
Burrard Peninsula
Encyclopedia
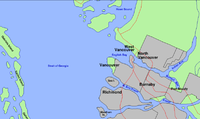



Lower Mainland
The Lower Mainland is a name commonly applied to the region surrounding and including Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. As of 2007, 2,524,113 people live in the region; sixteen of the province's thirty most populous municipalities are located there.While the term Lower Mainland has been...
region of southwestern British Columbia
British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost of Canada's provinces and is known for its natural beauty, as reflected in its Latin motto, Splendor sine occasu . Its name was chosen by Queen Victoria in 1858...
, Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
, lying between Burrard Inlet
Burrard Inlet
Burrard Inlet is a relatively shallow-sided coastal fjord in southwestern British Columbia, Canada. Formed during the last Ice Age, it separates the City of Vancouver and the rest of the low-lying Burrard Peninsula from the slopes of the North Shore Mountains, home to the communities of West...
to the north and the Fraser River
Fraser River
The Fraser River is the longest river within British Columbia, Canada, rising at Fraser Pass near Mount Robson in the Rocky Mountains and flowing for , into the Strait of Georgia at the city of Vancouver. It is the tenth longest river in Canada...
to the south, and bounded by Georgia Strait on the west and the Pitt River
Pitt River
The Pitt River in British Columbia, Canada is a large tributary of the Fraser River, entering it a few miles upstream from New Westminster and about 25 km ESE of Downtown Vancouver. The river, which begins in the Garibaldi Ranges of the Coast Mountains, is in two sections above and below Pitt...
on the east. The City of Vancouver
Vancouver
Vancouver is a coastal seaport city on the mainland of British Columbia, Canada. It is the hub of Greater Vancouver, which, with over 2.3 million residents, is the third most populous metropolitan area in the country,...
occupies most of the western half of the peninsula.
The Squamish name for the Burrard Peninsula as a whole - or rather, for the long rise of land from Point Grey
West Point Grey
West Point Grey is a neighbourhood on the western side of the city of Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. It is bordered by 16th Avenue to the south, Alma Street to the east, English Bay to the north, and Blanca Street to the west...
to Central Park
Central Park (Burnaby)
Central Park is a 90-hectare urban park in Burnaby, British Columbia, founded in 1891. The park is located on the Vancouver-Burnaby border, just west of the Metrotown shopping complex, and is bounded by Boundary Road on the west, Kingsway on the north, Patterson and Willingdon Avenues on the east,...
, was Ulksen or Ulxen. The name Burrard Peninsula is rarely used in casual reference to the area among locals, in favour of "Lower Mainland," or a specific community or city therein.
Extent
There is no clear consensus on where the peninsula ends, as the Burrard Peninsula does not appear in official government gazeteers (directories of geographical features) and does not exist as a legal entity, and so has no legal definition. The peninsula is, however, attached to the mainland at its northeastern end, and as a matter of convenience, the isthmus may be taken to follow the main line of the Canadian Pacific RailwayCanadian Pacific Railway
The Canadian Pacific Railway , formerly also known as CP Rail between 1968 and 1996, is a historic Canadian Class I railway founded in 1881 and now operated by Canadian Pacific Railway Limited, which began operations as legal owner in a corporate restructuring in 2001...
(CPR) across the relatively narrow, low neck of land from Port Moody at the eastern end of Burrard Inlet, through Coquitlam and Port Coquitlam southeast to the Pitt River. From where the CPR tracks cross the Pitt River, the Burrard Peninsula runs due west for approximately 40 kilometres (24.9 mi) to Point Grey, a prominence protruding into Georgia Strait. The peninsula is approximately 6 to 8 kilometres (4 to 5 miles) wide for much of its length.
Municipalities
Municipalities on the peninsula include—in roughly west-to-east order—the Cities of VancouverVancouver
Vancouver is a coastal seaport city on the mainland of British Columbia, Canada. It is the hub of Greater Vancouver, which, with over 2.3 million residents, is the third most populous metropolitan area in the country,...
, Burnaby, New Westminster, Port Moody, Coquitlam, and Port Coquitlam. The University Endowment Lands (home to the main campus of the University of British Columbia
University of British Columbia
The University of British Columbia is a public research university. UBC’s two main campuses are situated in Vancouver and in Kelowna in the Okanagan Valley...
) occupy unincorporated territory at the far west end of the peninsula, at Point Grey. North of the isthmus separating the peninsula from the mainland are the Villages of Belcarra and Anmore which are not on the peninsula proper, but are only accessible by road via the Burrard Peninsula.
Landforms
The Burrard Peninsula consists for the most part of a hilly plateau, reaching a maximum height in most places of between 100 and 150 metres (300 and 500 feet) above sea level. The plateau is bisected by a low trench running northwest to southeast, consisting of (running from west to east):- False CreekFalse CreekFalse Creek is a short inlet in the heart of Vancouver. It separates downtown from the rest of the city. It was named by George Henry Richards during his Hydrographic survey of 1856-63. Science World is located at its eastern end and the Burrard Street Bridge crosses its western end. False Creek is...
, separating the peninsula proper from Downtown Vancouver, which sits on a peninsular offshoot occasionally referred to as "Coal Peninsula"; - the Canadian National RailwayCanadian National RailwayThe Canadian National Railway Company is a Canadian Class I railway headquartered in Montreal, Quebec. CN's slogan is "North America's Railroad"....
(CN) and Burlington Northern Santa Fe (BNSF) railway yards, which sit on reclaimed land at the east end of False Creek; - the Grandview Cut, a trench that accommodates CNR/BNSF and SkyTrainSkyTrain (Vancouver)SkyTrain is a light rapid transit system in Metro Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. SkyTrain has of track and uses fully automated trains on grade-separated tracks, running mostly on elevated guideways, which helps SkyTrain to hold consistently high on-time reliability...
tracks; - Still CreekStill CreekStill Creek is a long stream flowing across Central Burnaby, British Columbia and into Burnaby Lake . Still Creek's path lies mainly through the industrial area which contributes to its high level of pollution, although through dedicated work of local volunteers the creek is slowly recovering.In...
, which drains into Burnaby LakeBurnaby Lake Regional ParkBurnaby Lake is a lake located in Burnaby, British Columbia and is the focal geographic feature and namesake of Burnaby Lake Regional Park. Occupying of land, and is home to a large variety of wildlife. At least 70 species of birds make the lake and surrounding areas their home, and about 214...
; - Burnaby LakeBurnaby Lake Regional ParkBurnaby Lake is a lake located in Burnaby, British Columbia and is the focal geographic feature and namesake of Burnaby Lake Regional Park. Occupying of land, and is home to a large variety of wildlife. At least 70 species of birds make the lake and surrounding areas their home, and about 214...
, which drains into the Brunette RiverBrunette RiverThe Brunette River runs through East Burnaby and Coquitlam, flowing out of Burnaby Lake and to the Fraser River. According to a map and materials by Heritage Advisory Committee and Environment and Waste Management Committee of the City of Burnaby , the number of native campsites discovered on the...
; and - the Brunette RiverBrunette RiverThe Brunette River runs through East Burnaby and Coquitlam, flowing out of Burnaby Lake and to the Fraser River. According to a map and materials by Heritage Advisory Committee and Environment and Waste Management Committee of the City of Burnaby , the number of native campsites discovered on the...
, which is the last tributary of any significant size of the Fraser River, joining the Fraser at New Westminster.
Punctuating the plateau are several prominences of land including Little Mountain (a dormant volcano, approximately 170 metres above sea level) in Vancouver, and Capitol Hill (approximately 220 metres) and Burnaby Mountain
Burnaby Mountain
Burnaby Mountain, elev. , is a low, forested mountain in the city of Burnaby, British Columbia, overlooking the upper arms of Burrard Inlet. It is the location of Simon Fraser University, the Discovery Park research community, and the System Control Tower of BC Hydro and a new complex of...
(home to the main campus of Simon Fraser University
Simon Fraser University
Simon Fraser University is a Canadian public research university in British Columbia with its main campus on Burnaby Mountain in Burnaby, and satellite campuses in Vancouver and Surrey. The main campus in Burnaby, located from downtown Vancouver, was established in 1965 and has more than 34,000...
; approximately 380 metres) in Burnaby. The plateau is flanked at its eastern end by the Coquitlam River
Coquitlam River
The Coquitlam River is located in between the cities of Coquitlam and Port Coquitlam, suburban municipalities located in the Metro Vancouver. This river is a tributary for the Fraser River. Each year hundreds of salmon return to spawn in the Coquitlam River. There is a reservoir near the...
, which flows south from Coquitlam Lake
Coquitlam Lake
Coquitlam Lake is a reservoir located just north of Coquitlam, British Columbia. It is one of the three main water sources for Metro Vancouver, and also a part of BC Hydro's power generation system...
on the mainland into the Fraser River, its mouth lying upstream from the Brunette River. The land east of the Coquitlam River is largely flat and lying close to sea level, except for the stand-alone rise of Mary Hill in Port Coquitlam (approximately 70 metres).
Land use
The Burrard Peninsula has been extensively urbanized, and includes the largest and densest populations in the Metro Vancouver region, and in British Columbia more generally.While originally extensively forested, since the mid-19th century the Burrard Peninsula has gradually become essentially one large cityscape. Its largest remaining green spaces include Pacific Spirit Regional Park
Pacific Spirit Regional Park
Pacific Spirit Regional Park is located in the University Endowment Lands, on Point Grey to the west of the city of Vancouver, British Columbia. It surrounds the endowment lands of the University of British Columbia on the shores of Georgia Strait in the Pacific Ocean...
in Point Grey, Stanley Park
Stanley Park
Stanley Park is a 404.9 hectare urban park bordering downtown Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. It was opened in 1888 by David Oppenheimer in the name of Lord Stanley of Preston, the Governor-General of Canada....
in Downtown Vancouver, the areas around Burnaby Mountain, Central Park
Central Park (Burnaby)
Central Park is a 90-hectare urban park in Burnaby, British Columbia, founded in 1891. The park is located on the Vancouver-Burnaby border, just west of the Metrotown shopping complex, and is bounded by Boundary Road on the west, Kingsway on the north, Patterson and Willingdon Avenues on the east,...
, Burnaby Lake
Burnaby Lake Regional Park
Burnaby Lake is a lake located in Burnaby, British Columbia and is the focal geographic feature and namesake of Burnaby Lake Regional Park. Occupying of land, and is home to a large variety of wildlife. At least 70 species of birds make the lake and surrounding areas their home, and about 214...
, and Deer Lake
Deer Lake (British Columbia)
Deer Lake is a lake in central Burnaby, British Columbia, Canada. Deer Lake is home to a wide variety of flora and fauna and features a number of walking trails...
in Burnaby, and Mundy Park and the Coquitlam River
Coquitlam River
The Coquitlam River is located in between the cities of Coquitlam and Port Coquitlam, suburban municipalities located in the Metro Vancouver. This river is a tributary for the Fraser River. Each year hundreds of salmon return to spawn in the Coquitlam River. There is a reservoir near the...
in Coquitlam.

