
Border Agreement between Poland and the USSR of 16 August 1945
Encyclopedia
The Border Agreement between Poland and the USSR of 16 August 1945 refers to the ratification of borders between the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) and the Republic of Poland
signed by the Provisional Government of National Unity
(Tymczasowy Rząd Jedności Narodowej) formed by the Polish communists
. According to the treaty, Poland officially accepted the ceding its pre-war Eastern territory to the USSR (Kresy
) which was decided earlier in Yalta
already. Some of the territory along the Curzon line
established by Stalin during the course of the war, was returned to Poland as a small token of thanks (see insert). The treaty also recognised the division of the former German East Prussia
and ultimately approved the finalised delimitation line between the Soviet Union and Poland: from the Baltic sea
, to the border tripoint with Czechoslovakia
in the Carpathians.
Polish territories were administered by a Vistula Land
, whose eastern frontier roughly determined the ethnic border between the Polish people on the west, and the Ukrainian
s and Belarusians (the referred to as Little
and White Russians respectively) on the east. In Austrian Galicia there was no administrative border which marked the ethnic one the Polish and the Galician Ukrainians (Ruthenians
).
During the First World War, the Russian Civil
, the Polish-Soviet
and Polish-Ukrainian
wars, the territory passed hands several times, and each of the controlling powers tried to create its own administration on the region. During the conflict, the Supreme War Council
, tried several times to intervene and create an agreeable border between the Second Polish Republic
and Bolshevik Russia, the most notable outcome, was the border presented by the British Foreign Secretary George Curzon
, after whom the proposed line was named
. The line mostly followed the 19th century border between the Vistula Land
, but also extended further south and portioned Galicia along the rough ethnic border between Poles and Ukrainians.
Though accepted by the Bolshevik government, the line was ignored by Poland, and after the Polish-Soviet War
's conclusion, on the Treaty of Riga, Bolshevik Russia recognised a new border almost 250 km east of the Curzon Line. The border was recognised by the League of Nations
in 1923, and confirmed by numerous Polish-Soviet treaties and delimited in due course.
of August 1939 provided for the partition of the Second Polish Republic
between the USSR and Nazi Germany
. Following the corresponding invasions, a new border was drawn up, though based on the Curzon Line
, deviated west of it in several regions. Most notably, was the Belastok Voblast
, that was added to the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, although most of the region was populated by Poles.
After Germany's invasion of the USSR, the territory in question was also re-partitioned by the Nazis. Whilst Ukraine and Belarus, were administered by the occupation Ostland
and Reichskommissariat Ukraine
Reichskommissariats. Galician territory east of the 1939 border and the Belastok Voblast
plus adjacent territory to the east of this were transformed respectively into the Distrikt Galizien and Bezirk Bialystok
, and subjugated directly to the Reich
.
Following the Soviet Union's liberation of Ukraine and Belarus, in 1943/1944 the Tehran
and Yalta
discussed upon the future of the Polish-Soviet borders, and the Allied leaders recognised the Soviet right to the territory east of the 1939 border. However, after the liberation of Western Ukraine and Belarus in summer of 1944, a Polish committee formed in the town of Sapotskin sent a letter to Moscow asking that they remain part of Poland. Stalin agreed, and on 29th of September, administration of 17 (of the 23) districts of Belastok Voblast
(including the city of Bialystok
) and an additional three (Siemiatycze
, Hajnówka
and Kleszczele
) of the Brest Voblast
was passed to the Polish Committee of National Liberation
from the BSSR.
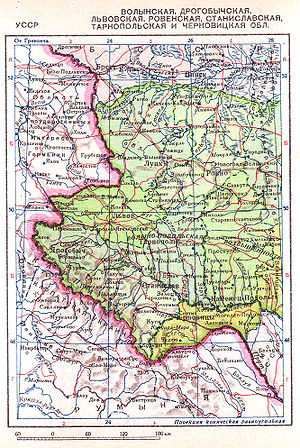 In October of 1944 these were joined by a further transfer of Lubaczów
In October of 1944 these were joined by a further transfer of Lubaczów
, Horyniec
, Laszki, Uhnów
and Sieniawa
raions of the Lviv Oblast
from the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic. In March of 1945, an additional batch of land, the Bieszczady
, Lesko
, and most of Przemyśl raions(including Przemyśl city) were transferred to Poland from the Drohobych Oblast
of Ukraine to the now Provisional Government of the Republic of Poland.
Soon afterwards World War II finished, and as the Provisional Government continued to transfer administration from military to civil bodies, it also finalised its new borders with its neighbours, and in particular, the Soviet Union. On 16th of August 1945, the border agreement was officially signed by Edward Osóbka-Morawski
, on behalf of the Provisional Government of National Unity
and Vyacheslav Molotov
, the Soviet Minister of Foreign affairs. The exchange of ratified documents occurred on 5 February 1946 in Warsaw, and from that date the agreement was in force.
was transferred from the Drohobych Oblast
of Ukraine to the Republic of Poland
. And finally a 1951 Polish–Soviet territorial exchange, saw Poland return its pre-1939 territory of Ustrzyki Dolne
raion from the Drohobych Oblast
, and instead it passed the USSR part of the Lublin Voivodship, with the cities of Belz
, Uhniv
(which was part of the Ukraine in 1939-1941 and in 1944-1945), Chervonohrad
Varyazh. The border between Poland and Belarus, and Poland and Ukraine has remained the same since.
People's Republic of Poland
The People's Republic of Poland was the official name of Poland from 1952 to 1990. Although the Soviet Union took control of the country immediately after the liberation from Nazi Germany in 1944, the name of the state was not changed until eight years later...
signed by the Provisional Government of National Unity
Provisional Government of National Unity
The Provisional Government of National Unity was a government formed by a decree of the State National Council on 28 June 1945. It was created as a coalition government between Polish Communists and the Polish government-in-exile...
(Tymczasowy Rząd Jedności Narodowej) formed by the Polish communists
Polish communism
Polish communists can trace their origins to early 20th century, as is the case in nearby countries. The first significant Polish Marxist was Stanisław Brzozowski ....
. According to the treaty, Poland officially accepted the ceding its pre-war Eastern territory to the USSR (Kresy
Kresy
The Polish term Kresy refers to a land considered by Poles as historical eastern provinces of their country. Today, it makes western Ukraine, western Belarus, as well as eastern Lithuania, with such major cities, as Lviv, Vilnius, and Hrodna. This territory belonged to the Polish-Lithuanian...
) which was decided earlier in Yalta
Yalta Conference
The Yalta Conference, sometimes called the Crimea Conference and codenamed the Argonaut Conference, held February 4–11, 1945, was the wartime meeting of the heads of government of the United States, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union, represented by President Franklin D...
already. Some of the territory along the Curzon line
Curzon Line
The Curzon Line was put forward by the Allied Supreme Council after World War I as a demarcation line between the Second Polish Republic and Bolshevik Russia and was supposed to serve as the basis for a future border. In the wake of World War I, which catalysed the Russian Revolution of 1917, the...
established by Stalin during the course of the war, was returned to Poland as a small token of thanks (see insert). The treaty also recognised the division of the former German East Prussia
East Prussia
East Prussia is the main part of the region of Prussia along the southeastern Baltic Coast from the 13th century to the end of World War II in May 1945. From 1772–1829 and 1878–1945, the Province of East Prussia was part of the German state of Prussia. The capital city was Königsberg.East Prussia...
and ultimately approved the finalised delimitation line between the Soviet Union and Poland: from the Baltic sea
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
, to the border tripoint with Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia or Czecho-Slovakia was a sovereign state in Central Europe which existed from October 1918, when it declared its independence from the Austro-Hungarian Empire, until 1992...
in the Carpathians.
Prelude
Prior to the First World War, within the Russian EmpireRussian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
Polish territories were administered by a Vistula Land
Vistula land
Vistula Land or Vistula Country was the name applied to the lands of the Kingdom of Poland following the defeats of the November Uprising and January Uprising as it was increasingly stripped of autonomy and incorporated into Imperial Russia...
, whose eastern frontier roughly determined the ethnic border between the Polish people on the west, and the Ukrainian
Ukrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine* The Ukrainians, people from Ukraine or of Ukrainian descent.* Something relating to Ukrainian culture....
s and Belarusians (the referred to as Little
Little Russia
Little Russia , sometimes Little or Lesser Rus’ , is a historical political and geographical term in the Russian language referring to most of the territory of modern-day Ukraine before the 20th century. It is similar to the Polish term Małopolska of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth...
and White Russians respectively) on the east. In Austrian Galicia there was no administrative border which marked the ethnic one the Polish and the Galician Ukrainians (Ruthenians
Ruthenians
The name Ruthenian |Rus']]) is a culturally loaded term and has different meanings according to the context in which it is used. Initially, it was the ethnonym used for the East Slavic peoples who lived in Rus'. Later it was used predominantly for Ukrainians...
).
During the First World War, the Russian Civil
Russian Civil War
The Russian Civil War was a multi-party war that occurred within the former Russian Empire after the Russian provisional government collapsed to the Soviets, under the domination of the Bolshevik party. Soviet forces first assumed power in Petrograd The Russian Civil War (1917–1923) was a...
, the Polish-Soviet
Polish-Soviet War
The Polish–Soviet War was an armed conflict between Soviet Russia and Soviet Ukraine and the Second Polish Republic and the Ukrainian People's Republic—four states in post–World War I Europe...
and Polish-Ukrainian
Polish-Ukrainian War
The Polish–Ukrainian War of 1918 and 1919 was a conflict between the forces of the Second Polish Republic and West Ukrainian People's Republic for the control over Eastern Galicia after the dissolution of Austria-Hungary.-Background:...
wars, the territory passed hands several times, and each of the controlling powers tried to create its own administration on the region. During the conflict, the Supreme War Council
Supreme War Council
The Supreme War Council was a central command created by British Prime Minister David Lloyd George to coordinate Allied military strategy during World War I. It was founded in 1917, and was based in Versailles...
, tried several times to intervene and create an agreeable border between the Second Polish Republic
Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, Second Commonwealth of Poland or interwar Poland refers to Poland between the two world wars; a period in Polish history in which Poland was restored as an independent state. Officially known as the Republic of Poland or the Commonwealth of Poland , the Polish state was...
and Bolshevik Russia, the most notable outcome, was the border presented by the British Foreign Secretary George Curzon
George Curzon
George Curzon may refer to:* George Curzon, 1st Marquess Curzon of Kedleston , former Viceroy of India and British Foreign Secretary* George Curzon-Howe, 2nd Earl Howe , British peer* George Curzon...
, after whom the proposed line was named
Curzon Line
The Curzon Line was put forward by the Allied Supreme Council after World War I as a demarcation line between the Second Polish Republic and Bolshevik Russia and was supposed to serve as the basis for a future border. In the wake of World War I, which catalysed the Russian Revolution of 1917, the...
. The line mostly followed the 19th century border between the Vistula Land
Vistula land
Vistula Land or Vistula Country was the name applied to the lands of the Kingdom of Poland following the defeats of the November Uprising and January Uprising as it was increasingly stripped of autonomy and incorporated into Imperial Russia...
, but also extended further south and portioned Galicia along the rough ethnic border between Poles and Ukrainians.
Though accepted by the Bolshevik government, the line was ignored by Poland, and after the Polish-Soviet War
Polish-Soviet War
The Polish–Soviet War was an armed conflict between Soviet Russia and Soviet Ukraine and the Second Polish Republic and the Ukrainian People's Republic—four states in post–World War I Europe...
's conclusion, on the Treaty of Riga, Bolshevik Russia recognised a new border almost 250 km east of the Curzon Line. The border was recognised by the League of Nations
League of Nations
The League of Nations was an intergovernmental organization founded as a result of the Paris Peace Conference that ended the First World War. It was the first permanent international organization whose principal mission was to maintain world peace...
in 1923, and confirmed by numerous Polish-Soviet treaties and delimited in due course.
World War II partitions
The Molotov-Ribbentrop PactMolotov-Ribbentrop Pact
The Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, named after the Soviet foreign minister Vyacheslav Molotov and the German foreign minister Joachim von Ribbentrop, was an agreement officially titled the Treaty of Non-Aggression between Germany and the Soviet Union and signed in Moscow in the late hours of 23 August 1939...
of August 1939 provided for the partition of the Second Polish Republic
Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, Second Commonwealth of Poland or interwar Poland refers to Poland between the two world wars; a period in Polish history in which Poland was restored as an independent state. Officially known as the Republic of Poland or the Commonwealth of Poland , the Polish state was...
between the USSR and Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany , also known as the Third Reich , but officially called German Reich from 1933 to 1943 and Greater German Reich from 26 June 1943 onward, is the name commonly used to refer to the state of Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a totalitarian dictatorship ruled by...
. Following the corresponding invasions, a new border was drawn up, though based on the Curzon Line
Curzon Line
The Curzon Line was put forward by the Allied Supreme Council after World War I as a demarcation line between the Second Polish Republic and Bolshevik Russia and was supposed to serve as the basis for a future border. In the wake of World War I, which catalysed the Russian Revolution of 1917, the...
, deviated west of it in several regions. Most notably, was the Belastok Voblast
Belastok Voblast
Belastok Voblast or Belostok Oblast was a territorial unit in the Belarusian Soviet Socialist Republic from September 1939 to August 1945.- Administrative units :The administrative center of the voblast was the city of Belastok ....
, that was added to the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, although most of the region was populated by Poles.
After Germany's invasion of the USSR, the territory in question was also re-partitioned by the Nazis. Whilst Ukraine and Belarus, were administered by the occupation Ostland
Reichskommissariat Ostland
Reichskommissariat Ostland, literally "Reich Commissariat Eastland", was the civilian occupation regime established by Nazi Germany in the Baltic states and much of Belarus during World War II. It was also known as Reichskommissariat Baltenland initially...
and Reichskommissariat Ukraine
Reichskommissariat Ukraine
Reichskommissariat Ukraine , literally "Reich Commissariat of Ukraine", was the civilian occupation regime of much of German-occupied Ukraine during World War II. Between September 1941 and March 1944, the Reichskommissariat was administered by Reichskommissar Erich Koch as a colony...
Reichskommissariats. Galician territory east of the 1939 border and the Belastok Voblast
Belastok Voblast
Belastok Voblast or Belostok Oblast was a territorial unit in the Belarusian Soviet Socialist Republic from September 1939 to August 1945.- Administrative units :The administrative center of the voblast was the city of Belastok ....
plus adjacent territory to the east of this were transformed respectively into the Distrikt Galizien and Bezirk Bialystok
Bezirk Bialystok
The Bezirk Bialystok , also Belostok was an administrative unit that existed during the World War II occupation of Poland by Nazi Germany...
, and subjugated directly to the Reich
Reich
Reich is a German word cognate with the English rich, but also used to designate an empire, realm, or nation. The qualitative connotation from the German is " sovereign state." It is the word traditionally used for a variety of sovereign entities, including Germany in many periods of its history...
.
Following the Soviet Union's liberation of Ukraine and Belarus, in 1943/1944 the Tehran
Tehran Conference
The Tehran Conference was the meeting of Joseph Stalin, Franklin D. Roosevelt and Winston Churchill between November 28 and December 1, 1943, most of which was held at the Soviet Embassy in Tehran, Iran. It was the first World War II conference amongst the Big Three in which Stalin was present...
and Yalta
Yalta Conference
The Yalta Conference, sometimes called the Crimea Conference and codenamed the Argonaut Conference, held February 4–11, 1945, was the wartime meeting of the heads of government of the United States, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union, represented by President Franklin D...
discussed upon the future of the Polish-Soviet borders, and the Allied leaders recognised the Soviet right to the territory east of the 1939 border. However, after the liberation of Western Ukraine and Belarus in summer of 1944, a Polish committee formed in the town of Sapotskin sent a letter to Moscow asking that they remain part of Poland. Stalin agreed, and on 29th of September, administration of 17 (of the 23) districts of Belastok Voblast
Belastok Voblast
Belastok Voblast or Belostok Oblast was a territorial unit in the Belarusian Soviet Socialist Republic from September 1939 to August 1945.- Administrative units :The administrative center of the voblast was the city of Belastok ....
(including the city of Bialystok
Bialystok
Białystok is the largest city in northeastern Poland and the capital of the Podlaskie Voivodeship. Located on the Podlaskie Plain on the banks of the Biała River, Białystok ranks second in terms of population density, eleventh in population, and thirteenth in area, of the cities of Poland...
) and an additional three (Siemiatycze
Siemiatycze
Siemiatycze is a town in north-eastern Poland, with 15,209 inhabitants . It is situated in the Podlaskie Voivodeship ; previously it was in Białystok Voivodeship . It is the capital of Siemiatycze County....
, Hajnówka
Hajnówka
Hajnówka is a town and a powiat seat in north-eastern Poland with 21,583 inhabitants . It is a notable centre of Belarusian culture in Poland and one of the centres of Orthodox faith. It is also notable for its proximity to the Białowieża Forest, the biggest primaeval forest in Europe. It is the...
and Kleszczele
Kleszczele
Kleszczele is a town in Hajnówka County, Podlaskie Voivodeship, north-eastern Poland. Prior to 1999, it was in Białystok Voivodeship .The Yiddish playwright Peretz Hirschbein was born in Kleszczele in 1881....
) of the Brest Voblast
Brest Voblast
Brest Voblast or Brest Oblast is a province of Belarus with its administrative center being Brest.Important cities within the voblast' include: Baranovichi, Brest, and Pinsk.-Geography:...
was passed to the Polish Committee of National Liberation
Polish Committee of National Liberation
The Polish Committee of National Liberation , also known as the Lublin Committee, was a provisional government of Poland, officially proclaimed 21 July 1944 in Chełm under the direction of State National Council in opposition to the Polish government in exile...
from the BSSR.

Lubaczów
Lubaczów is a town in southeastern Poland, close to the border with Ukraine, with 12,405 inhabitants .Situated in the Subcarpathian Voivodeship , it is the capital of Lubaczów County and is located 50 kilometers northeast of Przemyśl....
, Horyniec
Horyniec-Zdrój
Horyniec-Zdrój is a village in Lubaczów County, Subcarpathian Voivodeship, in south-eastern Poland, about from the border with Ukraine. It is the seat of the gmina called Gmina Horyniec-Zdrój. It lies approximately east of Lubaczów and east of the regional capital Rzeszów...
, Laszki, Uhnów
Uhniv
Uhniv is a city in the Lviv Oblast of western Ukraine. Population is 1,021 .Uhniv is the smallest city of Ukraine aside couple of cities in the Zone of alienation in the northern Ukraine. It is part of Sokal Raion and is located 22 km from Belz and 21 km from Rava Ruska. The capital of...
and Sieniawa
Sieniawa
Sieniawa is a town in southeastern Poland. It had a population of 2,127 inhabitants . Since 1999, Sieniawa has been part of Subcarpathian Province.-References:Notes...
raions of the Lviv Oblast
Lviv Oblast
Lviv Oblast is an oblast in western Ukraine. The administrative center of the oblast is the city of Lviv.-History:The oblast was created as part of the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic on December 4, 1939...
from the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic. In March of 1945, an additional batch of land, the Bieszczady
Bieszczady County
Bieszczady County is a unit of territorial administration and local government in Subcarpathian Voivodeship, in the extreme south-east of Poland, on the border with Ukraine. It takes its name from the Bieszczady mountain range. The county was created on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish...
, Lesko
Lesko
Lesko ; is a town in south-eastern Poland with a population of 5,755 . situated in the Bieszczady mountains. It is located in the heartland of the Doły , and its average altitude is above sea level, although there are some hills located within the confines of the city...
, and most of Przemyśl raions(including Przemyśl city) were transferred to Poland from the Drohobych Oblast
Drohobych Oblast
Drohobych Oblast , was an oblast in the Ukrainian SSR. It had a territory of 9.6 thousands of km³, and population of 853 thousand .-History:...
of Ukraine to the now Provisional Government of the Republic of Poland.
Soon afterwards World War II finished, and as the Provisional Government continued to transfer administration from military to civil bodies, it also finalised its new borders with its neighbours, and in particular, the Soviet Union. On 16th of August 1945, the border agreement was officially signed by Edward Osóbka-Morawski
Edward Osóbka-Morawski
Edward Osóbka-Morawski was a Polish activist in PPS before World War II, and after the Soviet takover of Poland, Chairman of the Communist interim government called the Polish Committee of National Liberation formed in Lublin with Stalin's approval and backing.In October 1944, Osóbka-Morawski...
, on behalf of the Provisional Government of National Unity
Provisional Government of National Unity
The Provisional Government of National Unity was a government formed by a decree of the State National Council on 28 June 1945. It was created as a coalition government between Polish Communists and the Polish government-in-exile...
and Vyacheslav Molotov
Vyacheslav Molotov
Vyacheslav Mikhailovich Molotov was a Soviet politician and diplomat, an Old Bolshevik and a leading figure in the Soviet government from the 1920s, when he rose to power as a protégé of Joseph Stalin, to 1957, when he was dismissed from the Presidium of the Central Committee by Nikita Khrushchev...
, the Soviet Minister of Foreign affairs. The exchange of ratified documents occurred on 5 February 1946 in Warsaw, and from that date the agreement was in force.
Aftermath
Although the treaty finalised the 1939 line, with the 1944/45 adjustments, the border would receive a few more alterations. On 15th of May 1948, the raion of MedykaMedyka
Medyka is a village in Przemyśl County, Subcarpathian Voivodeship, in south-eastern Poland, close to the border with Ukraine. It is the seat of the gmina called Gmina Medyka...
was transferred from the Drohobych Oblast
Drohobych Oblast
Drohobych Oblast , was an oblast in the Ukrainian SSR. It had a territory of 9.6 thousands of km³, and population of 853 thousand .-History:...
of Ukraine to the Republic of Poland
People's Republic of Poland
The People's Republic of Poland was the official name of Poland from 1952 to 1990. Although the Soviet Union took control of the country immediately after the liberation from Nazi Germany in 1944, the name of the state was not changed until eight years later...
. And finally a 1951 Polish–Soviet territorial exchange, saw Poland return its pre-1939 territory of Ustrzyki Dolne
Ustrzyki Dolne
Ustrzyki Dolne is a town in south-eastern Poland, close to the border with Ukraine, with 9,383 inhabitants .Situated in the Subcarpathian Voivodeship , it is the capital of Bieszczady County....
raion from the Drohobych Oblast
Drohobych Oblast
Drohobych Oblast , was an oblast in the Ukrainian SSR. It had a territory of 9.6 thousands of km³, and population of 853 thousand .-History:...
, and instead it passed the USSR part of the Lublin Voivodship, with the cities of Belz
Belz
Belz , a small city in the Lviv Oblast of Western Ukraine, near the border with Poland, is located between the Solokiya river and the Rzeczyca stream....
, Uhniv
Uhniv
Uhniv is a city in the Lviv Oblast of western Ukraine. Population is 1,021 .Uhniv is the smallest city of Ukraine aside couple of cities in the Zone of alienation in the northern Ukraine. It is part of Sokal Raion and is located 22 km from Belz and 21 km from Rava Ruska. The capital of...
(which was part of the Ukraine in 1939-1941 and in 1944-1945), Chervonohrad
Chervonohrad
Chervonohrad is a city located in the Lviv Oblast of western Ukraine. The city is designated as a separate raion within the oblast. It about 62 km north of Lviv and 7 km from Sokal. The population numbers 68,300 inhabitants....
Varyazh. The border between Poland and Belarus, and Poland and Ukraine has remained the same since.

