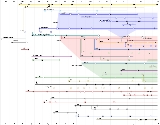
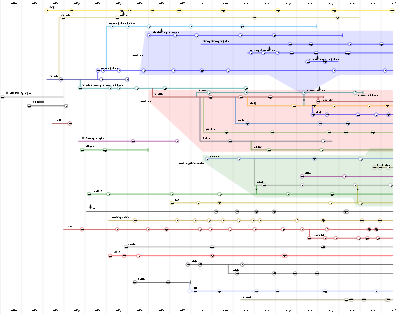
Browser wars
Encyclopedia
Metaphor
A metaphor is a literary figure of speech that uses an image, story or tangible thing to represent a less tangible thing or some intangible quality or idea; e.g., "Her eyes were glistening jewels." Metaphor may also be used for any rhetorical figures of speech that achieve their effects via...
ical term that refers to competitions for dominance in usage share
Usage share of web browsers
The usage share of a web browser is the proportion, often expressed as a percentage, of users of all web browsers who use that particular browser. This figure can only be estimated, typically by determining the proportion of visitors to a group of websites that use a particular web browser...
in the web browser
Web browser
A web browser is a software application for retrieving, presenting, and traversing information resources on the World Wide Web. An information resource is identified by a Uniform Resource Identifier and may be a web page, image, video, or other piece of content...
marketplace. The term is often used to denote two specific rivalries: the competition that saw Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American public multinational corporation headquartered in Redmond, Washington, USA that develops, manufactures, licenses, and supports a wide range of products and services predominantly related to computing through its various product divisions...
's Internet Explorer
Internet Explorer
Windows Internet Explorer is a series of graphical web browsers developed by Microsoft and included as part of the Microsoft Windows line of operating systems, starting in 1995. It was first released as part of the add-on package Plus! for Windows 95 that year...
replace Netscape
Netscape
Netscape Communications is a US computer services company, best known for Netscape Navigator, its web browser. When it was an independent company, its headquarters were in Mountain View, California...
's Navigator
Netscape Navigator
Netscape Navigator was a proprietary web browser that was popular in the 1990s. It was the flagship product of the Netscape Communications Corporation and the dominant web browser in terms of usage share, although by 2002 its usage had almost disappeared...
as the dominant browser during the late 1990s and the erosion of Internet Explorer's market share since 2003 by a collection of emerging browsers including Mozilla Firefox
Mozilla Firefox
Mozilla Firefox is a free and open source web browser descended from the Mozilla Application Suite and managed by Mozilla Corporation. , Firefox is the second most widely used browser, with approximately 25% of worldwide usage share of web browsers...
, Google Chrome
Google Chrome
Google Chrome is a web browser developed by Google that uses the WebKit layout engine. It was first released as a beta version for Microsoft Windows on September 2, 2008, and the public stable release was on December 11, 2008. The name is derived from the graphical user interface frame, or...
, Safari
Safari (web browser)
Safari is a web browser developed by Apple Inc. and included with the Mac OS X and iOS operating systems. First released as a public beta on January 7, 2003 on the company's Mac OS X operating system, it became Apple's default browser beginning with Mac OS X v10.3 "Panther". Safari is also the...
, and Opera
Opera (web browser)
Opera is a web browser and Internet suite developed by Opera Software with over 200 million users worldwide. The browser handles common Internet-related tasks such as displaying web sites, sending and receiving e-mail messages, managing contacts, chatting on IRC, downloading files via BitTorrent,...
.
Background
The World Wide WebWorld Wide Web
The World Wide Web is a system of interlinked hypertext documents accessed via the Internet...
is an Internet
Internet
The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
-based hypertext
Hypertext
Hypertext is text displayed on a computer or other electronic device with references to other text that the reader can immediately access, usually by a mouse click or keypress sequence. Apart from running text, hypertext may contain tables, images and other presentational devices. Hypertext is the...
system invented in the late 1980s and early 1990s by Tim Berners-Lee
Tim Berners-Lee
Sir Timothy John "Tim" Berners-Lee, , also known as "TimBL", is a British computer scientist, MIT professor and the inventor of the World Wide Web...
. Berners-Lee wrote the first web browser WorldWideWeb
WorldWideWeb
WorldWideWeb, later renamed to Nexus to avoid confusion between the software and the World Wide Web, was the first web browser and editor. When it was written, WorldWideWeb was the only way to view the Web....
, later renamed Nexus, and released it for the NeXTstep
NEXTSTEP
NeXTSTEP was the object-oriented, multitasking operating system developed by NeXT Computer to run on its range of proprietary workstation computers, such as the NeXTcube...
platform in 1991.
By the end of 1992 other browsers had appeared, many of them based on the libwww
Libwww
libwww is a highly-modular client-side web API for Unix and Windows, and is also the name of the reference implementation of this API....
library. These included Unix
Unix
Unix is a multitasking, multi-user computer operating system originally developed in 1969 by a group of AT&T employees at Bell Labs, including Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, Brian Kernighan, Douglas McIlroy, and Joe Ossanna...
browsers such as Line Mode Browser, ViolaWWW
ViolaWWW
ViolaWWW, first developed in the early 1990s, for Unix and the X Windowing System, was the first popular web browser which, until Mosaic, was the most frequently used web browser for access to the World Wide Web...
, Erwise
Erwise
Erwise was a pioneering web browser, and the first commonly available with a graphical user interface.Released in April 1992, the browser was written for Unix computers running X and used the W3 common access library...
and MidasWWW, and MacWWW
MacWWW
MacWWW, also known as Samba, is an early minimalist web browser from 1992 meant to run on Macintosh computers. It was the first web browser for the Mac OS platform, and the first for any non-Unix operating system. MacWWW tries to emulate the design of WorldWideWeb. Unlike modern browsers it opens...
/Samba for the Mac. This created choice between browsers and hence the first real competition, especially on Unix.
Mosaic wars
Further browsers were released in 1993, including CelloCello (web browser)
Cello was an early shareware 16-bit multipurpose web browser for Windows 3.1 developed by Thomas R. Bruce of the Legal Information Institute at Cornell Law School. It was the first web browser for Microsoft Windows, and thus was among the first free winsock browsers...
, Arena
Arena (web browser)
The Arena browser was an early testbed web browser and web authoring tool for Unix. Originally authored by Dave Raggett in 1993, the browser continued its development at CERN and the World Wide Web Consortium and subsequently by Yggdrasil Computing...
, Lynx
Lynx (web browser)
Lynx is a text-based web browser for use on cursor-addressable character cell terminals and is very configurable.-Usage:Browsing in Lynx consists of highlighting the chosen link using cursor keys, or having all links on a page numbered and entering the chosen link's number. Current versions support...
, tkWWW
TkWWW
tkWWW was an early web browser/WYSIWYG HTML editor written by Joseph Wang at the MIT as part of the Project Athena and the Globewide Network Academy project. The browser was based on the Tcl language and the tk toolkit extension but did not achieve broad user acceptance or market share although it...
and Mosaic
Mosaic (web browser)
Mosaic is the web browser credited with popularizing the World Wide Web. It was also a client for earlier protocols such as FTP, NNTP, and gopher. Its clean, easily understood user interface, reliability, Windows port and simple installation all contributed to making it the application that opened...
. The most influential of these was Mosaic, a multiplatform browser developed at National Center for Supercomputing Applications
National Center for Supercomputing Applications
The National Center for Supercomputing Applications is an American state-federal partnership to develop and deploy national-scale cyberinfrastructure that advances science and engineering. NCSA operates as a unit of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign but it provides high-performance...
(NCSA). By October 1994, Mosaic was "well on its way to becoming the world's standard interface", according to Gary Wolfe of Wired.
Several companies licensed Mosaic to create their own commercial browsers, such as AirMosaic
AirMosaic
AirMosaic was an early commercial web browser based on the NCSA Mosaic browser.The browser won Datamation's Best Product of the Year award for 1994....
and Spyglass Mosaic. One of the Mosaic developers, Marc Andreessen
Marc Andreessen
Marc Andreessen is an American entrepreneur, investor, software engineer, and multi-millionaire best known as co-author of Mosaic, the first widely-used web browser, and co-founder of Netscape Communications Corporation. He founded and later sold the software company Opsware to Hewlett-Packard...
, founded Mosaic Communications Corporation and created a new web browser named Mosaic Netscape. To resolve legal issues with NCSA, the company was renamed Netscape Communications Corporation and the browser Netscape Navigator. The Netscape browser improved on Mosaic's usability and reliability and was able to display pages as they loaded. By 1995, helped by the fact that it was free for non-commercial use, the browser dominated the emerging World Wide Web.
Other browsers launched during 1994 included IBM Web Explorer
IBM Web Explorer
IBM WebExplorer was an early web browser designed at IBM facilities in the Research Triangle Park for OS/2.-History:Presented in 1994 with OS/2 Warp , it was hailed as the best browser by Internet Magazine in their November issue and leveraged its position as the only native browser in OS/2 at that...
, Navipress, SlipKnot
SlipKnot (web browser)
SlipKnot was one of the earliest World Wide Web browsers, available to Microsoft Windows users between November 1994 and January 1998. It was created by Peter Brooks of MicroMind, Inc. to provide a fully graphical view of the web for users without a SLIP or other TCP/IP connection to the net,...
, MacWeb
MacWeb
MacWeb was an early Mac OS-only web browser for 68k and PowerPC Apple Macintosh computers, developed by TradeWave between 1994 and 1996....
, and Browse.
In 1995, Netscape faced new competition from OmniWeb
OmniWeb
OmniWeb is a proprietary Internet web browser developed and marketed by The Omni Group. It is available exclusively for Apple Inc.'s Mac OS X operating system...
, WebRouser, UdiWWW
UdiWWW
The UdiWWW HTML3 browser was an early freeware graphical HTML 3 web browser for 16-bit and 32-bit Microsoft Windows. It was written and developed by Bernd Richter in C/C++ from 1995 to 1996...
, and Microsoft's Internet Explorer 1.0, but continued to dominate the market.
The first browser war
By mid-1995 the World Wide Web had received a great deal of attention in popular culturePopular culture
Popular culture is the totality of ideas, perspectives, attitudes, memes, images and other phenomena that are deemed preferred per an informal consensus within the mainstream of a given culture, especially Western culture of the early to mid 20th century and the emerging global mainstream of the...
and the mass media
Mass media
Mass media refers collectively to all media technologies which are intended to reach a large audience via mass communication. Broadcast media transmit their information electronically and comprise of television, film and radio, movies, CDs, DVDs and some other gadgets like cameras or video consoles...
. Netscape Navigator was the most widely used web browser and Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American public multinational corporation headquartered in Redmond, Washington, USA that develops, manufactures, licenses, and supports a wide range of products and services predominantly related to computing through its various product divisions...
had licensed Mosaic to create Internet Explorer 1.0, which it had released as part of the Microsoft Windows 95
Windows 95
Windows 95 is a consumer-oriented graphical user interface-based operating system. It was released on August 24, 1995 by Microsoft, and was a significant progression from the company's previous Windows products...
Plus!
Microsoft Plus!
Microsoft Plus! was a commercial operating system enhancement product by Microsoft. The last edition is the Plus! SuperPack, which includes an assortment of screensavers, themes, and games, as well as multimedia applications...
Pack in August.
Internet Explorer 2.0 was released as a free download three months later. Unlike Netscape Navigator it was available to all Windows users for free, even commercial companies. Other companies later followed and gave their browsers away for free. Both Netscape Navigator and competitor products like InternetWorks, Quarterdeck Browser, InterAp, and WinTapestry were bundled with other applications to full internet suite
Internet suite
An Internet suite is an Internet-related software suite. Internet suites usually include a web browser, e-mail client , download manager, HTML editor, and an IRC client....
s. New versions of Internet Explorer and Netscape (branded as Netscape Communicator
Netscape Communicator
Netscape Communicator was an Internet suite produced by Netscape Communications Corporation. Initially released in June 1997, Netscape Communicator 4.0 was the successor to Netscape Navigator 3.x and included more groupware features intended to appeal to enterprises.- Editions :Netscape...
) were released at a rapid pace over the following few years.
Development was rapid and new features were routinely added, including Netscape's JavaScript
JavaScript
JavaScript is a prototype-based scripting language that is dynamic, weakly typed and has first-class functions. It is a multi-paradigm language, supporting object-oriented, imperative, and functional programming styles....
(subsequently replicated by Microsoft as JScript
JScript
JScript is a scripting language based on the ECMAScript standard that is used in Microsoft's Internet Explorer.JScript is implemented as a Windows Script engine. This means that it can be "plugged in" to any application that supports Windows Script, such as Internet Explorer, Active Server Pages,...
) and proprietary HTML tags such as
<blink> and <marqueeMarquee tagThe marquee tag is a non-standard HTML element which causes text to scroll up, down, left or right automatically. The tag was first introduced in early versions of Microsoft's Internet Explorer, and was compared to Netscape's blink element, as a proprietary non-standard extension to the HTML...
>.Internet Explorer began to approach feature parity with Netscape with version 3.0 (1996), which offered scripting support and the market's first commercial Cascading Style Sheets
Cascading Style Sheets
Cascading Style Sheets is a style sheet language used to describe the presentation semantics of a document written in a markup language...
(CSS) implementation.
In October 1997, Internet Explorer 4.0 was released. The release party in San Francisco featured a ten-foot-tall letter "e" logo. Netscape employees showing up to work the following morning found the giant logo on their front lawn, with a sign attached that read "From the IE team ... We Love You". The Netscape employees promptly knocked it over and set a giant figure of their Mozilla
Mozilla
Mozilla is a term used in a number of ways in relation to the Mozilla.org project and the Mozilla Foundation, their defunct commercial predecessor Netscape Communications Corporation, and their related application software....
dinosaur mascot atop it, holding a sign reading "Netscape 72, Microsoft 18" representing the market distribution.
Internet Explorer 4 changed the tides of the browser wars. It was integrated into Microsoft Windows, which IT professionals and industry critics considered technologically disadvantageous and an apparent exploitation of Microsoft's monopoly on the PC platform. Users were discouraged from using competing products because IE was "already there" on their PCs.
During these releases it was common for web designers to display 'best viewed in Netscape' or 'best viewed in Internet Explorer' logos. These images often identified a specific browser version and were commonly linked to a source from which the stated browser could be downloaded. These logos generally recognized the divergence between the standards supported by the browsers and signified which browser was used for testing the pages. In response, supporters of the principle that web sites should be compliant with World Wide Web Consortium
World Wide Web Consortium
The World Wide Web Consortium is the main international standards organization for the World Wide Web .Founded and headed by Tim Berners-Lee, the consortium is made up of member organizations which maintain full-time staff for the purpose of working together in the development of standards for the...
standards and hence viewable with any browser started the "Viewable With Any Browser" campaign, which employed its own logo similar to the partisan ones.
Internet Explorer 5 & 6
Microsoft had three strong advantages in the browser wars.One was resources: Netscape began with about 80% market share and a good deal of public goodwill, but as a relatively small company deriving the great bulk of its income from what was essentially a single product (Navigator and its derivatives), it was financially vulnerable. Netscape's total revenue never exceeded the interest income generated by Microsoft's cash on hand. Microsoft's vast resources allowed IE to remain free as the enormous revenues from Windows were used to fund its development and marketing. Netscape was commercial software for businesses but provided for free for home and education users; Internet Explorer was provided as free for Windows users, cutting off a significant revenue stream: As it was told by Jim Barksdale, President and CEO of Netscape Communications: "Very few times in warfare have smaller forces overtaken bigger forces..."
Another advantage was that Microsoft Windows had over 90% share of the desktop operating system market. IE was bundled with every copy of Windows; therefore Microsoft was able to dominate the market share easily as customers had IE as a default. In this time period, many new computer purchases were first computer purchases for home users or offices, and many of the users had never extensively used a web browser before, so had nothing to compare with and little motivation to consider alternatives; the great set of features they had gained in gaining access to the Internet and the World Wide Web at all made any modest differences in browser features or ergonomics pale in comparison.
During the United States Microsoft antitrust case in 1998, Intel vice president Steven McGeady
Steven McGeady
Steven McGeady is a former Intel executive best known as a witness in the Microsoft antitrust trial. His notes contained colorful quotes by Microsoft executives threatening to "cut off Netscape's air supply" and Bill Gates' guess that "this anti-trust thing will blow over"...
, a witness called by the government, said on the stand that a senior executive at Microsoft told him in 1995 of his company's intention to "cut off Netscape's air supply". Microsoft attorney said that McGeady's testimony is not credible. That same year, Netscape, the company, was acquired by America Online
AOL
AOL Inc. is an American global Internet services and media company. AOL is headquartered at 770 Broadway in New York. Founded in 1983 as Control Video Corporation, it has franchised its services to companies in several nations around the world or set up international versions of its services...
for USD $4.2 billion. Internet Explorer became the new dominant browser, attaining a peak of about 96% of the web browser usage share
Usage share of web browsers
The usage share of a web browser is the proportion, often expressed as a percentage, of users of all web browsers who use that particular browser. This figure can only be estimated, typically by determining the proportion of visitors to a group of websites that use a particular web browser...
during 2002, more than Netscape had at its peak.
The first browser war ended with Internet Explorer having no remaining serious competition for its market share. This also brought an end to the rapid innovation in web browsers; until 2006 there was only one new version of Internet Explorer since version 6.0
Internet Explorer 6
Internet Explorer 6 is the sixth major revision of Internet Explorer, a web browser developed by Microsoft for Windows operating systems...
had been released in 2001. Internet Explorer 6.0 Service Pack 1 was developed as part of Windows XP SP1, and integrated into Windows Server 2003
Windows Server 2003
Windows Server 2003 is a server operating system produced by Microsoft, introduced on 24 April 2003. An updated version, Windows Server 2003 R2, was released to manufacturing on 6 December 2005...
. Further enhancements were made to Internet Explorer in Windows XP SP2 (released in 2004), including a pop-up blocker and stronger default security settings against the installation of ActiveX controls.
Consequences
The browser wars encouraged three specific kinds of behavior among their combatants.- Adding new features instead of fixing bugs: A web browser had to have more new features than its competitor, or else it would be considered to be "falling behind." But with limited manpower to put towards development, this often meant that quality assurance suffered and that the software was released with serious bugs.
- Adding proprietary features instead of obeying standards: A web browser is expected to follow the standards set down by standards committees (for example, by adhering to the HTML specifications) in order to assure interoperability of the Web for all users. But competition and innovation led to web browsers "extending" the standards with proprietary features (such as the HTML tags <font>, <marqueeMarquee tagThe marquee tag is a non-standard HTML element which causes text to scroll up, down, left or right automatically. The tag was first introduced in early versions of Microsoft's Internet Explorer, and was compared to Netscape's blink element, as a proprietary non-standard extension to the HTML...
>, and <blinkBlink tagThe blink element is a non-standard presentational HTML element that indicates to a user agent that the page author intends the content of the element to blink...
>) without waiting for committee approval. Sometimes these extensions produced useful features that were adopted by other browsers, such as the XMLHttpRequestXMLHttpRequestXMLHttpRequest is an API available in web browser scripting languages such as JavaScript. It is used to send HTTP or HTTPS requests directly to a web server and load the server response data directly back into the script. The data might be received from the server as XML text or as plain text...
technology that resulted in AjaxAjax (programming)Ajax is a group of interrelated web development methods used on the client-side to create asynchronous web applications...
. - Inadvertently creating security loopholes: In the race to add development features, the line between document and application is crossed, and the Active Content Exploit is born. This is because, whenever applications have been allowed to masquerade as documents (e.g. Master Mode, Office macros, etc.) anyone can slip malicious code into what is otherwise a trustworthy format. As a virus scanner can only detect a virus that is old enough to be catalogued (usually more than 48 hours), it cannot protect against a zero day attack. Thus this blurring of the boundary between application and document creates an easy access point that is the basis for delivery of nearly all of today's drive-by downloadDrive-by downloadDrive-by download means three things, each concerning the unintended download of computer software from the Internet:# Downloads which a person authorized but without understanding the consequences Drive-by download means three things, each concerning the unintended download of computer software...
s and auto-loading malicious code.
Support for web standards was severely weakened. For years, innovation in web development stagnated as developers had to use obsolete and unnecessarily complex techniques to ensure their pages would render properly in Netscape Navigator and Internet Explorer. Netscape Navigator 4 and IE6 lacked full compliance with several standards, including CSS
Cascading Style Sheets
Cascading Style Sheets is a style sheet language used to describe the presentation semantics of a document written in a markup language...
and the PNG image format.
On February 2, 2008 the last update to Netscape Navigator 9
Netscape Navigator 9
Netscape Navigator 9 is a web browser produced by the Netscape Communications division of parent AOL, first announced on January 23, 2007. After AOL outsourced the development of Netscape Browser 8 to Mercurial Communications in 2004, Netscape Navigator 9 marked the first Netscape browser to be...
was released, based on Mozilla Firefox 2
Mozilla Firefox 2
Mozilla Firefox 2 was a version of Firefox, a web browser released on October 24, 2006 by the Mozilla Corporation.Firefox 2 uses version 1.8 of the Gecko layout engine for displaying web pages...
. However, it never regained its market share. Netscape was discontinued on March 1, 2008.
The second browser war
Internet Explorer
Windows Internet Explorer is a series of graphical web browsers developed by Microsoft and included as part of the Microsoft Windows line of operating systems, starting in 1995. It was first released as part of the add-on package Plus! for Windows 95 that year...
, Netscape open-sourced their browser code, and entrusted it to the newly formed non-profit Mozilla Foundation—a primarily community-driven project to create a successor to Netscape. Development continued for several years with little widespread adoption until a stripped-down browser-only version of the full suite was created, which included features, such as tabbed browsing and a separate search bar, that had previously only appeared in Opera
Opera (web browser)
Opera is a web browser and Internet suite developed by Opera Software with over 200 million users worldwide. The browser handles common Internet-related tasks such as displaying web sites, sending and receiving e-mail messages, managing contacts, chatting on IRC, downloading files via BitTorrent,...
. The browser-only version was initially named Phoenix, but because of trademark issues that name was changed, first to Firebird, then to Firefox. This browser became the focus of the Mozilla Foundation's development efforts and Mozilla Firefox 1.0 was released on November 9, 2004. Since then it has continued to gain an increasing share of the browser market, until a peak in 2010, after which it has remained largely stable.
In 2003, Microsoft announced that Internet Explorer 6 Service Pack 1 would be the last standalone version of its browser. Future enhancements would be dependent on Windows Vista
Windows Vista
Windows Vista is an operating system released in several variations developed by Microsoft for use on personal computers, including home and business desktops, laptops, tablet PCs, and media center PCs...
, which would include new tools such as the WPF
Windows Presentation Foundation
Developed by Microsoft, the Windows Presentation Foundation is a computer-software graphical subsystem for rendering user interfaces in Windows-based applications. WPF, previously known as "Avalon", was initially released as part of .NET Framework 3.0. Rather than relying on the older GDI...
and XAML to enable developers to build extensive Web applications.
In response, in April 2004, the Mozilla Foundation
Mozilla Foundation
The Mozilla Foundation is a non-profit organization that exists to support and provide leadership for the open source Mozilla project. The organization sets the policies that govern development, operates key infrastructure and controls trademarks and other intellectual property...
and Opera Software
Opera Software
Opera Software ASA is a Norwegian software company, primarily known for its Opera family of web browsers with over 220 million users worldwide. Opera Software is also involved in promoting Web standards through participation in the W3C. The company has its headquarters in Oslo, Norway and is...
joined efforts to develop new open technology standards which add more capability while remaining backward-compatible with existing technologies. The result of this collaboration was the WHATWG
Web Hypertext Application Technology Working Group
The Web Hypertext Application Technology Working Group is a community of people interested in evolving HTML and related technologies. The WHATWG was founded by individuals from Apple, the Mozilla Foundation and Opera Software in 2004. Since then, the editor of the WHATWG specifications, Ian...
, a working group devoted to the fast creation of new standard definitions that would be submitted to the W3C
World Wide Web Consortium
The World Wide Web Consortium is the main international standards organization for the World Wide Web .Founded and headed by Tim Berners-Lee, the consortium is made up of member organizations which maintain full-time staff for the purpose of working together in the development of standards for the...
for approval.
2006–2007
On February 15, 2005, Microsoft announced that Internet Explorer 7Internet Explorer 7
Windows Internet Explorer 7 is a web browser released by Microsoft in October 2006. Internet Explorer 7 is part of a long line of versions of Internet Explorer and was the first major update to the browser in more than 5 years...
would be available for Windows XP SP2 and later versions of Windows by mid-2005. The announcement introduced the new version of the browser as a major upgrade over Internet Explorer 6 SP1.
Opera had been a long-time small player in the browser wars, known for introducing innovative features such as tabbed browsing and mouse gestures, as well as being lightweight but feature-rich. The software, however, was commercial, which hampered its adoption compared to its free rivals until 2005, when the browser became freeware
Freeware
Freeware is computer software that is available for use at no cost or for an optional fee, but usually with one or more restricted usage rights. Freeware is in contrast to commercial software, which is typically sold for profit, but might be distributed for a business or commercial purpose in the...
. On June 20, 2006, Opera Software released Opera 9 including an integrated source viewer, a BitTorrent client implementation and widgets. It was the first Windows browser to pass the Acid2
Acid2
Acid2 is a test page published and promoted by the Web Standards Project to expose web page rendering flaws in web browsers and other applications that render HTML. Named after the acid test for gold, it was developed in the spirit of Acid1, a relatively narrow test of compliance with the Cascading...
test. Opera Mini
Opera Mini
Opera Mini is a web browser designed primarily for mobile phones, smartphones and personal digital assistants. Until version 4 it used the Java ME platform, requiring the mobile device to run Java ME applications. From version 5 it is also available as a native application for Android, iOS, Symbian...
, a mobile browser, has significant mobile market share as well as being available on the Nintendo DS
Nintendo DS
The is a portable game console produced by Nintendo, first released on November 21, 2004. A distinctive feature of the system is the presence of two separate LCD screens, the lower of which is a touchscreen, encompassed within a clamshell design, similar to the Game Boy Advance SP...
and Wii
Wii
The Wii is a home video game console released by Nintendo on November 19, 2006. As a seventh-generation console, the Wii primarily competes with Microsoft's Xbox 360 and Sony's PlayStation 3. Nintendo states that its console targets a broader demographic than that of the two others...
.
On October 18, 2006, Microsoft released Internet Explorer 7. It included tabbed browsing, a search bar, a phishing
Phishing
Phishing is a way of attempting to acquire information such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details by masquerading as a trustworthy entity in an electronic communication. Communications purporting to be from popular social web sites, auction sites, online payment processors or IT...
filter, and improved support for Web standards — all features already familiar to Opera and Firefox users. Microsoft distributed Internet Explorer 7 to genuine Windows users
Windows Genuine Advantage
Windows Genuine Advantage is an anti-piracy system created by Microsoft that enforces online validation of the licensing of several recent Microsoft Windows operating systems when accessing several services, such as Windows Update, and downloading Windows components from the Microsoft Download...
(WGA) as a high priority update through Windows Update
Windows Update
Windows Update is a service provided by Microsoft that provides updates for the Microsoft Windows operating system and its installed components, including Internet Explorer...
. Typical market share analysis showed only a slow uptake of Internet Explorer 7 and Microsoft decided to drop the requirement for WGA and made Internet Explorer 7 available to all Windows users in October 2007.
On October 24, 2006, Mozilla released Mozilla Firefox 2.0. It included the ability to reopen recently closed tabs, a session restore feature to resume work where it had been left after a crash, a phishing filter and a spell-checker for text fields.
In 2002 Apple created a fork of the open-source KHTML
KHTML
KHTML is the HTML layout engine developed by the KDE project. It is the engine used by the Konqueror web browser. A forked version of KHTML called WebKit is used by several web browsers, among them Safari and Google Chrome...
and KJS
KJS (KDE)
KJS is KDE's ECMAScript/JavaScript engine that was originally developed for the KDE project's Konqueror web browser by Harri Porten in 2000.On June 13, 2002, Maciej Stachowiak announced on a mailing list that Apple was releasing JavaScriptCore, a framework for Mac OS X that was based on KJS...
layout and javascript engines from the KDE
KDE
KDE is an international free software community producing an integrated set of cross-platform applications designed to run on Linux, FreeBSD, Microsoft Windows, Solaris and Mac OS X systems...
project Konqueror
Konqueror
Not to be confused with the Conqueror web browser.Konqueror is a web browser and file manager that provides file-viewer functionality for file systems such as local files, files on a remote ftp server and files in a disk image. It is a core part of the KDE desktop environment...
browser, explaining that those would provide easier development than other technologies by virtue of being small (fewer than 140,000 lines of code), cleanly designed and standards compliant, now known as WebKit
WebKit
WebKit is a layout engine designed to allow web browsers to render web pages. WebKit powers Google Chrome and Apple Safari and by October 2011 held over 33% of the browser market share between them. It is also used as the basis for the experimental browser included with the Amazon Kindle ebook...
project. A Safari browser was first shipped with Mac OS X v10.3
Mac OS X v10.3
Mac OS X Panther is the fourth major release of Mac OS X, Apple’s desktop and server operating system. It followed Mac OS X v10.2 "Jaguar" and preceded Mac OS X Tiger...
. In June 13, 2003 Microsoft said it was discontinuing their browser on the Mac platform. On June 6, 2007, Apple released their initial beta version of Safari for Microsoft Windows.
On December 19, 2007, Microsoft announced that an internal build of Internet Explorer 8 has passed the Acid2
Acid2
Acid2 is a test page published and promoted by the Web Standards Project to expose web page rendering flaws in web browsers and other applications that render HTML. Named after the acid test for gold, it was developed in the spirit of Acid1, a relatively narrow test of compliance with the Cascading...
CSS test in "IE8 standards mode" – the last of the major browsers to do so.
On December 28, 2007, Netscape announced that support for its Mozilla-derived Netscape Navigator would be discontinued on February 1, 2008, suggesting its users migrate to Mozilla Firefox.
However, on January 28, 2008, Netscape announced that support would be extended to March 1, 2008, and mentioned Flock
Flock (web browser)
Flock was a web browser that specialized in providing social networking and Web 2.0 facilities built into its user interface.Earlier versions of Flock used the Gecko HTML rendering engine by Mozilla....
, alongside Firefox, as an alternative to its users.
2008–2010
Mozilla released Firefox 3.0Mozilla Firefox 3
Mozilla Firefox 3.0 is a version of the Firefox web browser released on June 17, 2008 by the Mozilla Corporation.Firefox 3.0 uses version 1.9 of the Gecko layout engine for displaying web pages. This version fixes many bugs, improves standard compliance, and implements many new web APIs compared to...
on June 17, 2008, with performance improvements, and other new features. Firefox 3.5
Mozilla Firefox 3.5
Mozilla Firefox 3.5 is a version of the Firefox web browser released in June 2009, adding a variety of new features to Firefox. Version 3.5 was touted as being twice as fast as 3.0...
followed on June 30, 2009 with further performance improvements, native integration of audio and video, and more privacy features.
Google
Google Inc. is an American multinational public corporation invested in Internet search, cloud computing, and advertising technologies. Google hosts and develops a number of Internet-based services and products, and generates profit primarily from advertising through its AdWords program...
released the Chrome
Google Chrome
Google Chrome is a web browser developed by Google that uses the WebKit layout engine. It was first released as a beta version for Microsoft Windows on September 2, 2008, and the public stable release was on December 11, 2008. The name is derived from the graphical user interface frame, or...
browser for Microsoft Windows on December 11, 2008, using the same WebKit rendering engine as Safari and a faster JavaScript engine called V8. An open sourced version for the Windows, Mac OS X and Linux platforms was released under the name Chromium
Chromium (web browser)
Chromium is the open source web browser project from which Google Chrome draws its source code. The project's hourly Chromium snapshots appear essentially similar to the latest builds of Google Chrome aside from the omission of certain Google additions, most noticeable among them: Google's...
. According to Net Applications, Chrome had gained a 3.6% usage share by October 2009. After the release of the beta for Mac OS X and Linux, the market share had increased rapidly.
On March 19, 2009, Microsoft released Internet Explorer 8
Internet Explorer 8
Windows Internet Explorer 8 is a web browser developed by Microsoft in the Internet Explorer browser series. The browser was released on March 19, 2009 for Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, and Windows 7. Both 32-bit and 64-bit builds are available...
, which added accelerators
Selection-based search
A selection-based search system is a search engine system in which the user invokes a search query using only the mouse. A selection-based search system allows the user to search the internet for more information about any keyword or phrase contained within a document or webpage in any software...
, improved privacy protection, a compatibility mode for pages designed for Internet Explorer 7 and improved support for various web standards.
During December 2009 and January 2010, StatCounter
StatCounter
StatCounter is a web traffic analysis tool. Access to basic services is free and advanced services can cost between $9 and $119 a month. The company is based in Dublin. The statistics from StatCounter are used to compute web usage share for example....
reported that its statistics indicated that Firefox 3.5 was the most popular browser, when counting individual browser versions, passing Internet Explorer 7 and 8 by a small margin. This is the first time a global statistic has reported that a non-Internet Explorer browser version has exceeded the top Internet Explorer version in usage share since the fall of Netscape Navigator. This feat, which GeekSmack called the "dethron[ing of] Microsoft and its Internet Explorer 7 browser," can largely be attributed to the fact that it came at a time when IE 8 was replacing IE 7 as the dominant Internet Explorer version. No more than two months later IE 8 had established itself as the most popular browser version, a position which it still holds as of March 2011. It should also be noted that other major statistics, such as Net Applications
Net Applications
Net Applications is a web analytics firm. The company is commonly known in the web browser development and technology news communities for its global market share statistics.-Net Applications History:...
, never report any non-IE browser version as having a higher usage share than the most popular Internet Explorer version, although Firefox 3.5 was reported as the third most popular browser version between December 2009 and February 2010, to be replaced by Firefox 3.6 since April 2010, each ahead of IE7 and behind IE6 and IE8.
On January 21, 2010, Mozilla released Mozilla Firefox 3.6
Mozilla Firefox 3.6
Mozilla Firefox 3.6 is a version of the Firefox web browser released in January 2010. The release's main improvement over Firefox 3.5 is improved performance . It uses the Gecko 1.9.2 engine , which improves compliance with web standards...
, which allows support for a new type of theme display, 'Personas', which allows users to change Firefox's appearance with a single click. Version 3.6 also improves JavaScript performance, overall browser responsiveness and startup times.
In October 2010, StatCounter reported that Internet Explorer had for the first time dropped below 50% market share to 49.87% in their figures. Also, StatCounter reported Internet Explorer 8's first drop in usage share in the same month.
Race to HTML5
On February 3, 2011, Google released Chrome 9. New features introduced include: support for WebGLWebGL
WebGL is a software library that extends the capability of the JavaScript programming language to allow it to generate interactive 3D graphics within any compatible web browser...
, Chrome Instant, and the Chrome Web Store.
StatCounter global market share figures were as follows for February 2011. Internet Explorer 45%, Firefox 30%, Chrome 17%, Safari 5%, and Opera 2%, leaving all the others sharing the remaining 1%.
On March 8, 2011, Google released Chrome 10. New features can be found on the blogspot release.
On March 14, 2011, Microsoft released Internet Explorer 9
Internet Explorer 9
Windows Internet Explorer 9 is the current version of the Internet Explorer web browser from Microsoft. It was released to the public on March 14, 2011 at 21:00 PDT. Internet Explorer 9 supports several CSS 3 properties, embedded ICC v2 or v4 color profiles support via Windows Color System, and...
.
On March 22, 2011, Mozilla released Firefox 4.0.
On April 4, 2011, Google released Chrome 11.
On June 7, 2011, Google released Chrome 12.
On June 21, 2011, Mozilla released Firefox 5.0.
On August 2, 2011, Google released Chrome 13.
On August 16, 2011, Mozilla released Firefox 6.0.
On September 15, 2011, Google released Chrome 14.
On September 27, 2011, Mozilla released Firefox 7.0.
On October 25, 2011, Google released Chrome 15.
On November 8, 2011 Mozilla released Firefox 8.
In development
Microsoft's Internet Explorer 10Internet Explorer 10
Windows Internet Explorer 10 is the next version of Internet Explorer currently being developed by Microsoft, and the successor to Internet Explorer 9. On April 12, 2011, Microsoft released the first "IE10 Platform Preview", which only runs on Windows 7; later platform previews only run on Windows 8...
which supports Windows 7 or later.
Google's Chrome 16 and Chrome 17, in Beta and Dev respectively.
Mozilla's Firefox 9, Firefox 10, and Firefox 11, in Beta, Aurora (Alpha 2), and Nightly (Alpha 1) respectively.
Opera Software's Opera 12, in pre-Alpha.
Microsoft Windows
Although its usage share has been dropping since the mid-2000s, Internet Explorer still has, as of January 2011, the largest usage shareUsage share of web browsers
The usage share of a web browser is the proportion, often expressed as a percentage, of users of all web browsers who use that particular browser. This figure can only be estimated, typically by determining the proportion of visitors to a group of websites that use a particular web browser...
on Microsoft Windows, with Mozilla Firefox the second most used web browser. Google Chrome, released in September 2008, is gaining ground in third place. In March 2008, Apple released Safari 3.1, began including it as a pre-selected update in the Apple Software Update program and its market share on Windows tripled. It is now in fourth place followed by Opera. Other browsers based on Internet Explorer's Trident
Trident (layout engine)
Trident is the name of the layout engine for the Microsoft Windows version of Internet Explorer.It was first introduced with the release of Internet Explorer version 4.0 in October 1997; it has been steadily upgraded and remains in use today...
layout engine
Layout engine
A web browser engine, , is a software component that takes marked up content and formatting information and displays the formatted content on the screen. It "paints" on the content area of a window, which is displayed on a monitor or a printer...
, such as Maxthon
Maxthon
Maxthon is a free web browser for Microsoft Windows. The latest release, Maxthon 3, supports both the Trident and the WebKit rendering engines....
, included features like tabbed browsing and were once popular but fell out of use when IE began adding such features itself from version 7 onwards.
Linux and Unix
The Unix-based KonquerorKonqueror
Not to be confused with the Conqueror web browser.Konqueror is a web browser and file manager that provides file-viewer functionality for file systems such as local files, files on a remote ftp server and files in a disk image. It is a core part of the KDE desktop environment...
browser is part of the KDE
KDE
KDE is an international free software community producing an integrated set of cross-platform applications designed to run on Linux, FreeBSD, Microsoft Windows, Solaris and Mac OS X systems...
project and is the primary competitor against Mozilla-based browsers (Firefox, Mozilla Application Suite/SeaMonkey
SeaMonkey
SeaMonkey is a free and open source cross-platform Internet suite. It is the continuation of the former Mozilla Application Suite, based on the same source code...
, Epiphany
Epiphany (web browser)
Epiphany is an open source web browser for the GNOME desktop environment. The browser is a descendant of Galeon, and was created after developer disagreements about Galeon's growing complexity...
, Galeon
Galeon
Galeon is a web browser for GNOME based on Mozilla’s Gecko layout engine. Galeon’s self-declared mission was to deliver the web and only the web. Galeon was discontinued in September 2008....
, etc.) for market share on Unix-like systems.
Konqueror's KHTML
KHTML
KHTML is the HTML layout engine developed by the KDE project. It is the engine used by the Konqueror web browser. A forked version of KHTML called WebKit is used by several web browsers, among them Safari and Google Chrome...
engine is an API for the KDE desktop. Derivative browsers and web-browsing functionality (for example, Amarok
Amarok (audio)
Amarok is a cross-platform free and open source music player for KDE, but is released independently of the central KDE Software Compilation release cycle...
has a Wikipedia sidebar that gives information about the current artist) based on KDE use KHTML.
Mac OS X
Safari is Apple's web browser for Mac OS X, and also has the highest usage share on Mac OS X. The web browser is based on WebKitWebKit
WebKit is a layout engine designed to allow web browsers to render web pages. WebKit powers Google Chrome and Apple Safari and by October 2011 held over 33% of the browser market share between them. It is also used as the basis for the experimental browser included with the Amazon Kindle ebook...
, a derivative of the KHTML
KHTML
KHTML is the HTML layout engine developed by the KDE project. It is the engine used by the Konqueror web browser. A forked version of KHTML called WebKit is used by several web browsers, among them Safari and Google Chrome...
engine. Other Mac browsers including iCab
ICab
iCab is a web browser for the Macintosh by Alexander Clauss, derived from Crystal Atari Browser for Atari TOS compatible computers. It is the most recently actively developed browser for 68k-based Macintoshes that features tabbed browsing and one of a very few browsers that was still updated in...
(since 4.0), OmniWeb
OmniWeb
OmniWeb is a proprietary Internet web browser developed and marketed by The Omni Group. It is available exclusively for Apple Inc.'s Mac OS X operating system...
(since 4.5), and Shiira
Shiira
Shiira is an open source web browser for the Mac OS X operating system. According to its website, the goal of Shiira was "to create a browser that is better and more useful than Safari". Shiira uses WebKit for rendering and scripting.Shiira Project was led by Makoto Kinoshita. The latest release...
, use the WebKit
WebKit
WebKit is a layout engine designed to allow web browsers to render web pages. WebKit powers Google Chrome and Apple Safari and by October 2011 held over 33% of the browser market share between them. It is also used as the basis for the experimental browser included with the Amazon Kindle ebook...
API, and many other Macintosh programs add web-browsing functionality through WebKit
WebKit
WebKit is a layout engine designed to allow web browsers to render web pages. WebKit powers Google Chrome and Apple Safari and by October 2011 held over 33% of the browser market share between them. It is also used as the basis for the experimental browser included with the Amazon Kindle ebook...
. Mozilla Firefox and Opera Browser also have high usage on Mac OS X.
Camino
Camino
Camino is a free, open source, GUI-based Web browser based on Mozilla's Gecko layout engine and specifically designed for the Mac OS X operating system...
is a Mozilla-based Gecko
Gecko (layout engine)
Gecko is a free and open source layout engine used in many applications developed by Mozilla Foundation and the Mozilla Corporation , as well as in many other open source software projects....
browser for the Mac OS X platform, and uses Mac's native Cocoa
Cocoa (API)
Cocoa is Apple's native object-oriented application programming interface for the Mac OS X operating system and—along with the Cocoa Touch extension for gesture recognition and animation—for applications for the iOS operating system, used on Apple devices such as the iPhone, the iPod Touch, and...
interface like Safari does, instead of Mozilla's XUL
XUL
In computer programming, XUL , the XML User Interface Language, is an XML user interface markup language developed by the Mozilla project. XUL operates in Mozilla cross-platform applications such as Firefox...
which is used in Firefox. It was initially developed by Dave Hyatt
Dave Hyatt
Dave Hyatt is an American software developer currently employed by Apple Inc. , where he is part of the development team responsible for the Safari web browser and WebKit framework. Hyatt was part of the original team that shipped the beta releases and 1.0 release of Safari...
, until he was hired by Apple to develop Safari.
Embedded devices
Opera MiniOpera Mini
Opera Mini is a web browser designed primarily for mobile phones, smartphones and personal digital assistants. Until version 4 it used the Java ME platform, requiring the mobile device to run Java ME applications. From version 5 it is also available as a native application for Android, iOS, Symbian...
is a popular web browser on mobile devices such as most Java ME enabled internet connected phones and smartphone
Smartphone
A smartphone is a high-end mobile phone built on a mobile computing platform, with more advanced computing ability and connectivity than a contemporary feature phone. The first smartphones were devices that mainly combined the functions of a personal digital assistant and a mobile phone or camera...
s because of its small footprint. It has also recently been released for the iPhone and iPod Touch. Opera Mobile for smartphones main competition is from Netfront
NetFront
NetFront Browser is a mobile browser for embedded devices, developed by Access Co. Ltd. of Japan, and was designed to function as an embedded browser....
. Sony developed a mobile browser for their PSP
PlayStation Portable
The is a handheld game console manufactured and marketed by Sony Corporation Development of the console was announced during E3 2003, and it was unveiled on , 2004, at a Sony press conference before E3 2004...
, using Netfront's codebase. Sony's PlayStation 3
PlayStation 3
The is the third home video game console produced by Sony Computer Entertainment and the successor to the PlayStation 2 as part of the PlayStation series. The PlayStation 3 competes with Microsoft's Xbox 360 and Nintendo's Wii as part of the seventh generation of video game consoles...
also includes a web browser. PC Site Viewer, the web browser included on many Japanese cellular phones, is based on Opera. In February, 2006 it was announced that Nintendo
Nintendo
is a multinational corporation located in Kyoto, Japan. Founded on September 23, 1889 by Fusajiro Yamauchi, it produced handmade hanafuda cards. By 1963, the company had tried several small niche businesses, such as a cab company and a love hotel....
"will release an add-on card" with a version of Opera for the Nintendo DS
Nintendo DS
The is a portable game console produced by Nintendo, first released on November 21, 2004. A distinctive feature of the system is the presence of two separate LCD screens, the lower of which is a touchscreen, encompassed within a clamshell design, similar to the Game Boy Advance SP...
(Nintendo DS Browser
Nintendo DS Browser
The Nintendo DS Browser is a version of the Opera web browser for use on the Nintendo DS, developed by Opera Software and Nintendo. The Nintendo DS Browser comes in separate versions for the Nintendo DS and the Nintendo DS Lite; this is due to differing physical size requirements for the memory...
). This DS browser has since been criticized for its lack of Flash support and slowness. Opera is also used as a web browser on the Wii
Wii
The Wii is a home video game console released by Nintendo on November 19, 2006. As a seventh-generation console, the Wii primarily competes with Microsoft's Xbox 360 and Sony's PlayStation 3. Nintendo states that its console targets a broader demographic than that of the two others...
console.
Nokia
Nokia
Nokia Corporation is a Finnish multinational communications corporation that is headquartered in Keilaniemi, Espoo, a city neighbouring Finland's capital Helsinki...
released a WebKit
WebKit
WebKit is a layout engine designed to allow web browsers to render web pages. WebKit powers Google Chrome and Apple Safari and by October 2011 held over 33% of the browser market share between them. It is also used as the basis for the experimental browser included with the Amazon Kindle ebook...
-based browser in 2005, which comes with every Symbian
Symbian
Symbian is a mobile operating system and computing platform designed for smartphones and currently maintained by Accenture. The Symbian platform is the successor to Symbian OS and Nokia Series 60; unlike Symbian OS, which needed an additional user interface system, Symbian includes a user...
S60 platform
S60 platform
The S60 Platform is a software platform for mobile phones that runs on Symbian OS. It was created by Nokia, who made the platform open source and contributed it to the Symbian Foundation. S60 has been used by mobile device manufacturers including Siemens mobile, Lenovo, LG Electronics, Panasonic...
-based smartphone. On Nokia's N900 is MicroB, a Firefox derivate, preinstalled. It competes with Opera for the N900.
Windows Phone 7
Windows Phone 7
Windows Phone is a mobile operating system developed by Microsoft, and is the successor to its Windows Mobile platform, although incompatible with it. Unlike its predecessor, it is primarily aimed at the consumer market rather than the enterprise market...
comes with a version of Internet Explorer Mobile with a rendering engine which Steve Ballmer
Steve Ballmer
Steven Anthony "Steve" Ballmer is an American business magnate. He is the chief executive officer of Microsoft, having held that post since January 2000. , his personal wealth is estimated at US$13.9 billion, ranking number 19 on the Forbes 400.-Early life:Ballmer was born in Detroit, Michigan to...
said to be "somewhere between Internet Explorer 7 and Internet Explorer 8". Microsoft plans to update the layout engine to that of Internet Explorer 9.
Windows Mobile
Windows Mobile
Windows Mobile is a mobile operating system developed by Microsoft that was used in smartphones and Pocket PCs, but by 2011 was rarely supplied on new phones. The last version is "Windows Mobile 6.5.5"; it is superseded by Windows Phone, which does not run Windows Mobile software.Windows Mobile is...
comes with Internet Explorer Mobile by default and competes with Opera Mobile, Netfront, Iris, and Mozilla's Minimo
Minimo
Minimo was a project to create a version of the Mozilla web browser for small devices like PDAs and mobile phones.The project aimed to make it easier for developers to embed parts of Mozilla into systems with limited system resources...
, and lately the Skyfire browser (also available for Android and Symbian
Symbian
Symbian is a mobile operating system and computing platform designed for smartphones and currently maintained by Accenture. The Symbian platform is the successor to Symbian OS and Nokia Series 60; unlike Symbian OS, which needed an additional user interface system, Symbian includes a user...
).
MobileSafari, Apple's browser based on WebKit/KHTML, comes with iPhone
IPhone
The iPhone is a line of Internet and multimedia-enabled smartphones marketed by Apple Inc. The first iPhone was unveiled by Steve Jobs, then CEO of Apple, on January 9, 2007, and released on June 29, 2007...
, iPod Touch
IPod Touch
The iPod Touch is a portable media player, personal digital assistant, handheld game console, and Wi-Fi mobile device designed and marketed by Apple Inc. The iPod Touch adds the multi-touch graphical user interface to the iPod line...
and the iPad
IPad
The iPad is a line of tablet computers designed, developed and marketed by Apple Inc., primarily as a platform for audio-visual media including books, periodicals, movies, music, games, and web content. The iPad was introduced on January 27, 2010 by Apple's then-CEO Steve Jobs. Its size and...
.
Android, Google's open-source OS for mobile devices, uses a browser based on WebKit
WebKit
WebKit is a layout engine designed to allow web browsers to render web pages. WebKit powers Google Chrome and Apple Safari and by October 2011 held over 33% of the browser market share between them. It is also used as the basis for the experimental browser included with the Amazon Kindle ebook...
. Since March 2010, Opera Mini has been available for Android. Other browsers include Opera Mobile and Firefox 4.
See also
- After the Software WarsAfter the Software WarsAfter the Software Wars is a book by Keith Curtis about free software and its importance in the computing industry, specifically about its impact on Microsoft and the proprietary software development model....
- Comparison of web browsersComparison of web browsersThe following tables compare general and technical information for a number of web browsers. Please see the individual products' articles for further information.-Historical web browsers:...
- Usage share of web browsersUsage share of web browsersThe usage share of a web browser is the proportion, often expressed as a percentage, of users of all web browsers who use that particular browser. This figure can only be estimated, typically by determining the proportion of visitors to a group of websites that use a particular web browser...
External links
- Browser Statistics – Month by month comparison spanning from 2002 and onward displaying the usage share of browsers among web developers.
- Browser Stats – Chuck Upsdell's Browser Statistics
- Browser Stats – Net Applications' Browser Statistics
- StatCounter Global Stats – tracks the market share of browsers including mobile from over 4 billion monthly page views.
- Browser war, RIA and future of web development
- Browser Wars II: The Saga Continues – an article about the development of the browser wars
- Thomas Haigh, "Protocols for Profit: Web and Email Technologies as Product and Infrastructure" in The Internet & American Business, eds. Ceruzzi & Aspray, MIT Press, 2008– business & technological history of web browsers, online preprint
- stephenbrooks.org – browserwars – a multiplayer browser game, shows the logo of the browsers used

