
Stripboard
Encyclopedia

Electronics
Electronics is the branch of science, engineering and technology that deals with electrical circuits involving active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies...
prototyping board characterized by a 0.1 inch (2.54 mm) regular (rectangular) grid of holes, with wide parallel strips of copper cladding running in one direction all the way across one side of the board. It is usually known by the name Veroboard, which is a trademark, in the UK, of British company Vero Technologies Ltd, & Pixel Print LTD Canada. In using the board, breaks are made in the tracks, usually around holes, to divide the strips into multiple electrical nodes. With care, it is possible to break between holes to allow for components that have two pin rows only one position apart such as twin row headers for IDCs
Insulation-displacement connector
An Insulation-displacement connector, insulation-displacement technology/termination or insulation-piercing connector is an electrical connector designed to be connected to the conductor of an insulated wire or cable by a connection process which forces a selectively sharpened blade or blades...
.
Variations
Stripboard is available from many different vendors. All versions have copper strips on one side. Some are made using printed circuit boardPrinted circuit board
A printed circuit board, or PCB, is used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks or signal traces etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. It is also referred to as printed wiring board or etched wiring...
etching and drilling techniques, although some have milled strips and punched holes. The original Veroboard used FR-2 synthetic-resin-bonded paper (SRBP)
FR-2
FR-2 is an abbreviation for Flame Resistant 2. It is a NEMA designation for synthetic resin bonded paper, a composite material made of paper impregnated with a plasticized phenol formaldehyde resin, used in the manufacture of printed circuit boards...
(also known as phenolic board) as the base board material. Some versions of stripboard now use higher quality FR-4
FR-4
FR-4 is a grade designation assigned to glass-reinforced epoxy laminate sheets, tubes, rods and printed circuit boards . FR-4 is a composite material composed of woven fiberglass cloth with an epoxy resin binder that is flame resistant .FR-4 glass epoxy is a popular and versatile high-pressure...
(fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminate) material.
Hole spacing
Stripboard holes are drilled on 0.1 inch (2.54 mm) centers. This spacing allows components having pins with a 0.1 inch (2.54 mm) spacing to be inserted. Compatible parts include DIPDual in-line package
In microelectronics, a dual in-line package is an electronic device package with a rectangular housing and two parallel rows of electrical connecting pins. The package may be through-hole mounted to a printed circuit board or inserted in a socket.A DIP is usually referred to as a DIPn, where n is...
ICs
Integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is an electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material...
, sockets for ICs, some types of connectors, and other devices.
Stripboards have evolved over time into several variants and related products. For example, a larger version using a 0.15 inch (3.81 mm) grid and larger holes is available, but is generally less popular (presumably because it doesn't match up with standard IC pin spacing).
Assemblies
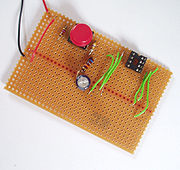
Soldering
Soldering is a process in which two or more metal items are joined together by melting and flowing a filler metal into the joint, the filler metal having a lower melting point than the workpiece...
to the copper tracks on the other side of the board to make the desired connections, and any excess wire is cut off. The continuous tracks may be easily and neatly cut as desired to form breaks between conductors using a 5 mm twist drill
Drill
A drill or drill motor is a tool fitted with a cutting tool attachment or driving tool attachment, usually a drill bit or driver bit, used for drilling holes in various materials or fastening various materials together with the use of fasteners. The attachment is gripped by a chuck at one end of...
, a hand cutter made for the purpose, or a knife. Tracks may be linked up on either side of the board using wire. With practice, very neat and reliable assemblies can be created, though such a method is labour-intensive and therefore unsuitable for production assemblies except in very small quantity.
External wire connections to the board are made either by soldering the wires through the holes or, for wires too thick to pass through the holes, by soldering them to specially made pins called Veropins which fit tightly into the holes. Alternatively, some types of connectors have a suitable pin spacing to be inserted directly into the board.
Wire wrap
Stripboard is not designed for surface-mount components. For high density prototyping, especially of digital circuits, wire wrapWire wrap
Wire wrap is a technology used to assemble electronics. It is a method to construct circuit boards without having to make a printed circuit board. Wires can be wrapped by hand or by machine, and can be hand-modified afterwards. It was popular for large-scale manufacturing in the 60s and early 70s,...
is faster and more reliable than Stripboard for experienced personnel.
Breadboard
Veroboard is similar in concept and usage to breadboardBreadboard
A breadboard is a construction base for prototyping of electronics. The term is commonly used to refer to solderless breadboard ....
, but is cheaper and more permanent—connections are soldered and while some limited reuse may be possible, more than a few cycles of soldering and desoldering are likely to render both the components and the board unusable. In contrast, breadboard connections are held by friction, and the breadboard can be reused many times. However, a breadboard is not very suitable for prototyping that needs to remain in a set configuration for an appreciable period of time nor for physical mock-ups containing a working circuit or for any environment subject to vibration or movement.
Prototype boards
Stripboards have further evolved into a larger class of prototype boards, available in different shapes and sizes, with different conductive trace layouts.TriPad
For example, one variant is called a TriPad board. This is similar to stripboard, except that the conductive tracks do not run continuously along the board but are broken into sections, each of which spans three holes. This allows the legs of two or three components to be easily linked together in the circuit conveniently without the need for track breaks to be made. However, in order to link more than three holes together, wire links or bridges must be formed and this can result in a less compact layout than is possible with ordinary stripboard.Other
Other prototype board variants have generic layouts to simplify building prototypes with integrated circuits, typically in DIPDual in-line package
In microelectronics, a dual in-line package is an electronic device package with a rectangular housing and two parallel rows of electrical connecting pins. The package may be through-hole mounted to a printed circuit board or inserted in a socket.A DIP is usually referred to as a DIPn, where n is...
shapes, or with transistors (pads forming triangles). In particular, some boards mimic the layout of breadboards, to simplify moving a non-permanent prototype on a breadboard to a permanent construction on a PCB
Printed circuit board
A printed circuit board, or PCB, is used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks or signal traces etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. It is also referred to as printed wiring board or etched wiring...
. Some types of boards have patterns for connectors on the periphery, like DB9 or IDCC headers, to allow connectors with non-standard pin spacings to be easily used. Some come in special physical shapes, to be used to prototype plug-in boards for computer bus systems.

