
Cadbury Castle, Somerset
Encyclopedia
Cadbury Castle is an Iron Age
hill fort
in the civil parish of South Cadbury
in the English
county of Somerset
. It is a Scheduled Ancient Monument
and associated with King Arthur
.
and Early Iron Age
, roughly the start of the first millennium BC
.
The reason for their emergence in Britain, and their purpose, has been a subject of debate. It has been argued that they could have been military sites constructed in response to invasion from continental Europe, sites built by invaders, or a military reaction to social tensions caused by an increasing population and consequent pressure on agriculture. The dominant view since the 1960s has been that the increasing use of iron led to social changes in Britain. Deposits of iron ore were located in different places to the tin and copper ore necessary to make bronze, and as a result trading patterns shifted and the old elites lost their economic and social status. Power passed into the hands of a new group of people.
Archaeologist Barry Cunliffe
believes that population increase still played a role and has stated "[the forts] provided defensive possibilities for the community at those times when the stress [of an increasing population] burst out into open warfare. But I wouldn't see them as having been built because there was a state of war. They would be functional as defensive strongholds when there were tensions and undoubtedly some of them were attacked and destroyed, but this was not the only, or even the most significant, factor in their construction".
at . It stands on the summit of Cadbury Hill, a limestone
hill situated on the southern edge of the Somerset Levels
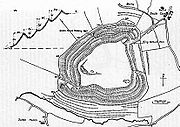
, with flat lowland to the north. The summit is 153 metres (502 ft) above sea-level. The hill is surrounded by four terraced earthwork banks and ditches and a stand of trees.
, Roman
and Saxon
artefacts. Excavations were undertaken by Bennett in 1890 and Gray in 1913 followed by major work led by archaeologist Leslie Alcock
from 1966-1970. He identified a long sequence of occupation on the site and many of the finds are displayed in the Somerset County Museum
in Taunton
.
 The earliest settlement was represented by pits and post holes dated with Neolithic
The earliest settlement was represented by pits and post holes dated with Neolithic
pottery and flints. A bank under the later Iron Age defences is likely to be a lynchet or terrace derived from early ploughing of the hilltop. The site was also occupied in the Late Bronze Age and throughout the Iron Age
. It was the object of a major programme of excavations from 1966–70, directed by Leslie Alcock.
The castle is a multivallate hill fort
built around 400 BC. Large ramparts and elaborate timber defenses were constructed and refortified at least five times over the following centuries. Excavation revealed round and rectangular house foundations, metalworking, and a possible sequence of small rectangular temples or shrines indicating permanent oppidum
-like occupation. There is evidence that the fort was violently taken in around AD43 and that the defences were further slighted later in the 1st century AD after the construction of a Roman army barrack block on the hill top. A report of the prehistoric and Roman activity identified by Alcock's excavations was published in 2000 This modified somewhat the earlier conclusions of Alcock.
Radical revisions of the Bronze Age archaeology on the lower slopes, derived from discoveries during excavations and survey work by the South Cadbury Environs Project, show the area to have been very busy during the second millennium BC. Finds include the first Bronze Age shield from an excavation in north west Europe discovered during work by the South Cadbury Environs Project. The shield is an example of the distinctive Yetholm-type. Although carbon dating implies that the shield was deposited in the 10th century BC, metallurgical evidence suggests that it was manufactured two centuries earlier. A metal-working building and associated enclosure, roughly contemporary with the period of manufacture, was discovered two kilometres south east of the hillfort.
Excavations of the south west gate in 1968 and 1969 revealed evidence for one or more severe violent episodes, associated with weaponry and destruction by fire. Whereas the excavator, Leslie Alcock, believed this to have been dated to around AD70, Tabor argues for a date associated with the initial invasion, AD43-44. Havinden states that it was the site of vigorous resistance by the Durotriges
and Dobunni
to the second Augusta Legion
under the command of Vespasian
.
(castle or palace) of a major Brython
ic ruler and home to his royal family, his teulu (band of faithful followers), servants and horses.
Between 1010 and 1020 the hill was reoccupied for use as a temporary Saxon mint
, briefly standing in for that at Bruton
.
The detailed report on the historical period of the site was published by Alcock in 1995.
.
As for the name "Camelot", one must acknowledge the British toponymy
over centuries, for instance the word "bury" referring to a fortification. Certainly this castle stands close to the River Cam with the villages of West Camel
and Queen Camel
in proximity.
The site and the Great Hall are extensive, and the writer Geoffrey Ashe
argued in an article in the journal Speculum
that it was the base for the Arthur
of history. His opinion has not been widely accepted by all students of the period.
Militarily, the location makes sense as a place where the south-western Brython
s (perhaps from the kingdom of Dumnonia
) could have defended themselves against attacks from lowland Brythons. Refortification may have been a response to the great Saxon raid of c. 473. If Arthur was indeed conceived at Tintagel
, as tradition asserts, as a prince of Dumnonia, Cadbury would have been close to his eastern frontier. The name 'Cadbury' is generally considered to be a Saxo
-Brythonic
hybrid meaning 'Battle-Fort'. Other scholars suggest a derivation from the personal name Cado, borne by a figure associated with the area.
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the archaeological period generally occurring after the Bronze Age, marked by the prevalent use of iron. The early period of the age is characterized by the widespread use of iron or steel. The adoption of such material coincided with other changes in society, including differing...
hill fort
Hill fort
A hill fort is a type of earthworks used as a fortified refuge or defended settlement, located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typically European and of the Bronze and Iron Ages. Some were used in the post-Roman period...
in the civil parish of South Cadbury
South Cadbury
South Cadbury is a village and civil parish in the South Somerset council area of the English county of Somerset. The parish includes the village of Sutton Montis...
in the English
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
county of Somerset
Somerset
The ceremonial and non-metropolitan county of Somerset in South West England borders Bristol and Gloucestershire to the north, Wiltshire to the east, Dorset to the south-east, and Devon to the south-west. It is partly bounded to the north and west by the Bristol Channel and the estuary of the...
. It is a Scheduled Ancient Monument
Scheduled Ancient Monument
In the United Kingdom, a scheduled monument is a 'nationally important' archaeological site or historic building, given protection against unauthorized change. The various pieces of legislation used for legally protecting heritage assets from damage and destruction are grouped under the term...
and associated with King Arthur
King Arthur
King Arthur is a legendary British leader of the late 5th and early 6th centuries, who, according to Medieval histories and romances, led the defence of Britain against Saxon invaders in the early 6th century. The details of Arthur's story are mainly composed of folklore and literary invention, and...
.
Background
Hill forts developed in the Late BronzeBronze Age
The Bronze Age is a period characterized by the use of copper and its alloy bronze as the chief hard materials in the manufacture of some implements and weapons. Chronologically, it stands between the Stone Age and Iron Age...
and Early Iron Age
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the archaeological period generally occurring after the Bronze Age, marked by the prevalent use of iron. The early period of the age is characterized by the widespread use of iron or steel. The adoption of such material coincided with other changes in society, including differing...
, roughly the start of the first millennium BC
1st millennium BC
The 1st millennium BC encompasses the Iron Age and sees the rise of many successive empires, and spanned from 1000 BC to 1 BC.The Neo-Assyrian Empire, followed by the Achaemenids. In Greece, Classical Antiquity begins with the colonization of Magna Graecia and peaks with the rise of Hellenism. The...
.
The reason for their emergence in Britain, and their purpose, has been a subject of debate. It has been argued that they could have been military sites constructed in response to invasion from continental Europe, sites built by invaders, or a military reaction to social tensions caused by an increasing population and consequent pressure on agriculture. The dominant view since the 1960s has been that the increasing use of iron led to social changes in Britain. Deposits of iron ore were located in different places to the tin and copper ore necessary to make bronze, and as a result trading patterns shifted and the old elites lost their economic and social status. Power passed into the hands of a new group of people.
Archaeologist Barry Cunliffe
Barry Cunliffe
Sir Barrington Windsor Cunliffe, CBE, known professionally as Barry Cunliffe is a former Professor of European Archaeology at the University of Oxford, a position held from 1972 to 2007...
believes that population increase still played a role and has stated "[the forts] provided defensive possibilities for the community at those times when the stress [of an increasing population] burst out into open warfare. But I wouldn't see them as having been built because there was a state of war. They would be functional as defensive strongholds when there were tensions and undoubtedly some of them were attacked and destroyed, but this was not the only, or even the most significant, factor in their construction".
Location
Cadbury Castle is located 5 miles (8 km) north east of YeovilYeovil
Yeovil is a town and civil parish in south Somerset, England. The parish had a population of 27,949 at the 2001 census, although the wider urban area had a population of 42,140...
at . It stands on the summit of Cadbury Hill, a limestone
Limestone
Limestone is a sedimentary rock composed largely of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Many limestones are composed from skeletal fragments of marine organisms such as coral or foraminifera....
hill situated on the southern edge of the Somerset Levels
Somerset Levels
The Somerset Levels, or the Somerset Levels and Moors as they are less commonly but more correctly known, is a sparsely populated coastal plain and wetland area of central Somerset, South West England, between the Quantock and Mendip Hills...
, with flat lowland to the north. The summit is 153 metres (502 ft) above sea-level. The hill is surrounded by four terraced earthwork banks and ditches and a stand of trees.
Excavations
Excavation at and around the site has discovered Iron AgeIron Age
The Iron Age is the archaeological period generally occurring after the Bronze Age, marked by the prevalent use of iron. The early period of the age is characterized by the widespread use of iron or steel. The adoption of such material coincided with other changes in society, including differing...
, Roman
Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the part of the island of Great Britain controlled by the Roman Empire from AD 43 until ca. AD 410.The Romans referred to the imperial province as Britannia, which eventually comprised all of the island of Great Britain south of the fluid frontier with Caledonia...
and Saxon
Anglo-Saxons
Anglo-Saxon is a term used by historians to designate the Germanic tribes who invaded and settled the south and east of Great Britain beginning in the early 5th century AD, and the period from their creation of the English nation to the Norman conquest. The Anglo-Saxon Era denotes the period of...
artefacts. Excavations were undertaken by Bennett in 1890 and Gray in 1913 followed by major work led by archaeologist Leslie Alcock
Leslie Alcock
Leslie Alcock was Professor of Archaeology at the University of Glasgow, and one of the leading archaeologists of Early Mediaeval Britain. His major excavations included Dinas Powys hill fort in Wales, Cadbury Castle, South Cadbury in Somerset and a series of major hillforts in Scotland.-Early...
from 1966-1970. He identified a long sequence of occupation on the site and many of the finds are displayed in the Somerset County Museum
Somerset County Museum
The Museum of Somerset is located in the 12th century great hall of Taunton Castle, in Taunton in the county of Somerset, England. The museum is run by Somerset County Council and includes objects initially collected by the Somerset Archaeological and Natural History Society who own the...
in Taunton
Taunton
Taunton is the county town of Somerset, England. The town, including its suburbs, had an estimated population of 61,400 in 2001. It is the largest town in the shire county of Somerset....
.
Prehistoric occupation


Neolithic
The Neolithic Age, Era, or Period, or New Stone Age, was a period in the development of human technology, beginning about 9500 BC in some parts of the Middle East, and later in other parts of the world. It is traditionally considered as the last part of the Stone Age...
pottery and flints. A bank under the later Iron Age defences is likely to be a lynchet or terrace derived from early ploughing of the hilltop. The site was also occupied in the Late Bronze Age and throughout the Iron Age
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the archaeological period generally occurring after the Bronze Age, marked by the prevalent use of iron. The early period of the age is characterized by the widespread use of iron or steel. The adoption of such material coincided with other changes in society, including differing...
. It was the object of a major programme of excavations from 1966–70, directed by Leslie Alcock.
The castle is a multivallate hill fort
Hill fort
A hill fort is a type of earthworks used as a fortified refuge or defended settlement, located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typically European and of the Bronze and Iron Ages. Some were used in the post-Roman period...
built around 400 BC. Large ramparts and elaborate timber defenses were constructed and refortified at least five times over the following centuries. Excavation revealed round and rectangular house foundations, metalworking, and a possible sequence of small rectangular temples or shrines indicating permanent oppidum
Oppidum
Oppidum is a Latin word meaning the main settlement in any administrative area of ancient Rome. The word is derived from the earlier Latin ob-pedum, "enclosed space," possibly from the Proto-Indo-European *pedóm-, "occupied space" or "footprint."Julius Caesar described the larger Celtic Iron Age...
-like occupation. There is evidence that the fort was violently taken in around AD43 and that the defences were further slighted later in the 1st century AD after the construction of a Roman army barrack block on the hill top. A report of the prehistoric and Roman activity identified by Alcock's excavations was published in 2000 This modified somewhat the earlier conclusions of Alcock.
Radical revisions of the Bronze Age archaeology on the lower slopes, derived from discoveries during excavations and survey work by the South Cadbury Environs Project, show the area to have been very busy during the second millennium BC. Finds include the first Bronze Age shield from an excavation in north west Europe discovered during work by the South Cadbury Environs Project. The shield is an example of the distinctive Yetholm-type. Although carbon dating implies that the shield was deposited in the 10th century BC, metallurgical evidence suggests that it was manufactured two centuries earlier. A metal-working building and associated enclosure, roughly contemporary with the period of manufacture, was discovered two kilometres south east of the hillfort.
Excavations of the south west gate in 1968 and 1969 revealed evidence for one or more severe violent episodes, associated with weaponry and destruction by fire. Whereas the excavator, Leslie Alcock, believed this to have been dated to around AD70, Tabor argues for a date associated with the initial invasion, AD43-44. Havinden states that it was the site of vigorous resistance by the Durotriges
Durotriges
The Durotriges were one of the Celtic tribes living in Britain prior to the Roman invasion. The tribe lived in modern Dorset, south Wiltshire and south Somerset...
and Dobunni
Dobunni
The Dobunni were one of the Celtic tribes living in the British Isles prior to the Roman invasion of Britain. There are seven known references to the tribe in Roman histories and inscriptions. The latter part of the name possibly derives from Bune, a cup or vessel...
to the second Augusta Legion
Legio II Augusta
Legio secunda Augusta , was a Roman legion, levied by Gaius Vibius Pansa Caetronianus in 43 BC, and still operative in Britannia in the 4th century...
under the command of Vespasian
Vespasian
Vespasian , was Roman Emperor from 69 AD to 79 AD. Vespasian was the founder of the Flavian dynasty, which ruled the Empire for a quarter century. Vespasian was descended from a family of equestrians, who rose into the senatorial rank under the Emperors of the Julio-Claudian dynasty...
.
Historic occupation
Following the withdrawal of the Roman administration, the site is thought to have been in use from c. 470 until some time after 580. Alcock revealed a substantial 'Great Hall' (20 x 10 metres) and showed that the innermost Iron Age defenses had been refortified, providing a defended site double the size of any other known fort of the period. Shards of pottery from the eastern Mediterranean were also found from this period, indicating wide trade links. It therefore seems probable that it was the chief caerCaer
In the Welsh language, caer means "fortress", "fort" or "citadel"/"castle".Caer is the Welsh name for the city of Chester, situated in northwest England. It also forms, as a prefix, the Welsh equivalent of -caster, -cester and -chester in place names...
(castle or palace) of a major Brython
Brython
The Britons were the Celtic people culturally dominating Great Britain from the Iron Age through the Early Middle Ages. They spoke the Insular Celtic language known as British or Brythonic...
ic ruler and home to his royal family, his teulu (band of faithful followers), servants and horses.
Between 1010 and 1020 the hill was reoccupied for use as a temporary Saxon mint
Mint (coin)
A mint is an industrial facility which manufactures coins for currency.The history of mints correlates closely with the history of coins. One difference is that the history of the mint is usually closely tied to the political situation of an era...
, briefly standing in for that at Bruton
Bruton
Bruton is a town and civil parish in Somerset, England, situated on the River Brue seven miles south-east of Shepton Mallet, just south of Snakelake Hill and Coombe Hill, ten miles north-west of Gillingham and twelve miles south-west of Frome in the South Somerset district. The town has a...
.
The detailed report on the historical period of the site was published by Alcock in 1995.
Interpretation
Local tradition, first written down by John Leland in 1542, holds that Cadbury Castle was King Arthur's CamelotCamelot
Camelot is a castle and court associated with the legendary King Arthur. Absent in the early Arthurian material, Camelot first appeared in 12th-century French romances and eventually came to be described as the fantastic capital of Arthur's realm and a symbol of the Arthurian world...
.
As for the name "Camelot", one must acknowledge the British toponymy
British toponymy
The toponymy of England examines the linguistic origins of place names in England, and trends in naming. Toponymy is distinct from the study of etymology, which is concerned mainly with the origins of the words themselves. English toponymy is rich, complex and diverse...
over centuries, for instance the word "bury" referring to a fortification. Certainly this castle stands close to the River Cam with the villages of West Camel
West Camel
West Camel is a village and civil parish in south Somerset, England, about north of the town of Yeovil. Situated either side of the River Cam it lies just south of the A303 and has a population of 490...
and Queen Camel
Queen Camel
Queen Camel is a village and civil parish, on the River Cam and the A359 road, in the South Somerset district of Somerset, England. It is about north of Yeovil. According to the 2001 census it had a population of 926. The parish includes the hamlet of Wales...
in proximity.
The site and the Great Hall are extensive, and the writer Geoffrey Ashe
Geoffrey Ashe
Geoffrey Ashe is a British cultural historian, a writer of non-fiction books and novels.-Early life:Born in London, Ashe spent several years in Canada growing up, graduating from the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, before continuing at Cambridge.-Work:Many of his historical books are...
argued in an article in the journal Speculum
Speculum (journal)
Speculum: A Journal of Medieval Studies is a quarterly academic journal published by the Medieval Academy of America. It was established in 1926. The journal's primary focus is on the time period from 500-1500 in Western Europe, but also on related subjects such as Byzantine, Hebrew, Arabic, and...
that it was the base for the Arthur
King Arthur
King Arthur is a legendary British leader of the late 5th and early 6th centuries, who, according to Medieval histories and romances, led the defence of Britain against Saxon invaders in the early 6th century. The details of Arthur's story are mainly composed of folklore and literary invention, and...
of history. His opinion has not been widely accepted by all students of the period.
Militarily, the location makes sense as a place where the south-western Brython
Brython
The Britons were the Celtic people culturally dominating Great Britain from the Iron Age through the Early Middle Ages. They spoke the Insular Celtic language known as British or Brythonic...
s (perhaps from the kingdom of Dumnonia
Dumnonia
Dumnonia is the Latinised name for the Brythonic kingdom in sub-Roman Britain between the late 4th and late 8th centuries, located in the farther parts of the south-west peninsula of Great Britain...
) could have defended themselves against attacks from lowland Brythons. Refortification may have been a response to the great Saxon raid of c. 473. If Arthur was indeed conceived at Tintagel
Tintagel
Tintagel is a civil parish and village situated on the Atlantic coast of Cornwall, United Kingdom. The population of the parish is 1,820 people, and the area of the parish is ....
, as tradition asserts, as a prince of Dumnonia, Cadbury would have been close to his eastern frontier. The name 'Cadbury' is generally considered to be a Saxo
Old English language
Old English or Anglo-Saxon is an early form of the English language that was spoken and written by the Anglo-Saxons and their descendants in parts of what are now England and southeastern Scotland between at least the mid-5th century and the mid-12th century...
-Brythonic
Southwestern Brythonic language
The Southwestern Brythonic languages are the Brythonic Celtic tongues spoken in Southwestern Britain and Brittany since the Early Middle Ages. During the period of their earliest attestation, the languages appear to be indistinguishable, but eventually they evolved into the Cornish and Breton...
hybrid meaning 'Battle-Fort'. Other scholars suggest a derivation from the personal name Cado, borne by a figure associated with the area.
See also
- List of hill forts and ancient settlements in Somerset
- History of SomersetHistory of SomersetSomerset is a historic county in the south west of England. There is evidence of human occupation since prehistoric times with hand axes and flint points from the Palaeolithic and Mesolithic eras, and a range of burial mounds, hill forts and other artifacts dating from the Neolithic, Bronze and...
- BurgheadBurgheadBurghead is a small town in Moray, Scotland, about 8 miles north-west of Elgin. The town is mainly built on a Peninsula which projects north-westward into the Moray Firth, meaning that most of the town has sea on 3 sides. The present town was built between 1805 and 1809, destroying in the...

