Benzimidazoline
Encyclopedia
Benzimidazolines are a family of heterocyclic compound
s, based on a benzene
ring fused with an imidazoline
. The parent compound has the chemical formula
C7H8N2.
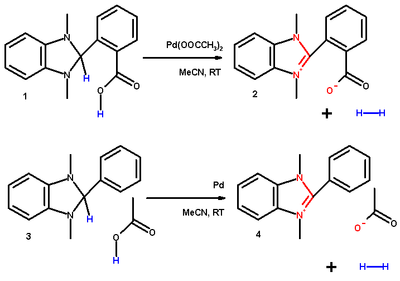
s that can be applied in chemical hydrogen storage. Benzimidazoline 1 converts in presence of palladium(II) acetate
in acetonitrile
at room temperature
to the internal salt 2 with formation of hydrogen
gas. The salt forms between the benzoic acid
anion and the imidazolium cation where the positive charge is delocalized over 3 atoms. This reaction even takes place in a 3.5 atmosphere
of hydrogen. The reaction of benzimidazoline 3 with acetic acid
over palladium
powder has the same result and 1,3-dimethylbenzimidazoline without a 2-substituent
even reacts with water.
This type of reactivity is unusual. Few exergonic reaction
s exist that liberate hydrogen like the chemical decomposition
of formic acid
to hydrogen and carbon dioxide
. Computations
show that the conversion of 1 too is an exergonic reaction
with a Gibbs free energy
of - 21.8 kJ
/mol
. The formation of (persistent) carbene
s from certain imidazolium salts with sodium hydride
also generates hydrogen but these reactions are endergonic
.
Heterocyclic compound
A heterocyclic compound is a cyclic compound which has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring. The counterparts of heterocyclic compounds are homocyclic compounds, the rings of which are made of a single element....
s, based on a benzene
Benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound. It is composed of 6 carbon atoms in a ring, with 1 hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom, with the molecular formula C6H6....
ring fused with an imidazoline
Imidazoline
Imidazoline is a nitrogen-containing heterocycle with formula C3H6N2, derived from imidazole. The ring contains an imine bond, and the carbons at the 4 and 5 positions are singly bonded, rather than doubly bonded for the case of imidazole...
. The parent compound has the chemical formula
Chemical formula
A chemical formula or molecular formula is a way of expressing information about the atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound....
C7H8N2.
Benzimidazolines in dihydrogen storage
In one study certain benzimidazolines have been identified as organic hydrideHydride
In chemistry, a hydride is the anion of hydrogen, H−, or, more commonly, a compound in which one or more hydrogen centres have nucleophilic, reducing, or basic properties. In compounds that are regarded as hydrides, hydrogen is bonded to a more electropositive element or group...
s that can be applied in chemical hydrogen storage. Benzimidazoline 1 converts in presence of palladium(II) acetate
Palladium(II) acetate
Palladium acetate is a chemical compound of palladium described by the formula Pd2 or Pd2. It is considered more reactive than the analogous platinum compound...
in acetonitrile
Acetonitrile
Acetonitrile is the chemical compound with formula . This colourless liquid is the simplest organic nitrile. It is produced mainly as a byproduct of acrylonitrile manufacture...
at room temperature
Room temperature
-Comfort levels:The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers has listings for suggested temperatures and air flow rates in different types of buildings and different environmental circumstances. For example, a single office in a building has an occupancy ratio per...
to the internal salt 2 with formation of hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
gas. The salt forms between the benzoic acid
Benzoic acid
Benzoic acid , C7H6O2 , is a colorless crystalline solid and the simplest aromatic carboxylic acid. The name derived from gum benzoin, which was for a long time the only source for benzoic acid. Its salts are used as a food preservative and benzoic acid is an important precursor for the synthesis...
anion and the imidazolium cation where the positive charge is delocalized over 3 atoms. This reaction even takes place in a 3.5 atmosphere
Atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure is the force per unit area exerted into a surface by the weight of air above that surface in the atmosphere of Earth . In most circumstances atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point...
of hydrogen. The reaction of benzimidazoline 3 with acetic acid
Acetic acid
Acetic acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3CO2H . It is a colourless liquid that when undiluted is also called glacial acetic acid. Acetic acid is the main component of vinegar , and has a distinctive sour taste and pungent smell...
over palladium
Palladium
Palladium is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Pd and an atomic number of 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1803 by William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas, which was itself named after the epithet of the Greek goddess Athena, acquired...
powder has the same result and 1,3-dimethylbenzimidazoline without a 2-substituent
Substituent
In organic chemistry and biochemistry, a substituent is an atom or group of atoms substituted in place of a hydrogen atom on the parent chain of a hydrocarbon...
even reacts with water.
This type of reactivity is unusual. Few exergonic reaction
Exergonic reaction
An exergonic reaction is a chemical reaction where the change in the Gibbs free energy is negative, indicating a spontaneous reaction. Symbolically, the release of Gibbs free energy, G, in an exergonic reaction is denoted as...
s exist that liberate hydrogen like the chemical decomposition
Chemical decomposition
Chemical decomposition, analysis or breakdown is the separation of a chemical compound into elements or simpler compounds. It is sometimes defined as the exact opposite of a chemical synthesis. Chemical decomposition is often an undesired chemical reaction...
of formic acid
Formic acid
Formic acid is the simplest carboxylic acid. Its chemical formula is HCOOH or HCO2H. It is an important intermediate in chemical synthesis and occurs naturally, most notably in the venom of bee and ant stings. In fact, its name comes from the Latin word for ant, formica, referring to its early...
to hydrogen and carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
. Computations
Computational chemistry
Computational chemistry is a branch of chemistry that uses principles of computer science to assist in solving chemical problems. It uses the results of theoretical chemistry, incorporated into efficient computer programs, to calculate the structures and properties of molecules and solids...
show that the conversion of 1 too is an exergonic reaction
Exergonic reaction
An exergonic reaction is a chemical reaction where the change in the Gibbs free energy is negative, indicating a spontaneous reaction. Symbolically, the release of Gibbs free energy, G, in an exergonic reaction is denoted as...
with a Gibbs free energy
Gibbs free energy
In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy is a thermodynamic potential that measures the "useful" or process-initiating work obtainable from a thermodynamic system at a constant temperature and pressure...
of - 21.8 kJ
Joule
The joule ; symbol J) is a derived unit of energy or work in the International System of Units. It is equal to the energy expended in applying a force of one newton through a distance of one metre , or in passing an electric current of one ampere through a resistance of one ohm for one second...
/mol
Mole (unit)
The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value...
. The formation of (persistent) carbene
Carbene
In chemistry, a carbene is a molecule containing a neutral carbon atom with a valence of two and two unshared valence electrons. The general formula is RR'C:, but the carbon can instead be double-bonded to one group. The term "carbene" may also merely refer to the compound H2C:, also called...
s from certain imidazolium salts with sodium hydride
Sodium hydride
Sodium hydride is the chemical compound with the empirical formula NaH. It is primarily used as a strong base in organic synthesis. NaH is representative of the saline hydrides, meaning it is a salt-like hydride, composed of Na+ and H− ions, in contrast to the more molecular hydrides such as...
also generates hydrogen but these reactions are endergonic
Endergonic reaction
In chemical thermodynamics, an endergonic reaction is a chemical reaction in which the standard change in free energy is positive, and energy is absorbed...
.


