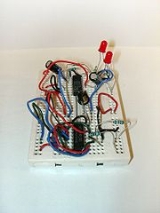
Breadboard
Encyclopedia
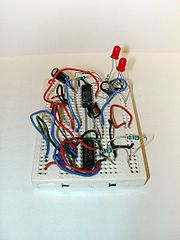

Prototype
A prototype is an early sample or model built to test a concept or process or to act as a thing to be replicated or learned from.The word prototype derives from the Greek πρωτότυπον , "primitive form", neutral of πρωτότυπος , "original, primitive", from πρῶτος , "first" and τύπος ,...
of electronics
Electronic circuit
An electronic circuit is composed of individual electronic components, such as resistors, transistors, capacitors, inductors and diodes, connected by conductive wires or traces through which electric current can flow...
. The term is commonly used to refer to solderless breadboard (plugboard).
Because the solderless breadboard does not require soldering
Soldering
Soldering is a process in which two or more metal items are joined together by melting and flowing a filler metal into the joint, the filler metal having a lower melting point than the workpiece...
, it is reusable. This makes it easy to use for creating temporary prototypes and experimenting with circuit design. Older breadboard types did not have this property. A stripboard
Stripboard
Stripboard is a widely-used type of electronics prototyping board characterized by a 0.1 inch regular grid of holes, with wide parallel strips of copper cladding running in one direction all the way across one side of the board...
(veroboard) and similar prototyping printed circuit board
Printed circuit board
A printed circuit board, or PCB, is used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks or signal traces etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. It is also referred to as printed wiring board or etched wiring...
s, which are used to build permanent soldered prototypes or one-offs, cannot easily be reused. A variety of electronic systems may be prototyped by using breadboards, from small analog and digital circuits to complete central processing unit
Central processing unit
The central processing unit is the portion of a computer system that carries out the instructions of a computer program, to perform the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system. The CPU plays a role somewhat analogous to the brain in the computer. The term has been in...
s (CPUs).

Evolution
In the early days of radio, amateurs nailed bare copper wires or terminal strips to a wooden board (often literally a cutting boardCutting board
A cutting board is a durable board on which to place material for cutting. Common is the kitchen cutting board used in preparing food; other types exist for cutting raw materials such as leather or plastic....
for bread) and soldered electronic components to them. Sometimes a paper schematic diagram was first glued to the board as a guide to placing terminals, then components and wires were installed over their symbols on the schematic. Using thumbtacks or small nails as mounting posts was also common.
Breadboards have evolved over time, with the term now being used for all kinds of prototype electronic devices. For example, US Patent 3,145,483, filed in 1961 and granted in 1964, describes a wooden plate breadboard with mounted springs and other facilities. US Patent 3,496,419,, filed in 1967 and granted in 1970, refers to a particular printed circuit board
Printed circuit board
A printed circuit board, or PCB, is used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks or signal traces etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. It is also referred to as printed wiring board or etched wiring...
layout as a Printed Circuit Breadboard. Both examples refer to and describe other types of breadboards as prior art
Prior art
Prior art , in most systems of patent law, constitutes all information that has been made available to the public in any form before a given date that might be relevant to a patent's claims of originality...
.
The breadboard most commonly used today is usually made of white plastic and is a pluggable (solderless) breadboard. It was designed by Ronald J Portugal of EI Instruments Inc. in 1971.
Typical specifications
A modern solderless breadboard consists of a perforated block of plastic with numerous tin plated phosphor bronzePhosphor bronze
Phosphor bronze is an alloy of copper with 3.5 to 10% of tin and a significant phosphorus content of up to 1%. The phosphorus is added as deoxidizing agent during melting....
or nickel silver
Nickel silver
Nickel silver, also known as German silver, Argentann, new silver, nickel brass, albata,, or alpacca, is a copper alloy with nickel and often zinc. The usual formulation is 60% copper, 20% nickel and 20% zinc. Nickel silver is named for its silvery appearance, but it contains no elemental silver...
alloy spring clips under the perforations. The clips are often called tie points or contact points. The number of tie points is often given in the specification of the breadboard.
The spacing between the clips (lead pitch) is typically 0.1" (2.54 mm). Integrated circuit
Integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is an electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material...
s (ICs) in dual in-line package
Dual in-line package
In microelectronics, a dual in-line package is an electronic device package with a rectangular housing and two parallel rows of electrical connecting pins. The package may be through-hole mounted to a printed circuit board or inserted in a socket.A DIP is usually referred to as a DIPn, where n is...
s (DIPs) can be inserted to straddle the centerline of the block. Interconnecting wires and the leads of discrete components (such as capacitor
Capacitor
A capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors separated by a dielectric ; for example, one common construction consists of metal foils separated...
s, resistor
Resistor
A linear resistor is a linear, passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element.The current through a resistor is in direct proportion to the voltage across the resistor's terminals. Thus, the ratio of the voltage applied across a resistor's...
s, and inductor
Inductor
An inductor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in a magnetic field. An inductor's ability to store magnetic energy is measured by its inductance, in units of henries...
s) can be inserted into the remaining free holes to complete the circuit. Where ICs are not used, discrete components and connecting wires may use any of the holes. Typically the spring clips are rated for 1 ampere
Ampere
The ampere , often shortened to amp, is the SI unit of electric current and is one of the seven SI base units. It is named after André-Marie Ampère , French mathematician and physicist, considered the father of electrodynamics...
at 5 volt
Volt
The volt is the SI derived unit for electric potential, electric potential difference, and electromotive force. The volt is named in honor of the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta , who invented the voltaic pile, possibly the first chemical battery.- Definition :A single volt is defined as the...
s and 0.333 amperes at 15 volts (5 watt
Watt
The watt is a derived unit of power in the International System of Units , named after the Scottish engineer James Watt . The unit, defined as one joule per second, measures the rate of energy conversion.-Definition:...
s).
Bus and terminal strips

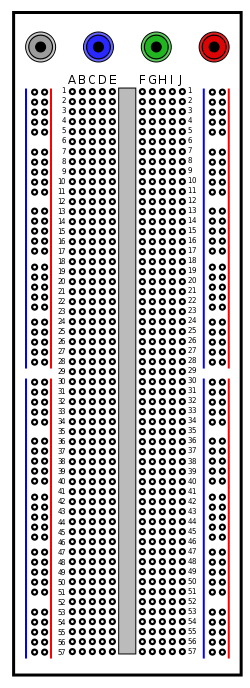

Terminal strips:The main areas, to hold most of the electronic components.
- In the middle of a terminal strip of a breadboard, one typically finds a notch running in parallel to the long side. The notch is to mark the centerline of the terminal strip and provides limited airflow (cooling) to DIP ICs straddling the centerline. The clips on the right and left of the notch are each connected in a radial way; typically five clips (i.e., beneath five holes) in a row on each side of the notch are electrically connected. The five clip columns on the left of the notch are often marked as A, B, C, D, and E, while the ones on the right are marked F, G, H, I and J. When a "skinny" Dual In-line Pin package (DIP) integrated circuit (such as a typical DIP-14 or DIP-16, which have a 0.3 inch separation between the pin rows) is plugged into a breadboard, the pins of one side of the chip are supposed to go into column E while the pins of the other side go into column F on the other side of the notch.
Bus strips:To provide power to the electronic components.
- A bus strip usually contains two columns: one for ground and one for a supply voltage. However, some breadboards only provide a single-column power distributions bus strip on each long side. Typically the column intended for a supply voltage is marked in red, while the column for ground is marked in blue or black. Some manufacturers connect all terminals in a column. Others just connect groups of, for example, 25 consecutive terminals in a column. The latter design provides a circuit designer with some more control over crosstalk (inductively coupled noise) on the power supply bus. Often the groups in a bus strip are indicated by gaps in the color marking.
- Bus strips typically run down one or both sides of a terminal strip or between terminal strips. On large breadboards additional bus strips can often be found on the top and bottom of terminal strips.
Some manufacturers provide separate bus and terminal strips. Others just provide breadboard blocks which contain both in one block. Often breadboard strips or blocks of one brand can be clipped together to make a larger breadboard.
In a more robust variant, one or more breadboard strips are mounted on a sheet of metal. Typically, that backing sheet also holds a number of binding post
Binding post
A binding post is a connector commonly used on electronic test equipment to terminate a single wire or test lead. They are also found on loudspeakers and audio amplifiers as well as other electrical equipment....
s. These posts provide a clean way to connect an external power supply. This type of breadboard may be slightly easier to handle. Several images in this article show such solderless breadboards.
Diagram
A "full size" terminal breadboard strip typically consists of around 56 to 65 rows of connectors, each row containing the above mentioned two sets of connected clips (A to E and F to J). Together with bus strips on each side this makes up a typical 784 to 910 tie point solderless breadboard. "Small size" strips typically come with around 30 rows. Miniature solderless breadboards as small as 17 rows (no bus strips, 170 tie points) can be found, but these are less well suited for practical use.Jump wires
Jump wiresJump wire
Jump Wires, commonly used with a breadboard, are used to transfer electrical signals from on part of the breadboard to the central microcontroller. Jump wires vary in size and color to distinguish what object they are working with...
for solderless breadboarding can be obtained in ready-to-use jump wire sets or can be manually manufactured. The latter can become tedious work for larger circuits. Ready-to-use jump wires come in different qualities, some even with tiny plugs attached to the wire ends. Jump wire material for ready-made or homemade wires should usually be 22 AWG
American wire gauge
American wire gauge , also known as the Brown & Sharpe wire gauge, is a standardized wire gauge system used since 1857 predominantly in the United States and Canada for the diameters of round, solid, nonferrous, electrically conducting wire...
(0.33 mm²) solid copper, tin-plated wire - assuming no tiny plugs are to be attached to the wire ends. The wire ends should be stripped 3/16" to 5/16" (approx. 5 mm to 8 mm). Shorter stripped wires might result in bad contact with the board's spring clips (insulation being caught in the springs). Longer stripped wires increase the likelihood of short-circuits on the board. Needle-nose pliers
Needle-nose pliers
Needle-nose pliers are both cutting and gripping pliers used by electricians and other tradesmen to bend, re-position and cut wire...
and tweezers
Tweezers
Tweezers are tools used for picking up and manipulating objects too small to be easily handled with the human hands. They are probably derived from tongs, pincers, or scissors-like pliers used to grab or hold hot objects since the dawn of recorded history...
are helpful when inserting or removing wires, particularly on crowded boards.
Differently colored wires and color coding discipline are often adhered to for consistency. However, the number of available colors is typically far fewer than the number of signal types or paths. Typically, a few wire colors are reserved for the supply voltages and ground (e.g., red, blue, black), some are reserved for main signals, and the rest are simply used where convenient. Some ready-to-use jump wire sets use the color to indicate the length of the wires, but these sets do not allow a meaningful color-coding schema.
Advanced solderless breadboards
Some manufacturers provide high-end versions of solderless breadboards. These are typically high-quality breadboard modules mounted on a flat casing. The casing contains additional equipment for breadboarding, such as a power supplyPower supply
A power supply is a device that supplies electrical energy to one or more electric loads. The term is most commonly applied to devices that convert one form of electrical energy to another, though it may also refer to devices that convert another form of energy to electrical energy...
, one or more signal generator
Signal generator
Signal generators, also known variously as function generators, RF and microwave signal generators, pitch generators, arbitrary waveform generators, digital pattern generators or frequency generators are electronic devices that generate repeating or non-repeating electronic signals...
s, serial interfaces, LED or LCD modules, and logic probes.
Solderless breadboard modules can also be found mounted on devices like microcontroller evaluation boards. They provide an easy way to add additional periphery circuits to the evaluation board.
Limitations
Inductance
In electromagnetism and electronics, inductance is the ability of an inductor to store energy in a magnetic field. Inductors generate an opposing voltage proportional to the rate of change in current in a circuit...
of some connections and a relatively high and not very reproducible contact resistance
Electrical resistance
The electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
, solderless breadboards are limited to operation at relatively low frequencies, usually fewer than 10 MHz, depending on the nature of the circuit. The relative high contact resistance can already be a problem for DC and very low frequency circuits. Solderless breadboards are further limited by their voltage and current ratings.
Solderless breadboards usually cannot accommodate surface-mount technology
Surface-mount technology
Surface mount technology is a method for constructing electronic circuits in which the components are mounted directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards . An electronic device so made is called a surface mount device...
devices (SMD) or components with grid spacing other than 0.1" (2.54 mm). Further, they cannot accommodate components with multiple rows of connectors if these connectors don't match the dual in-line
Dual in-line package
In microelectronics, a dual in-line package is an electronic device package with a rectangular housing and two parallel rows of electrical connecting pins. The package may be through-hole mounted to a printed circuit board or inserted in a socket.A DIP is usually referred to as a DIPn, where n is...
layout—it is impossible to provide the correct electrical connectivity. Sometimes small PCB
Printed circuit board
A printed circuit board, or PCB, is used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks or signal traces etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. It is also referred to as printed wiring board or etched wiring...
adapters called breakout adapters can be used to fit the component to the board. Such adapters carry one or more components and have 0.1" (2.54 mm) connectors in a single in-line
Single in-line package
A single in-line package is an electronic device package which has one row of connecting pins. It is not as popular as the dual in-line package which contain two rows of pins, but has been used for packaging RAM chips and multiple resistors with a common pin. SIPs group RAM chips together on a...
or dual in-line layout. Larger components are usually plugged into a socket on the adapter, while smaller components (e.g., SMD resistors) are usually soldered directly onto the adapter. The adapter is then plugged into the breadboard via the 0.1" connectors. However, the need to solder the components onto the adapter negates some of the advantage of using a solderless breadboard.
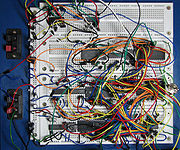
Complex circuits can become unmanageable on a breadboard due to the large amount of wiring required.
Alternatives
Alternative methods to create prototypes are point-to-point constructionPoint-to-point construction
Point-to-point construction refers to the method in which electronics circuits were constructed before the 1950s. Point-to-point construction is still used to construct prototype equipment with few or heavy electronic components....
, reminiscent of the original breadboards, wire wrap
Wire wrap
Wire wrap is a technology used to assemble electronics. It is a method to construct circuit boards without having to make a printed circuit board. Wires can be wrapped by hand or by machine, and can be hand-modified afterwards. It was popular for large-scale manufacturing in the 60s and early 70s,...
, wiring pencil
Wiring pencil
A wiring pencil is a tool for making electrical connections.A small reel of copper wire coated with a special insulating varnish is mounted on the end of the tool...
, and boards like the stripboard
Stripboard
Stripboard is a widely-used type of electronics prototyping board characterized by a 0.1 inch regular grid of holes, with wide parallel strips of copper cladding running in one direction all the way across one side of the board...
. Complicated systems, such as modern computers comprising millions of transistor
Transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and power. It is composed of a semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current...
s, diode
Diode
In electronics, a diode is a type of two-terminal electronic component with a nonlinear current–voltage characteristic. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material connected to two electrical terminals...
s, and resistor
Resistor
A linear resistor is a linear, passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element.The current through a resistor is in direct proportion to the voltage across the resistor's terminals. Thus, the ratio of the voltage applied across a resistor's...
s, do not lend themselves to prototyping using breadboards, as their complex designs can be difficult to lay out and debug on a breadboard. Modern circuit designs are generally developed using a schematic capture
Schematic capture
Schematic capture or schematic entry is a step in the design cycle of electronic design automation at which the electronic diagram, or electronic schematic of the designed electronic circuit is created by a designer...
and simulation system, and tested in software simulation before the first prototype circuits are built on a printed circuit board
Printed circuit board
A printed circuit board, or PCB, is used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks or signal traces etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. It is also referred to as printed wiring board or etched wiring...
. Integrated circuit
Integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is an electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material...
designs are a more extreme version of the same process: since producing prototype silicon is costly, extensive software simulations are performed before fabricating the first prototypes. However, prototyping techniques are still used for some applications such as RF
Radio frequency
Radio frequency is a rate of oscillation in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents which carry radio signals...
circuits, or where software models of components are inexact or incomplete.
See also
- Iterative designIterative designIterative design is a design methodology based on a cyclic process of prototyping, testing, analyzing, and refining a product or process. Based on the results of testing the most recent iteration of a design, changes and refinements are made. This process is intended to ultimately improve the...
- BrassboardBrassboardA brassboard or brass board is an experimental or demonstration test model, intended for field testing outside the laboratory environment. A brassboard follows an earlier prototyping stage called a breadboard. A brassboard contains both the functionality and approximate physical configuration of...
- PerfboardPerfboardPerfboard is a material for prototyping electronic circuits. It is a thin, rigid sheet with holes pre-drilled at standard intervals across a grid, usually a square grid of 2.54 mm spacing. These holes are ringed by round or square copper pads...
- StripboardStripboardStripboard is a widely-used type of electronics prototyping board characterized by a 0.1 inch regular grid of holes, with wide parallel strips of copper cladding running in one direction all the way across one side of the board...
- Wire wrapWire wrapWire wrap is a technology used to assemble electronics. It is a method to construct circuit boards without having to make a printed circuit board. Wires can be wrapped by hand or by machine, and can be hand-modified afterwards. It was popular for large-scale manufacturing in the 60s and early 70s,...

