
Brownian excursion
Encyclopedia
In probability theory
a Brownian excursion process is a stochastic processes that is closely related to a Wiener process
(or Brownian motion
). Realisations of Brownian excursion processes are essentially just realisations of a Weiner process seleced to satisfy certain conditions. In particular, a Brownian excursion process is a Wiener process conditioned
to be positive and to take the value 0 at time 1. Alternatively, it is a Brownian bridge
process conditioned to be positive.
 ,is a Wiener process
,is a Wiener process
(or Brownian motion
) conditioned
to be positive and to take the value 0 at time 1. Alternatively, it is a Brownian bridge
process conditioned to be positive.
Another representation of a Brownian excursion in terms of a Brownian motion process W (due to Lévy
in terms of a Brownian motion process W (due to Lévy
and noted by Itô
and Henry P. McKean, Jr.)
is in terms of the last time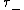 that W hits zero before time 1 and the first time
that W hits zero before time 1 and the first time 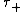 that Brownian motion
that Brownian motion 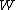 hits zero after time 1:
hits zero after time 1:
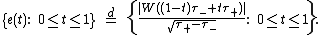
Let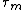 be the time that a
be the time that a
Brownian bridge process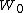 achieves its minimum on [0, 1]. Vervaat (1979) shows that
achieves its minimum on [0, 1]. Vervaat (1979) shows that
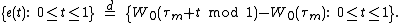
 . In particular:
. In particular:
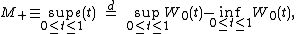
(this can also be derived by explicit calculations) and
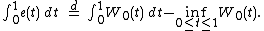
The following result holds:
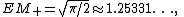
and the following values for the second moment and variance can be calculated by the exact form of the distribution and density:
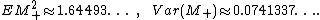
Groeneboom (1989), Lemma 4.2 gives an expression for the Laplace transform of (the density) of
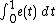 . A formula for a certain double transform of the distribution of
. A formula for a certain double transform of the distribution of
this area integral integral is given by Louchard (1984).
Groeneboom (1983) and Pitman (1983) give decompositions of Brownian motion
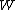 in terms of i.i.d Brownian excursions
in terms of i.i.d Brownian excursions
and the least concave majorant (or greatest convex minorant) of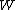 .
.
For an introduction to Itô's
general theory of Brownian excursions
and the Itô
Poisson process
of excursions, see Revuz and Yor (1994), chapter XII.
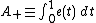
arises in connection with the enumeration of connected graphs, many other problems in combinatorial theory; see e.g.
,
,
,
,
,
and the limit distribution of the Betti numbers of certain varieties in cohomology theory
.
Takacs (1991a) shows that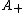 has density
has density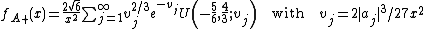
where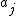 are the zeros of the Airy function and
are the zeros of the Airy function and 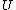 is the confluent hypergeometric function
is the confluent hypergeometric function
.
Janson
and Louchard (2007) show that
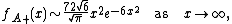
and
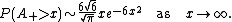
They also give higher-order expansions in both cases.
Janson (2007) gives moments of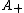 and many other area functionals. In particular,
and many other area functionals. In particular,
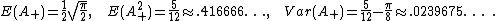
Brownian excursions also arise in connection with
queuing problems,
railway traffic, and
the heights of random rooted binary trees.
Probability theory
Probability theory is the branch of mathematics concerned with analysis of random phenomena. The central objects of probability theory are random variables, stochastic processes, and events: mathematical abstractions of non-deterministic events or measured quantities that may either be single...
a Brownian excursion process is a stochastic processes that is closely related to a Wiener process
Wiener process
In mathematics, the Wiener process is a continuous-time stochastic process named in honor of Norbert Wiener. It is often called standard Brownian motion, after Robert Brown...
(or Brownian motion
Brownian motion
Brownian motion or pedesis is the presumably random drifting of particles suspended in a fluid or the mathematical model used to describe such random movements, which is often called a particle theory.The mathematical model of Brownian motion has several real-world applications...
). Realisations of Brownian excursion processes are essentially just realisations of a Weiner process seleced to satisfy certain conditions. In particular, a Brownian excursion process is a Wiener process conditioned
Conditional probability
In probability theory, the "conditional probability of A given B" is the probability of A if B is known to occur. It is commonly notated P, and sometimes P_B. P can be visualised as the probability of event A when the sample space is restricted to event B...
to be positive and to take the value 0 at time 1. Alternatively, it is a Brownian bridge
Brownian bridge
A Brownian bridge is a continuous-time stochastic process B whose probability distribution is the conditional probability distribution of a Wiener process W given the condition that B = B = 0.The expected value of the bridge is zero, with variance t, implying that the most...
process conditioned to be positive.
Definition
A Brownian excursion process, ,is a Wiener process
,is a Wiener processWiener process
In mathematics, the Wiener process is a continuous-time stochastic process named in honor of Norbert Wiener. It is often called standard Brownian motion, after Robert Brown...
(or Brownian motion
Brownian motion
Brownian motion or pedesis is the presumably random drifting of particles suspended in a fluid or the mathematical model used to describe such random movements, which is often called a particle theory.The mathematical model of Brownian motion has several real-world applications...
) conditioned
Conditional probability
In probability theory, the "conditional probability of A given B" is the probability of A if B is known to occur. It is commonly notated P, and sometimes P_B. P can be visualised as the probability of event A when the sample space is restricted to event B...
to be positive and to take the value 0 at time 1. Alternatively, it is a Brownian bridge
Brownian bridge
A Brownian bridge is a continuous-time stochastic process B whose probability distribution is the conditional probability distribution of a Wiener process W given the condition that B = B = 0.The expected value of the bridge is zero, with variance t, implying that the most...
process conditioned to be positive.
Another representation of a Brownian excursion
 in terms of a Brownian motion process W (due to Lévy
in terms of a Brownian motion process W (due to LévyPaul Pierre Lévy
Paul Pierre Lévy was a Jewish French mathematician who was active especially in probability theory, introducing martingales and Lévy flights...
and noted by Itô
Kiyoshi Ito
was a Japanese mathematician whose work is now called Itō calculus. The basic concept of this calculus is the Itō integral, and among the most important results is Itō's lemma. The Itō calculus facilitates mathematical understanding of random events...
and Henry P. McKean, Jr.)
is in terms of the last time
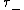 that W hits zero before time 1 and the first time
that W hits zero before time 1 and the first time 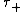 that Brownian motion
that Brownian motion 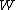 hits zero after time 1:
hits zero after time 1: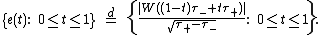
Let
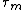 be the time that a
be the time that aBrownian bridge process
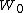 achieves its minimum on [0, 1]. Vervaat (1979) shows that
achieves its minimum on [0, 1]. Vervaat (1979) shows that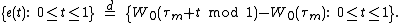
Properties
Vervaat's representation of a Brownian excursion has several consequences for various functions of . In particular:
. In particular: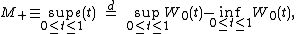
(this can also be derived by explicit calculations) and
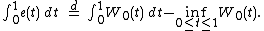
The following result holds:
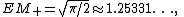
and the following values for the second moment and variance can be calculated by the exact form of the distribution and density:
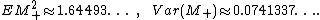
Groeneboom (1989), Lemma 4.2 gives an expression for the Laplace transform of (the density) of
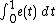 . A formula for a certain double transform of the distribution of
. A formula for a certain double transform of the distribution ofthis area integral integral is given by Louchard (1984).
Groeneboom (1983) and Pitman (1983) give decompositions of Brownian motion
Wiener process
In mathematics, the Wiener process is a continuous-time stochastic process named in honor of Norbert Wiener. It is often called standard Brownian motion, after Robert Brown...
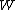 in terms of i.i.d Brownian excursions
in terms of i.i.d Brownian excursionsand the least concave majorant (or greatest convex minorant) of
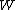 .
.For an introduction to Itô's
Kiyoshi Ito
was a Japanese mathematician whose work is now called Itō calculus. The basic concept of this calculus is the Itō integral, and among the most important results is Itō's lemma. The Itō calculus facilitates mathematical understanding of random events...
general theory of Brownian excursions
and the Itô
Kiyoshi Ito
was a Japanese mathematician whose work is now called Itō calculus. The basic concept of this calculus is the Itō integral, and among the most important results is Itō's lemma. The Itō calculus facilitates mathematical understanding of random events...
Poisson process
Poisson process
A Poisson process, named after the French mathematician Siméon-Denis Poisson , is a stochastic process in which events occur continuously and independently of one another...
of excursions, see Revuz and Yor (1994), chapter XII.
Connections and applications
The Brownian excursion area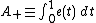
arises in connection with the enumeration of connected graphs, many other problems in combinatorial theory; see e.g.
,
,
,
,
,
and the limit distribution of the Betti numbers of certain varieties in cohomology theory
.
Takacs (1991a) shows that
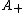 has density
has density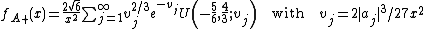
where
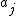 are the zeros of the Airy function and
are the zeros of the Airy function and 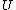 is the confluent hypergeometric function
is the confluent hypergeometric functionConfluent hypergeometric function
In mathematics, a confluent hypergeometric function is a solution of a confluent hypergeometric equation, which is a degenerate form of a hypergeometric differential equation where two of the three regular singularities merge into an irregular singularity...
.
Janson
Svante Janson
Svante Janson is a Swedish mathematician. A member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences since 1994, Janson has been the chaired professor of mathematics at Uppsala University since 1987....
and Louchard (2007) show that
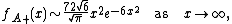
and
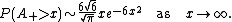
They also give higher-order expansions in both cases.
Janson (2007) gives moments of
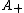 and many other area functionals. In particular,
and many other area functionals. In particular,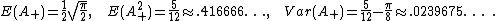
Brownian excursions also arise in connection with
queuing problems,
railway traffic, and
the heights of random rooted binary trees.
Related processes
- Brownian bridgeBrownian bridgeA Brownian bridge is a continuous-time stochastic process B whose probability distribution is the conditional probability distribution of a Wiener process W given the condition that B = B = 0.The expected value of the bridge is zero, with variance t, implying that the most...
- Brownian meander
- reflected Brownian motion
- skew Brownian motion

