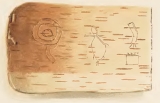
Birch bark scrolls
Encyclopedia

Birch bark
Birch bark or birchbark is the bark of several Eurasian and North American birch trees of the genus Betula.The strong and water-resistant cardboard-like bark can be easily cut, bent, and sewn, which made it a valuable building, crafting, and writing material, since pre-historic times...
scrolls, on which the Ojibwa
Ojibwa
The Ojibwe or Chippewa are among the largest groups of Native Americans–First Nations north of Mexico. They are divided between Canada and the United States. In Canada, they are the third-largest population among First Nations, surpassed only by Cree and Inuit...
(Anishinaabe
Anishinaabe
Anishinaabe or Anishinabe—or more properly Anishinaabeg or Anishinabek, which is the plural form of the word—is the autonym often used by the Odawa, Ojibwe, and Algonquin peoples. They all speak closely related Anishinaabemowin/Anishinaabe languages, of the Algonquian language family.The meaning...
) people of North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
wrote complex geometrical patterns and shapes. When used specifically for Midewiwin
Midewiwin
The Midewiwin or the Grand Medicine Society is a secretive religion of the aboriginal groups of the Maritimes, New England and Great Lakes regions in North America. Its practitioners are called Midew and the practices of Midewiwin referred to as Mide...
ceremonial use, these scrolls are called mide-wiigwaas. These writings enabled the memorization of complex ideas, and passing along history
History
History is the discovery, collection, organization, and presentation of information about past events. History can also mean the period of time after writing was invented. Scholars who write about history are called historians...
and stories to succeeding generations. Several such scrolls are in museums, including one on display at the Smithsonian Museum in Washington, DC. One recent study of a few scrolls details the complex math and memorizing scheme associated with the symbols that were used long ago. The complex writings also include astronomy, rituals, mapping, family lineage
Anishinaabe clan system
The Anishinaabe, like most Algonquian-speaking groups in North America, base their system of kinship on patrilineal clans or totems. The Anishinaabe word for clan was borrowed into English as totem. The clans, based mainly on animals, were instrumental in traditional occupations, inter-tribal...
, songs, and migration routes. In addition to birchbark, copper and slate may have also been used, along with hides, pottery, and other artifacts. Some archaeologists are presently trying to determine the exact origins, dates, and locations of their use. Many scrolls were hidden away in caves and underground man-made pits.
Construct
The barkBirch bark
Birch bark or birchbark is the bark of several Eurasian and North American birch trees of the genus Betula.The strong and water-resistant cardboard-like bark can be easily cut, bent, and sewn, which made it a valuable building, crafting, and writing material, since pre-historic times...
of the paper birch
Paper Birch
Betula papyrifera is a species of birch native to northern North America.-Description:...
tree provides an excellent writing material
Writing material
Writing material refers to the materials that provide the surfaces on which humans use writing instruments to inscribe writings. The same materials can also be used for symbolic or representational drawings. Building material on which writings or drawings are produced are not included...
. Usually, a stylus
Stylus
A stylus is a writing utensil, or a small tool for some other form of marking or shaping, for example in pottery. The word is also used for a computer accessory . It usually refers to a narrow elongated staff, similar to a modern ballpoint pen. Many styli are heavily curved to be held more easily...
of either bone, metal or wood is used to inscribe these ideographs on the soft inner bark. Black charcoal is often used to fill the scratches to make them easier to see. To form a scroll, pieces of inscribed bark are stitched together using wadab
Watap
Watap refers to the thread and cordage used by the Native Americans and First Nations peoples of Canada to sew together sheets and panels of birchbark. The word itself comes from the Algonquian language family, but watap cordage was used and sewn by all of the people who lived where the paper...
(cedar or spruce roots). To prevent unrolling, the scroll is lashed, then placed in a cylindrically-shaped wiigwaasi-makak
Wiigwaasi-makak
A wiigwaasi-makak , meaning "birch-bark box" in the Anishinaabe language, is a box made of panels of birchbark sewn together with watap...
(birch bark box) for safe-keeping. Scrolls were recopied after so many years, and stored in dry locations, often underground in special containers, or in caves. Elders recopied the scrolls over time, and some were hidden away in remote areas for safekeeping. Scrolls were often kept hidden to avoid improper interpretations and to avoid ridicule or disrespect of the teachings.
Purpose
Some scrolls are songs and details of Midewiwin rituals and medicine lodges. Some of the oldest maps of North America were made by natives, who wrote on birch bark for explorers and traders to follow.Some scrolls give the history of the Ojibway migration from Eastern North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
to further west. They indicate the discovery of miigis (white cowrie) shells along their migration through the Great Lakes
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes are a collection of freshwater lakes located in northeastern North America, on the Canada – United States border. Consisting of Lakes Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario, they form the largest group of freshwater lakes on Earth by total surface, coming in second by volume...
region. These shells are used in Midewiwin
Midewiwin
The Midewiwin or the Grand Medicine Society is a secretive religion of the aboriginal groups of the Maritimes, New England and Great Lakes regions in North America. Its practitioners are called Midew and the practices of Midewiwin referred to as Mide...
ceremonies, and Whiteshell Provincial Park
Whiteshell Provincial Park
Whiteshell Provincial Park is a 2,729 km2 park centrally located in Canada in the province of Manitoba. It can be found in the southeast of the province along the Manitoba-Ontario border, approximately 130 km east of Winnipeg. The park is located in the Canadian Shield region and has many...
is named after these kinds of shells that grow in salt water oceans, and not in fresh water, which indicates a large trading and traveling network.
The Ojibwa peoples of the Great Lakes region historically used birch bark to keep records for instructional and guidance purposes. Songs and healing recipes were readable by members of the tribe. Either through engraving or with the use of red and blue pigment, scrolls could contain any number of pictorial representations. Birch bark scrolls could measure anywhere from centimeters to several meters.
The scrolls and traditions are still alive today, and passed along from generation to generation. The Midewiwin
Midewiwin
The Midewiwin or the Grand Medicine Society is a secretive religion of the aboriginal groups of the Maritimes, New England and Great Lakes regions in North America. Its practitioners are called Midew and the practices of Midewiwin referred to as Mide...
are a traditional group that still keeps the scrolls and their teachings alive. There is some secrecy involved to keep the scrolls safe, to interpret them correctly, and to wait until there is more respect for this ancient language system. Scrolls are passed along and the oral teachings that go with them. Complex stories are represented and memorized with the use of the pictures on the scrolls.
There are many claims made by elders and aboriginal teachers that humans have existed in North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
before the last ice age
Ice age
An ice age or, more precisely, glacial age, is a generic geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental ice sheets, polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers...
, and ancient ways of writing and other ancient skills and artifacts may provide some clues to the migration patterns and history of North American and South American peoples.
Archaeological knowledge
Twentieth century archeology has confirmed that Native Americans have been using birch bark scrolls for over 400 years. In 1965 the archaeologist Kenneth Kidd reported on two finds of "trimmed and fashioned pieces of birch bark on which have been scratched figures of animals, birds, men, mythological creatures, and esoteric symbols" in the Head-of-the-Lakes region of Ontario. Some of these resembled scrolls used by the Mide Society of the OjibwaOjibwa
The Ojibwe or Chippewa are among the largest groups of Native Americans–First Nations north of Mexico. They are divided between Canada and the United States. In Canada, they are the third-largest population among First Nations, surpassed only by Cree and Inuit...
. Kidd concluded "These two finds of 'birch bark scrolls' and associated artifacts indicates that Indians of this region occasionally deposited such artifacts in out-of-the-way places in the woods, either by burying them or by secreting them in caves. The period or periods at which this was done is far from clear. But in any event, archaeologists should be aware of the custom and not overlook the possibility of their discovery." Another scroll from a different collection was later dated to about 1560+/-70.
See also
- Birch bark documentBirch bark documentA birch bark document is a document written on pieces of birch bark. Such documents existed in several cultures. For instance, some Gandharan Buddhist texts have been found written on birch bark and preserved in clay jars....
– medieval Russian documents - MidewiwinMidewiwinThe Midewiwin or the Grand Medicine Society is a secretive religion of the aboriginal groups of the Maritimes, New England and Great Lakes regions in North America. Its practitioners are called Midew and the practices of Midewiwin referred to as Mide...
- mazinibaganjigan – Birch bark folk artMazinibaganjiganMazinibaganjigan is an ancient folk art made by the Ojibwe , Cree and other Algonquian peoples who use birch bark, by biting down on small pieces of birch bark to form intricate designs. It is also known as mazinashkwemaganjigan and ozhibaganjigan...
- jiimaan – CanoeCanoeA canoe or Canadian canoe is a small narrow boat, typically human-powered, though it may also be powered by sails or small electric or gas motors. Canoes are usually pointed at both bow and stern and are normally open on top, but can be decked over A canoe (North American English) or Canadian...
typically made using birch bark - maniwiigwaasekomaan – KnifeKnifeA knife is a cutting tool with an exposed cutting edge or blade, hand-held or otherwise, with or without a handle. Knives were used at least two-and-a-half million years ago, as evidenced by the Oldowan tools...
for harvesting birch bark - wiigiwaam – WigwamWigwamA wigwam or wickiup is a domed room dwelling used by certain Native American tribes. The term wickiup is generally used to label these kinds of dwellings in American Southwest and West. Wigwam is usually applied to these structures in the American Northeast...
, typically made using birch bark - wiigwaasi-makak – boxBoxBox describes a variety of containers and receptacles for permanent use as storage, or for temporary use often for transporting contents. The word derives from the Greek πύξος , "box, boxwood"....
es and other containers made of birch bark - wiigwaas-onaagan – dishes and trays made of birch bark
- Petroforms
- Petroglyphs
- Rock ArtRock artRock art is a term used in archaeology for any human-made markings made on natural stone. They can be divided into:*Petroglyphs - carvings into stone surfaces*Pictographs - rock and cave paintings...

