
Born approximation
Encyclopedia
In scattering theory
and, in particular in quantum mechanics
, the Born approximation consists of taking the incident field in place of the total field as the driving field at each point in the scatterer. Born approximation is named after Max Born
, winner of the 1954 Nobel Prize
for physics.
It is the perturbation
method applied to scattering by an extended body. It is accurate if the scattered field is small, compared to the incident field, in the scatterer.
For example, the radar
scattering of radio
waves
by a light styrofoam
column can be approximated by assuming that each part of the plastic is polarized by the same electric field
that would be present at that point without the column, and then calculating the scattering as a radiation integral over that polarization distribution.
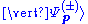 with a momentum p and out-going (+) or in-going (−) boundary conditions is
with a momentum p and out-going (+) or in-going (−) boundary conditions is
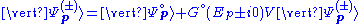
where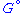 is the free particle
is the free particle
Green's function
, 0 is a positive infinitesimal
quantity, and V the interaction potential. is the corresponding free scattering solution sometimes called incident field. The factor
is the corresponding free scattering solution sometimes called incident field. The factor 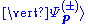 on the right hand side is sometimes called driving field.
on the right hand side is sometimes called driving field.
This equation becomes within Born approximation
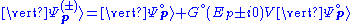
which is much easier to solve since the right hand side does not depend on the unknown state anymore.
anymore.
The obtained solution is the starting point of the Born series.
In neutron scattering
, the first-order Born approximation is almost always adequate, except for neutron optical phenomena like internal total reflection in a neutron guide, or grazing-incidence small-angle scattering.
 are plane waves. That is, the scatterer is treated as a perturbation to free space or to a homogeneous medium.
are plane waves. That is, the scatterer is treated as a perturbation to free space or to a homogeneous medium.
In the distorted wave Born approximation (DWBA),
the incident waves are solutions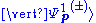 to a part
to a part 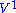 of the problem
of the problem  that is treated by some other method, either analytical or numerical. The interaction of interest
that is treated by some other method, either analytical or numerical. The interaction of interest 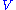 is treated as a perturbation
is treated as a perturbation 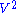 to some system
to some system 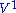 that can be solved by some other method. For nuclear reactions, numerical optical model waves are used. For scattering of charged particles by charged particles, analytic solutions for coulomb scattering are used. This gives the non-Born preliminary equation
that can be solved by some other method. For nuclear reactions, numerical optical model waves are used. For scattering of charged particles by charged particles, analytic solutions for coulomb scattering are used. This gives the non-Born preliminary equation
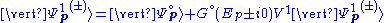
and the Born approximation
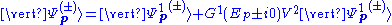
Other applications include bremsstrahlung
and the photoelectric effect
. For charged particle induced direct nuclear reaction, the procedure is used twice. There are similar methods that do not use Born approximations. In condensed-matter research, DWBA is used to analyze grazing-incidence small-angle scattering.
Scattering theory
In mathematics and physics, scattering theory is a framework for studying and understanding the scattering of waves and particles. Prosaically, wave scattering corresponds to the collision and scattering of a wave with some material object, for instance sunlight scattered by rain drops to form a...
and, in particular in quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics, also known as quantum physics or quantum theory, is a branch of physics providing a mathematical description of much of the dual particle-like and wave-like behavior and interactions of energy and matter. It departs from classical mechanics primarily at the atomic and subatomic...
, the Born approximation consists of taking the incident field in place of the total field as the driving field at each point in the scatterer. Born approximation is named after Max Born
Max Born
Max Born was a German-born physicist and mathematician who was instrumental in the development of quantum mechanics. He also made contributions to solid-state physics and optics and supervised the work of a number of notable physicists in the 1920s and 30s...
, winner of the 1954 Nobel Prize
Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes are annual international awards bestowed by Scandinavian committees in recognition of cultural and scientific advances. The will of the Swedish chemist Alfred Nobel, the inventor of dynamite, established the prizes in 1895...
for physics.
It is the perturbation
Perturbation theory
Perturbation theory comprises mathematical methods that are used to find an approximate solution to a problem which cannot be solved exactly, by starting from the exact solution of a related problem...
method applied to scattering by an extended body. It is accurate if the scattered field is small, compared to the incident field, in the scatterer.
For example, the radar
Radar
Radar is an object-detection system which uses radio waves to determine the range, altitude, direction, or speed of objects. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. The radar dish or antenna transmits pulses of radio...
scattering of radio
Radio
Radio is the transmission of signals through free space by modulation of electromagnetic waves with frequencies below those of visible light. Electromagnetic radiation travels by means of oscillating electromagnetic fields that pass through the air and the vacuum of space...
waves
WAVES
The WAVES were a World War II-era division of the U.S. Navy that consisted entirely of women. The name of this group is an acronym for "Women Accepted for Volunteer Emergency Service" ; the word "emergency" implied that the acceptance of women was due to the unusual circumstances of the war and...
by a light styrofoam
Styrofoam
Styrofoam is a trademark of The Dow Chemical Company for closed-cell currently made for thermal insulation and craft applications. In 1941, researchers in Dow's Chemical Physics Lab found a way to make foamed polystyrene...
column can be approximated by assuming that each part of the plastic is polarized by the same electric field
Electric field
In physics, an electric field surrounds electrically charged particles and time-varying magnetic fields. The electric field depicts the force exerted on other electrically charged objects by the electrically charged particle the field is surrounding...
that would be present at that point without the column, and then calculating the scattering as a radiation integral over that polarization distribution.
Born approximation to the Lippmann–Schwinger equation
The Lippmann–Schwinger equation for the scattering state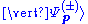 with a momentum p and out-going (+) or in-going (−) boundary conditions is
with a momentum p and out-going (+) or in-going (−) boundary conditions is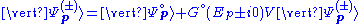
where
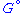 is the free particle
is the free particleFree particle
In physics, a free particle is a particle that, in some sense, is not bound. In classical physics, this means the particle is present in a "field-free" space.-Classical Free Particle:The classical free particle is characterized simply by a fixed velocity...
Green's function
Green's function
In mathematics, a Green's function is a type of function used to solve inhomogeneous differential equations subject to specific initial conditions or boundary conditions...
, 0 is a positive infinitesimal
Infinitesimal
Infinitesimals have been used to express the idea of objects so small that there is no way to see them or to measure them. The word infinitesimal comes from a 17th century Modern Latin coinage infinitesimus, which originally referred to the "infinite-th" item in a series.In common speech, an...
quantity, and V the interaction potential.
 is the corresponding free scattering solution sometimes called incident field. The factor
is the corresponding free scattering solution sometimes called incident field. The factor 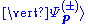 on the right hand side is sometimes called driving field.
on the right hand side is sometimes called driving field.This equation becomes within Born approximation
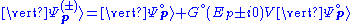
which is much easier to solve since the right hand side does not depend on the unknown state
 anymore.
anymore.The obtained solution is the starting point of the Born series.
Applications
The Born approximation is used in quite different physical contexts.In neutron scattering
Neutron scattering
Neutron scattering,the scattering of free neutrons by matter,is a physical processand an experimental technique using this processfor the investigation of materials.Neutron scattering as a physical process is of primordial importance...
, the first-order Born approximation is almost always adequate, except for neutron optical phenomena like internal total reflection in a neutron guide, or grazing-incidence small-angle scattering.
Distorted wave Born approximation (DWBA)
The Born approximation is simplest when the incident waves are plane waves. That is, the scatterer is treated as a perturbation to free space or to a homogeneous medium.
are plane waves. That is, the scatterer is treated as a perturbation to free space or to a homogeneous medium.In the distorted wave Born approximation (DWBA),
the incident waves are solutions
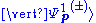 to a part
to a part 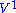 of the problem
of the problem  that is treated by some other method, either analytical or numerical. The interaction of interest
that is treated by some other method, either analytical or numerical. The interaction of interest 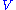 is treated as a perturbation
is treated as a perturbation 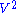 to some system
to some system 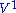 that can be solved by some other method. For nuclear reactions, numerical optical model waves are used. For scattering of charged particles by charged particles, analytic solutions for coulomb scattering are used. This gives the non-Born preliminary equation
that can be solved by some other method. For nuclear reactions, numerical optical model waves are used. For scattering of charged particles by charged particles, analytic solutions for coulomb scattering are used. This gives the non-Born preliminary equation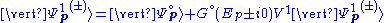
and the Born approximation
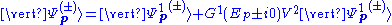
Other applications include bremsstrahlung
Bremsstrahlung
Bremsstrahlung is electromagnetic radiation produced by the deceleration of a charged particle when deflected by another charged particle, typically an electron by an atomic nucleus. The moving particle loses kinetic energy, which is converted into a photon because energy is conserved. The term is...
and the photoelectric effect
Photoelectric effect
In the photoelectric effect, electrons are emitted from matter as a consequence of their absorption of energy from electromagnetic radiation of very short wavelength, such as visible or ultraviolet light. Electrons emitted in this manner may be referred to as photoelectrons...
. For charged particle induced direct nuclear reaction, the procedure is used twice. There are similar methods that do not use Born approximations. In condensed-matter research, DWBA is used to analyze grazing-incidence small-angle scattering.

