
Bresler Pister yield criterion
Encyclopedia
The Bresler-Pister yield criterion is a function that was originally devised to predict the strength of concrete
under multiaxial stress states. This yield criterion is an extension of the Drucker-Prager yield criterion and can be expressed on terms of the stress invariants as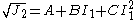
where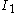 is the first invariant of the Cauchy stress,
is the first invariant of the Cauchy stress, 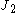 is the second invariant of the deviatoric part of the Cauchy stress, and
is the second invariant of the deviatoric part of the Cauchy stress, and 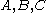 are material constants.
are material constants.
Yield criteria of this form have also been used for polypropylene
and polymeric foams
.
The parameters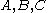 have to be chosen with care for reasonably shaped yield surface
have to be chosen with care for reasonably shaped yield surface
s. If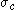 is the yield stress in uniaxial compression,
is the yield stress in uniaxial compression, 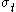 is the yield stress in uniaxial tension, and
is the yield stress in uniaxial tension, and 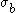 is the yield stress in biaxial compression, the parameters can be expressed as
is the yield stress in biaxial compression, the parameters can be expressed as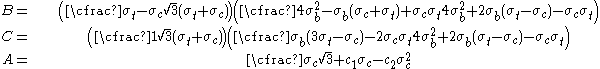
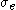 ) and the mean stress (
) and the mean stress (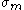 ), the Bresler-Pister yield criterion can be written as
), the Bresler-Pister yield criterion can be written as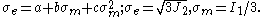
The Etse-Willam form of the Bresler-Pister yield criterion for concrete can be expressed as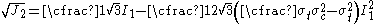
where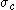 is the yield stress in uniaxial compression and
is the yield stress in uniaxial compression and 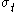 is the yield stress in uniaxial tension.
is the yield stress in uniaxial tension.
The GAZT yield criterion for plastic collapse of foams also has a form similar to the Bresler-Pister yield criterion and can be expressed as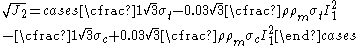
where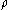 is the density of the foam and
is the density of the foam and 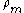 is the density of the matrix material.
is the density of the matrix material.
Concrete
Concrete is a composite construction material, composed of cement and other cementitious materials such as fly ash and slag cement, aggregate , water and chemical admixtures.The word concrete comes from the Latin word...
under multiaxial stress states. This yield criterion is an extension of the Drucker-Prager yield criterion and can be expressed on terms of the stress invariants as
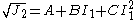
where
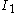 is the first invariant of the Cauchy stress,
is the first invariant of the Cauchy stress, 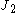 is the second invariant of the deviatoric part of the Cauchy stress, and
is the second invariant of the deviatoric part of the Cauchy stress, and 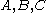 are material constants.
are material constants.Yield criteria of this form have also been used for polypropylene
Polypropylene
Polypropylene , also known as polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications including packaging, textiles , stationery, plastic parts and reusable containers of various types, laboratory equipment, loudspeakers, automotive components, and polymer banknotes...
and polymeric foams
Foam
-Definition:A foam is a substance that is formed by trapping gas in a liquid or solid in a divided form, i.e. by forming gas regions inside liquid regions, leading to different kinds of dispersed media...
.
The parameters
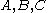 have to be chosen with care for reasonably shaped yield surface
have to be chosen with care for reasonably shaped yield surfaceYield surface
A yield surface is a five-dimensional surface in the six-dimensional space of stresses. The yield surface is usually convex and the state of stress of inside the yield surface is elastic. When the stress state lies on the surface the material is said to have reached its yield point and the...
s. If
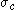 is the yield stress in uniaxial compression,
is the yield stress in uniaxial compression, 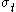 is the yield stress in uniaxial tension, and
is the yield stress in uniaxial tension, and 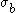 is the yield stress in biaxial compression, the parameters can be expressed as
is the yield stress in biaxial compression, the parameters can be expressed as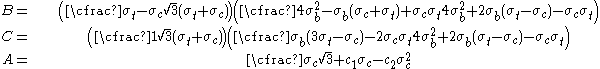
| Derivation of expressions for parameters A, B, C |
|---|
The Bresler-Pister yield criterion in terms of the principal stresses 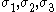 is is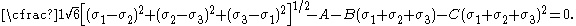 If 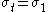 is the yield stress in uniaxial tension, then is the yield stress in uniaxial tension, then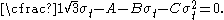 If 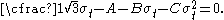 is the yield stress in uniaxial compression, then is the yield stress in uniaxial compression, then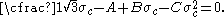 If 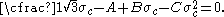 is the yield stress in equibiaxial compression, then is the yield stress in equibiaxial compression, then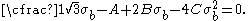 Solving these three equations for  (using Maple) gives us (using Maple) gives us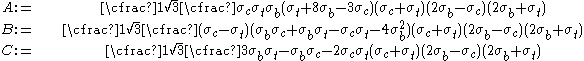 |
Alternative forms of the Bresler-Pister yield criterion
In terms of the equivalent stress (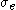 ) and the mean stress (
) and the mean stress (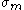 ), the Bresler-Pister yield criterion can be written as
), the Bresler-Pister yield criterion can be written as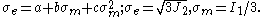
The Etse-Willam form of the Bresler-Pister yield criterion for concrete can be expressed as
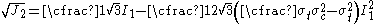
where
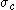 is the yield stress in uniaxial compression and
is the yield stress in uniaxial compression and 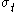 is the yield stress in uniaxial tension.
is the yield stress in uniaxial tension.The GAZT yield criterion for plastic collapse of foams also has a form similar to the Bresler-Pister yield criterion and can be expressed as
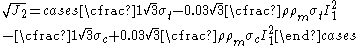
where
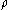 is the density of the foam and
is the density of the foam and 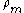 is the density of the matrix material.
is the density of the matrix material.See also
- Yield surfaceYield surfaceA yield surface is a five-dimensional surface in the six-dimensional space of stresses. The yield surface is usually convex and the state of stress of inside the yield surface is elastic. When the stress state lies on the surface the material is said to have reached its yield point and the...
- Yield (engineering)Yield (engineering)The yield strength or yield point of a material is defined in engineering and materials science as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically. Prior to the yield point the material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed...
- Plasticity (physics)Plasticity (physics)In physics and materials science, plasticity describes the deformation of a material undergoing non-reversible changes of shape in response to applied forces. For example, a solid piece of metal being bent or pounded into a new shape displays plasticity as permanent changes occur within the...

