for the posttranslational modification of certain proteins required for blood coagulation and in metabolic pathways in bone and other tissue. They are 2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone derivatives...
as a cofactor and performs the reaction in a processive manner. γ-carboxyglutamate binds calcium, which is essential for its activity. For example, in prothrombin, calcium binding allows the protein to associate with the plasma membrane in platelets, bringing it into close proximity with the proteins that cleave prothrombin to active thrombin
Thrombin
Thrombin is a "trypsin-like" serine protease protein that in humans is encoded by the F2 gene. Prothrombin is proteolytically cleaved to form thrombin in the first step of the coagulation cascade, which ultimately results in the stemming of blood loss...
after injury.

