
CUSUM
Encyclopedia
In statistical quality control
, the CUSUM (or cumulative sum control chart
) is a sequential analysis
technique due to E. S. Page of the University of Cambridge
. It is typically used for monitoring change detection
. CUSUM was announced in Biometrika
a few years after the publication of Wald
's SPRT algorithm.
Page referred to a "quality number"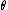 , by which he meant a parameter of the probability distribution
, by which he meant a parameter of the probability distribution
; for example, the mean
. He devised CUSUM as a method to determine changes in it, and proposed a criterion for deciding when to take corrective action.
A few years later, Barnard developed a visualization method, the V-mask chart, to detect both increases and decreases in .
.
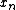 are assigned weights
are assigned weights 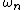 , and summed as follows:
, and summed as follows:

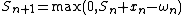
When the value of exceeds a certain threshold value, a change in value has been found. The above formula only detects changes in the positive direction. When negative changes need to be found as well, the
exceeds a certain threshold value, a change in value has been found. The above formula only detects changes in the positive direction. When negative changes need to be found as well, the 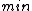 operation should be used instead of the
operation should be used instead of the 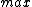 operation, and this time a change has been found when the value of
operation, and this time a change has been found when the value of 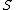 is below the (negative) value of the threshold value.
is below the (negative) value of the threshold value.
Page did not explicitly say that represents the likelihood function
represents the likelihood function
, but this is common usage.
Note that this differs from SPRT by always using zero function as the lower "holding barrier" rather than a lower "holding barrier". Also, CUSUM does not require the use of the likelihood function.
As a means of assessing CUSUM's performance, Page defined the average run length (A.R.L.) metric
; "the expected number of articles sampled before action is taken." He further wrote:
Statistical process control
Statistical process control is the application of statistical methods to the monitoring and control of a process to ensure that it operates at its full potential to produce conforming product. Under SPC, a process behaves predictably to produce as much conforming product as possible with the least...
, the CUSUM (or cumulative sum control chart
Control chart
Control charts, also known as Shewhart charts or process-behaviour charts, in statistical process control are tools used to determine whether or not a manufacturing or business process is in a state of statistical control.- Overview :...
) is a sequential analysis
Sequential analysis
In statistics, sequential analysis or sequential hypothesis testing is statistical analysis where the sample size is not fixed in advance. Instead data are evaluated as they are collected, and further sampling is stopped in accordance with a pre-defined stopping rule as soon as significant results...
technique due to E. S. Page of the University of Cambridge
University of Cambridge
The University of Cambridge is a public research university located in Cambridge, United Kingdom. It is the second-oldest university in both the United Kingdom and the English-speaking world , and the seventh-oldest globally...
. It is typically used for monitoring change detection
Change detection
In statistical analysis, change detection tries to identify changes in the probability distribution of a stochastic process or time series. In general the problem concerns both detecting whether or not a change has occurred, or whether several changes might have occurred, and identifying the times...
. CUSUM was announced in Biometrika
Biometrika
- External links :* . The Internet Archive. 2011....
a few years after the publication of Wald
Abraham Wald
- See also :* Sequential probability ratio test * Wald distribution* Wald–Wolfowitz runs test...
's SPRT algorithm.
Page referred to a "quality number"
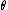 , by which he meant a parameter of the probability distribution
, by which he meant a parameter of the probability distributionProbability distribution
In probability theory, a probability mass, probability density, or probability distribution is a function that describes the probability of a random variable taking certain values....
; for example, the mean
Mean
In statistics, mean has two related meanings:* the arithmetic mean .* the expected value of a random variable, which is also called the population mean....
. He devised CUSUM as a method to determine changes in it, and proposed a criterion for deciding when to take corrective action.
A few years later, Barnard developed a visualization method, the V-mask chart, to detect both increases and decreases in
 .
.Method
As its name implies, CUSUM involves the calculation of a cumulative sum (which is what makes it "sequential"). Samples from a process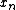 are assigned weights
are assigned weights 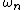 , and summed as follows:
, and summed as follows:
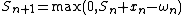
When the value of
 exceeds a certain threshold value, a change in value has been found. The above formula only detects changes in the positive direction. When negative changes need to be found as well, the
exceeds a certain threshold value, a change in value has been found. The above formula only detects changes in the positive direction. When negative changes need to be found as well, the 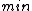 operation should be used instead of the
operation should be used instead of the 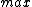 operation, and this time a change has been found when the value of
operation, and this time a change has been found when the value of 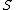 is below the (negative) value of the threshold value.
is below the (negative) value of the threshold value.Page did not explicitly say that
 represents the likelihood function
represents the likelihood functionLikelihood function
In statistics, a likelihood function is a function of the parameters of a statistical model, defined as follows: the likelihood of a set of parameter values given some observed outcomes is equal to the probability of those observed outcomes given those parameter values...
, but this is common usage.
Note that this differs from SPRT by always using zero function as the lower "holding barrier" rather than a lower "holding barrier". Also, CUSUM does not require the use of the likelihood function.
As a means of assessing CUSUM's performance, Page defined the average run length (A.R.L.) metric
Metric (mathematics)
In mathematics, a metric or distance function is a function which defines a distance between elements of a set. A set with a metric is called a metric space. A metric induces a topology on a set but not all topologies can be generated by a metric...
; "the expected number of articles sampled before action is taken." He further wrote:
When the quality of the output is satisfactory the A.R.L. is a measure of the expense incurred by the scheme when it gives false alarms, i.e. Type I errors (Neyman & Pearson, 1936). On the other hand, for constant poor quality the A.R.L. measures the delay and thus the amount of scrap produced before the rectifying action is taken, i.e. Type II errors.

