Biotinidase deficiency
Encyclopedia
Biotinidase deficiency is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder in which biotin
is not released from proteins in the diet during digestion or from normal protein turnover in the cell. This situation results in biotin deficiency.
Biotin, sometimes called vitamin B7, is an important water-soluble nutrient that aids in the metabolism
of fat
s, carbohydrate
s and protein
s. Biotin deficiency can result in behavioral disorders, lack of coordination, learning disabilities and seizure. Biotin supplementation can alleviate and sometimes totally arrest such symptoms.
s, hypotonia
and muscle/limb weakness, ataxia
, paresis
, hearing loss, optic atrophy, skin rashes (including seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis
), and alopecia
. If left untreated, the disorder can rapidly lead to coma
and death.
Biotinidase deficiency can also appear later in life. This is referred to as "late-onset" biotinidase deficiency. The symptoms are similar, but perhaps more mild, because if an individual survives the neonatal period they likely have some residual activity of biotin-related enzymes. Studies have noted individuals who were asymptomatic until adolescence or early adulthood. One study pointed out that untreated individuals may not show symptoms until age 21. Furthermore, in rare cases, even individuals with profound deficiencies of biotinidase can be asymptomatic.
Symptom severity is predictably correlated with the severity of the enzyme defect. Profound biotinidase deficiency refers to situations where enzyme activity is 10% or less. Individuals with partial biotinidase deficiency may have enzyme activity of 10-30%.
Functionally, there is no significant difference between dietary biotin deficiency and genetic loss of biotin-related enzyme activity. In both cases, supplementation with biotin
can often restore normal metabolic function and proper catabolism of leucine
and isoleucine
.
The symptoms of biotinidase deficiency (and dietary deficiency of biotin) can be quite severe. A 2004 case study from Metametrix detailed the effects of biotin deficiency, including aggression, cognitive delay, and reduced immune function.
deficiency, because egg whites contain high levels of avidin
. The name avidin literally means that the protein has an "avidity" for "biotin." Avidin binds to biotin, making it unavailable for use elsewhere in the body, and otherwise useful biotin molecules are excreted in the urine.
 Mutation
Mutation
s in the BTD gene
cause biotinidase deficiency. Biotinidase
is the enzyme
that is made by the BTD gene. Many mutations that cause the enzyme to be nonfunctional or to be produced at extremely low levels have been identified. Biotin is a vitamin that is chemically bound to proteins. (Most vitamins are only loosely associated with proteins.) Without biotinidase activity, the vitamin biotin cannot be separated from foods and therefore cannot be used by the body. Another function of the biotinidase enzyme is to recycle biotin from enzymes that are important in metabolism (processing of substances in cells). When biotin is lacking, specific enzymes called carboxylases cannot process certain proteins, fats, or carbohydrates. Specifically, two essential branched-chain amino acids (leucine
and isoleucine
) cannot be completely broken down, and are instead diverted into harmful by-products such as hydroxyisovalerate (also referred to as hydroxyisovaleric acid).
Individuals lacking functional biotinidase enzymes can still have normal carboxylase activity if they ingest adequate amounts of biotin. The standard treatment regimen calls for 5–10 mg of biotin per day.
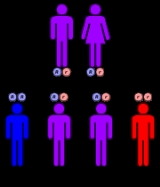
Biotinidase deficiency is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, which means the defective gene is located on an autosome
, and two copies of the defective gene - one from each parent - must be inherited for a person to be affected by the disorder. The parents of a child with an autosomal recessive disorder are usually not affected by the disorder, but are carriers of one copy of the defective gene. If both parents are carriers for the biotinidase deficiency, there is a 25% chance that their child will be born with it and a 75% chance that they will be carriers.
The chromosomal locus is at 3p25. The BTD gene has 4 exons of lengths 79 bp, 265 bp, 150 bp and 1502 bp, respectively. There are at least 21 different mutations that have been found to lead to biotinidase deficiency. The most common mutatations in severe biotinidase deficiency (<10% normal enzyme activity) are: p.Cys33PhefsX36, p.Gln456His, p.Arg538Cys, p.Asp444His, and p.[Ala171Thr;Asp444His]. Almost all individuals with partial biotinidase deficiency (10-30% enzyme activity) have the mutation p.Asp444His in one allele
of the BTD gene in combination with a second allele.
in several states throughout the United States. Results are found through testing a small amount of blood gathered through a heel prick of the infant. As not all states require that this test be done, it is often skipped in those where such testing is not required. Biotinidase deficiency can also be found by sequencing the BTD gene, particularly in those with a family history or known familial gene mutations.
Biotin
Biotin, also known as Vitamin H or Coenzyme R, is a water-soluble B-complex vitamin discovered by Bateman in 1916. It is composed of a ureido ring fused with a tetrahydrothiophene ring. A valeric acid substituent is attached to one of the carbon atoms of the tetrahydrothiophene ring...
is not released from proteins in the diet during digestion or from normal protein turnover in the cell. This situation results in biotin deficiency.
Biotin, sometimes called vitamin B7, is an important water-soluble nutrient that aids in the metabolism
Metabolism
Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that happen in the cells of living organisms to sustain life. These processes allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. Metabolism is usually divided into two categories...
of fat
Fat
Fats consist of a wide group of compounds that are generally soluble in organic solvents and generally insoluble in water. Chemically, fats are triglycerides, triesters of glycerol and any of several fatty acids. Fats may be either solid or liquid at room temperature, depending on their structure...
s, carbohydrate
Carbohydrate
A carbohydrate is an organic compound with the empirical formula ; that is, consists only of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, with a hydrogen:oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 . However, there are exceptions to this. One common example would be deoxyribose, a component of DNA, which has the empirical...
s and protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s. Biotin deficiency can result in behavioral disorders, lack of coordination, learning disabilities and seizure. Biotin supplementation can alleviate and sometimes totally arrest such symptoms.
Epidemiology
Based on the results of worldwide screening of biotinidase deficiency in 1991, the incidence of the disorder is:- One in 137,401 for profound biotinidase deficiency
- One in 109,921 for partial biotinidase deficiency
- One in 61,067 for the combined incidence of profound and partial biotinidase deficiency
- Carrier frequency in the general population is approximately one in 120.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a biotinidase deficiency can appear several days after birth. These include: seizureSeizure
An epileptic seizure, occasionally referred to as a fit, is defined as a transient symptom of "abnormal excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain". The outward effect can be as dramatic as a wild thrashing movement or as mild as a brief loss of awareness...
s, hypotonia
Hypotonia
Hypotonia is a state of low muscle tone , often involving reduced muscle strength. Hypotonia is not a specific medical disorder, but a potential manifestation of many different diseases and disorders that affect motor nerve control by the brain or muscle strength...
and muscle/limb weakness, ataxia
Ataxia
Ataxia is a neurological sign and symptom that consists of gross lack of coordination of muscle movements. Ataxia is a non-specific clinical manifestation implying dysfunction of the parts of the nervous system that coordinate movement, such as the cerebellum...
, paresis
Paresis
Paresis is a condition typified by partial loss of voluntary movement or by impaired movement. When used without qualifiers, it usually refers to the limbs, but it also can be used to describe the muscles of the eyes , the stomach , and also the vocal cords...
, hearing loss, optic atrophy, skin rashes (including seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease that appears on the skin. It occurs when the immune system mistakes the skin cells as a pathogen, and sends out faulty signals that speed up the growth cycle of skin cells. Psoriasis is not contagious. However, psoriasis has been linked to an increased risk of...
), and alopecia
Alopecia
Alopecia means loss of hair from the head or body. Alopecia can mean baldness, a term generally reserved for pattern alopecia or androgenic alopecia. Compulsive pulling of hair can also produce hair loss. Hairstyling routines such as tight ponytails or braids may induce Traction alopecia. Both...
. If left untreated, the disorder can rapidly lead to coma
Coma
In medicine, a coma is a state of unconsciousness, lasting more than 6 hours in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light or sound, lacks a normal sleep-wake cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. A person in a state of coma is described as...
and death.
Biotinidase deficiency can also appear later in life. This is referred to as "late-onset" biotinidase deficiency. The symptoms are similar, but perhaps more mild, because if an individual survives the neonatal period they likely have some residual activity of biotin-related enzymes. Studies have noted individuals who were asymptomatic until adolescence or early adulthood. One study pointed out that untreated individuals may not show symptoms until age 21. Furthermore, in rare cases, even individuals with profound deficiencies of biotinidase can be asymptomatic.
Symptom severity is predictably correlated with the severity of the enzyme defect. Profound biotinidase deficiency refers to situations where enzyme activity is 10% or less. Individuals with partial biotinidase deficiency may have enzyme activity of 10-30%.
Functionally, there is no significant difference between dietary biotin deficiency and genetic loss of biotin-related enzyme activity. In both cases, supplementation with biotin
Biotin
Biotin, also known as Vitamin H or Coenzyme R, is a water-soluble B-complex vitamin discovered by Bateman in 1916. It is composed of a ureido ring fused with a tetrahydrothiophene ring. A valeric acid substituent is attached to one of the carbon atoms of the tetrahydrothiophene ring...
can often restore normal metabolic function and proper catabolism of leucine
Leucine
Leucine is a branched-chain α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2CH2. Leucine is classified as a hydrophobic amino acid due to its aliphatic isobutyl side chain. It is encoded by six codons and is a major component of the subunits in ferritin, astacin and other 'buffer' proteins...
and isoleucine
Isoleucine
Isoleucine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCHCH2CH3. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested. Its codons are AUU, AUC and AUA....
.
The symptoms of biotinidase deficiency (and dietary deficiency of biotin) can be quite severe. A 2004 case study from Metametrix detailed the effects of biotin deficiency, including aggression, cognitive delay, and reduced immune function.
Dietary Concerns
It is recommended that raw eggs should be avoided in those affected by biotinBiotin
Biotin, also known as Vitamin H or Coenzyme R, is a water-soluble B-complex vitamin discovered by Bateman in 1916. It is composed of a ureido ring fused with a tetrahydrothiophene ring. A valeric acid substituent is attached to one of the carbon atoms of the tetrahydrothiophene ring...
deficiency, because egg whites contain high levels of avidin
Avidin
Avidin is a tetrameric biotin-binding protein produced in the oviducts of birds, reptiles and amphibians deposited in the whites of their eggs. In chicken egg white, avidin makes up approximately 0.05% of total protein...
. The name avidin literally means that the protein has an "avidity" for "biotin." Avidin binds to biotin, making it unavailable for use elsewhere in the body, and otherwise useful biotin molecules are excreted in the urine.
Genetics

Mutation
In molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
s in the BTD gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
cause biotinidase deficiency. Biotinidase
Biotinidase
Biotinidase also known as BTD is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the BTD gene.- Function :This enzyme allows the body to use and to recycle the B vitamin biotin, sometimes called vitamin H. Biotinidase extracts biotin from food because the body needs biotin in its free, unattached form...
is the enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that is made by the BTD gene. Many mutations that cause the enzyme to be nonfunctional or to be produced at extremely low levels have been identified. Biotin is a vitamin that is chemically bound to proteins. (Most vitamins are only loosely associated with proteins.) Without biotinidase activity, the vitamin biotin cannot be separated from foods and therefore cannot be used by the body. Another function of the biotinidase enzyme is to recycle biotin from enzymes that are important in metabolism (processing of substances in cells). When biotin is lacking, specific enzymes called carboxylases cannot process certain proteins, fats, or carbohydrates. Specifically, two essential branched-chain amino acids (leucine
Leucine
Leucine is a branched-chain α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2CH2. Leucine is classified as a hydrophobic amino acid due to its aliphatic isobutyl side chain. It is encoded by six codons and is a major component of the subunits in ferritin, astacin and other 'buffer' proteins...
and isoleucine
Isoleucine
Isoleucine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCHCH2CH3. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested. Its codons are AUU, AUC and AUA....
) cannot be completely broken down, and are instead diverted into harmful by-products such as hydroxyisovalerate (also referred to as hydroxyisovaleric acid).
Individuals lacking functional biotinidase enzymes can still have normal carboxylase activity if they ingest adequate amounts of biotin. The standard treatment regimen calls for 5–10 mg of biotin per day.
Biotinidase deficiency is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, which means the defective gene is located on an autosome
Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
, and two copies of the defective gene - one from each parent - must be inherited for a person to be affected by the disorder. The parents of a child with an autosomal recessive disorder are usually not affected by the disorder, but are carriers of one copy of the defective gene. If both parents are carriers for the biotinidase deficiency, there is a 25% chance that their child will be born with it and a 75% chance that they will be carriers.
The chromosomal locus is at 3p25. The BTD gene has 4 exons of lengths 79 bp, 265 bp, 150 bp and 1502 bp, respectively. There are at least 21 different mutations that have been found to lead to biotinidase deficiency. The most common mutatations in severe biotinidase deficiency (<10% normal enzyme activity) are: p.Cys33PhefsX36, p.Gln456His, p.Arg538Cys, p.Asp444His, and p.[Ala171Thr;Asp444His]. Almost all individuals with partial biotinidase deficiency (10-30% enzyme activity) have the mutation p.Asp444His in one allele
Allele
An allele is one of two or more forms of a gene or a genetic locus . "Allel" is an abbreviation of allelomorph. Sometimes, different alleles can result in different observable phenotypic traits, such as different pigmentation...
of the BTD gene in combination with a second allele.
Diagnosis
Biotinidase deficiency can be found by genetic testing. This is often done at birth as part of newborn screeningNewborn screening
Newborn screening is the process by which infants are screened shortly after birth for a list of disorders that are treatable, but difficult or impossible to detect clinically. Screening programs are often run by state or national governing bodies with the goal of screening all infants born in the...
in several states throughout the United States. Results are found through testing a small amount of blood gathered through a heel prick of the infant. As not all states require that this test be done, it is often skipped in those where such testing is not required. Biotinidase deficiency can also be found by sequencing the BTD gene, particularly in those with a family history or known familial gene mutations.
Pathophysiology
Symptoms of the disease are caused by the inability to reuse biotins that are needed for cell growth, production of fatty acids and the metabolism of fats and amino acids. For the most part, there is no real progression. If left untreated, the symptoms can lead to later problems such as comas or death. The problems that are prevalent early in life remain prevalent in old age unless treatment is administered daily.Treatment
Treatment is possible but unless continued daily, problems may arise. Currently, this is done through the taking of 5–10 mg of oral biotin a day. If symptoms have begun to show, standard treatments can take care of them, such as corrective lenses for mild cases of optic atrophy and hearing aids for poor hearing.Disease Database
BTD gene variant databaseSee also
- BiotinBiotinBiotin, also known as Vitamin H or Coenzyme R, is a water-soluble B-complex vitamin discovered by Bateman in 1916. It is composed of a ureido ring fused with a tetrahydrothiophene ring. A valeric acid substituent is attached to one of the carbon atoms of the tetrahydrothiophene ring...
- Biotin deficiencyBiotin deficiencyBiotin deficiency is a rare nutritional disorder which can become serious, even fatal, if allowed to progress untreated. It can occur in people of any age, ancestry, or gender...
- Multiple carboxylase deficiencyMultiple carboxylase deficiencyMultiple carboxylase deficiency is a form of metabolic disorder involving failures of carboxylation enzymes.The deficiency can be in biotinidase or holocarboxylase synthetase.These conditions respond to biotin.Forms include:...
- Holocarboxylase synthetase deficiencyHolocarboxylase synthetase deficiencyHolocarboxylase synthetase deficiency is an inherited metabolic disorder in which the body is unable to use the vitamin biotin effectively. This disorder is classified as a multiple carboxylase deficiency, a group of disorders characterized by impaired activity of certain enzymes that depend on...
- 3-Methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase deficiency3-methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase deficiency3-Methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase deficiency , also known as 3-Methylcrotonylglycinuria or BMCC deficiency is an inherited disorder in which the body is unable to process certain proteins properly. People with this disorder have inadequate levels of an enzyme that helps break down proteins...

