
Beat (music)
Encyclopedia

Music
Music is an art form whose medium is sound and silence. Its common elements are pitch , rhythm , dynamics, and the sonic qualities of timbre and texture...
, the pulse
Pulse (music)
In music and music theory, the pulse or tactus consists of beats in a series of identical yet distinct periodic short-duration stimuli perceived as points in time occurring at the mensural level...
of the mensural level (or beat level). In popular use, the beat can refer to a variety of related concepts including: tempo
Tempo
In musical terminology, tempo is the speed or pace of a given piece. Tempo is a crucial element of any musical composition, as it can affect the mood and difficulty of a piece.-Measuring tempo:...
, meter
Meter (music)
Meter or metre is a term that music has inherited from the rhythmic element of poetry where it means the number of lines in a verse, the number of syllables in each line and the arrangement of those syllables as long or short, accented or unaccented...
, rhythm
Rhythm
Rhythm may be generally defined as a "movement marked by the regulated succession of strong and weak elements, or of opposite or different conditions." This general meaning of regular recurrence or pattern in time may be applied to a wide variety of cyclical natural phenomena having a periodicity or...
and groove
Groove (popular music)
Groove is the sense of propulsive rhythmic "feel" or sense of "swing" created by the interaction of the music played by a band's rhythm section . Groove is a consideration in genres such as salsa, funk, rock, fusion, and soul...
. In hip hop
Hip hop music
Hip hop music, also called hip-hop, rap music or hip-hop music, is a musical genre consisting of a stylized rhythmic music that commonly accompanies rapping, a rhythmic and rhyming speech that is chanted...
and R&B
Contemporary R&B
Contemporary R&B is a music genre that combines elements of hip hop, soul, R&B and funk.Although the abbreviation “R&B” originates from traditional rhythm and blues music, today the term R&B is most often used to describe a style of African American music originating after the demise of disco in...
music, the term 'beat' commonly refers to the non-vocal layer of the song not including instrumental
Instrumental
An instrumental is a musical composition or recording without lyrics or singing, although it might include some non-articulate vocal input; the music is primarily or exclusively produced by musical instruments....
s, which is frequently based on a looped recording of a drum-rhythm. Much music is characterized by a repeating sequence of stressed and unstressed beats (often called "strong" and "weak") and divided into measures organized by time signature
Time signature
The time signature is a notational convention used in Western musical notation to specify how many beats are in each measure and which note value constitutes one beat....
and tempo
Tempo
In musical terminology, tempo is the speed or pace of a given piece. Tempo is a crucial element of any musical composition, as it can affect the mood and difficulty of a piece.-Measuring tempo:...
indications.
Downbeat
The downbeat is the impulse that occurs at the beginning of a barBar (music)
In musical notation, a bar is a segment of time defined by a given number of beats of a given duration. Typically, a piece consists of several bars of the same length, and in modern musical notation the number of beats in each bar is specified at the beginning of the score by the top number of a...
in measured music. Its name is derived from the downward stroke of the director or conductor's baton
Baton (conducting)
A baton is a stick that is used by conductors primarily to exaggerate and enhance the manual and bodily movements associated with directing an ensemble of musicians. They are generally made of a light wood, fiberglass or carbon fiber which is tapered to a grip shaped like a pear, drop, cylinder...
on the first beat of each measure. It frequently carries the strongest accent of the rhythmic cycle. However, in some cases, the downbeat may not be emphasized. Such departure from the normal stress pattern of a measure is a form of syncopation
Syncopation
In music, syncopation includes a variety of rhythms which are in some way unexpected in that they deviate from the strict succession of regularly spaced strong and weak but also powerful beats in a meter . These include a stress on a normally unstressed beat or a rest where one would normally be...
.
Upbeat
(Ger. Auftakt).
Bar (music)
In musical notation, a bar is a segment of time defined by a given number of beats of a given duration. Typically, a piece consists of several bars of the same length, and in modern musical notation the number of beats in each bar is specified at the beginning of the score by the top number of a...
. In other words, this is an impulse in a measured rhythm
Rhythm
Rhythm may be generally defined as a "movement marked by the regulated succession of strong and weak elements, or of opposite or different conditions." This general meaning of regular recurrence or pattern in time may be applied to a wide variety of cyclical natural phenomena having a periodicity or...
that immediately precedes, and hence anticipates, the downbeat. It can be the last beat in a bar
Bar (music)
In musical notation, a bar is a segment of time defined by a given number of beats of a given duration. Typically, a piece consists of several bars of the same length, and in modern musical notation the number of beats in each bar is specified at the beginning of the score by the top number of a...
where that bar precedes a new bar of music.
2. An anticipatory note or succession of notes occurring before the first barline of a piece, sometimes referred to as an ‘upbeat figure’, section or phrase. An alternative expression is "anacrusis
Anacrusis
In poetry, an anacrusis is the lead-in syllables, collectively, that precede the first full measure.In music, it is the note or sequence of notes which precedes the first downbeat in a bar. In the latter sense an anacrusis is often called a pickup, pickup note, or pickup measure, referring to the...
" (from Greek. ana: "up towards" and krousis: "to strike"; Fr. anacrouse). This term was borrowed from poetry
Poetry
Poetry is a form of literary art in which language is used for its aesthetic and evocative qualities in addition to, or in lieu of, its apparent meaning...
where it refers to one or more unstressed extrametrical syllable
Syllable
A syllable is a unit of organization for a sequence of speech sounds. For example, the word water is composed of two syllables: wa and ter. A syllable is typically made up of a syllable nucleus with optional initial and final margins .Syllables are often considered the phonological "building...
s at the beginning of a line.
3. The upward stroke made by a conductor to indicate the beat that leads into a new measure.
N.B. This expression is sometimes loosely used outside the field of music to denote anything positive-sounding; e.g. an "upbeat assessment of a company's prospects"
On-beat and off-beat
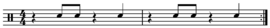
Counting (music)
In music, counting is a system of regularly occurring sounds that serve to assist with the performance or audition of music by allowing the easy identification of the beat. Commonly, this involves verbally counting the beats in each measure as they occur...
as "1 2 3 4, 1 2 3 4...", the first beat of the bar (down-beat) is usually the strongest accent in the melody and the likeliest place for a chord change, the third is the next strongest: these are "on" beats. The second and fourth are weaker - the "off-beats". Subdivisions (like eighth notes) that fall between the pulse
Pulse (music)
In music and music theory, the pulse or tactus consists of beats in a series of identical yet distinct periodic short-duration stimuli perceived as points in time occurring at the mensural level...
beats are even weaker and these, if used frequently in a rhythm, can also make it "off-beat". The effect can be easily simulated by evenly and repeatedly counting to four:
Bold denotes a stressed beat. As a background against which to compare these various rhythms a bass drum strike on the downbeat and a constant eighth note subdivision on ride cymbal have been added, which would be counted as follows:
- 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 --
- 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4—the stress here on the "on" beat But one may syncopate that pattern and alternately stress the odd and even beats, respectively, creating syncopationSyncopationIn music, syncopation includes a variety of rhythms which are in some way unexpected in that they deviate from the strict succession of regularly spaced strong and weak but also powerful beats in a meter . These include a stress on a normally unstressed beat or a rest where one would normally be...
: - 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 -- the stress is on the "unexpected" or syncopatedSyncopationIn music, syncopation includes a variety of rhythms which are in some way unexpected in that they deviate from the strict succession of regularly spaced strong and weak but also powerful beats in a meter . These include a stress on a normally unstressed beat or a rest where one would normally be...
beat
So Off-beat is a musical term commonly applied to syncopation
Syncopation
In music, syncopation includes a variety of rhythms which are in some way unexpected in that they deviate from the strict succession of regularly spaced strong and weak but also powerful beats in a meter . These include a stress on a normally unstressed beat or a rest where one would normally be...
that emphasizes the weak even beats of a bar, as opposed to the "normal" on-beat. This is a fundamental technique of African polyrhythm that transferred to popular western music. According to Grove Music, the “Offbeat” is [often] where the downbeat is replaced by a rest or is tied over from the preceding bar". The downbeat can never be the off-beat because it is the strongest beat in 4/4 time. Certain genres in particular tend to emphasize the off-beat. This emphasis is a defining characteristic of rock'n'roll and Ska
Ska
Ska |Jamaican]] ) is a music genre that originated in Jamaica in the late 1950s, and was the precursor to rocksteady and reggae. Ska combined elements of Caribbean mento and calypso with American jazz and rhythm and blues...
music.
Backbeat


Syncopation
In music, syncopation includes a variety of rhythms which are in some way unexpected in that they deviate from the strict succession of regularly spaced strong and weak but also powerful beats in a meter . These include a stress on a normally unstressed beat or a rest where one would normally be...
accentuation
Accent (music)
In music, an accent is an emphasis placed on a particular note,either as a result of its context or specifically indicated by an accent mark.Accents contribute to the articulation and prosody of a performance of a musical phrase....
on the "off" beat. In a simple 4/4 rhythm these are beats 2 and 4. Emphasized back beat, a feature of some African styles, defined rhythm and blues
Rhythm and blues
Rhythm and blues, often abbreviated to R&B, is a genre of popular African American music that originated in the 1940s. The term was originally used by record companies to describe recordings marketed predominantly to urban African Americans, at a time when "urbane, rocking, jazz based music with a...
recordings in the late 1940s and so became one of the defining characteristics of rock and roll
Rock and roll
Rock and roll is a genre of popular music that originated and evolved in the United States during the late 1940s and early 1950s, primarily from a combination of African American blues, country, jazz, and gospel music...
and much contemporary popular music
Popular music
Popular music belongs to any of a number of musical genres "having wide appeal" and is typically distributed to large audiences through the music industry. It stands in contrast to both art music and traditional music, which are typically disseminated academically or orally to smaller, local...
.
An early record with an emphasised back beat throughout was "Good Rockin' Tonight" by Wynonie Harris
Wynonie Harris
Wynonie Harris , born in Omaha, Nebraska, was an American blues shouter and rhythm and blues singer of upbeat songs, featuring humorous, often ribald lyrics. With fifteen Top 10 hits between 1946 and 1952, Harris is generally considered one of rock and roll's forerunners, influencing Elvis Presley...
in 1948. However drummer Earl Palmer
Earl Palmer
Earl Cyril Palmer was an American rock & roll and rhythm and blues drummer, and member of the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame....
claimed the honour for "The Fat Man
The Fat Man (song)
"The Fat Man" is a rhythm and blues song co-written by Fats Domino and Dave Bartholomew and recorded by Fats Domino. It is considered to be one of the first rock and roll records.-History:...
" by Fats Domino
Fats Domino
Antoine Dominique "Fats" Domino, Jr. is an American R&B and rock and roll pianist and singer-songwriter. He was born and raised in New Orleans, Louisiana, and Creole was his first language....
in 1949, which he played on, saying he adopted it from the final "shout" or "out" chorus common in Dixieland
Dixieland
Dixieland music, sometimes referred to as Hot jazz, Early Jazz or New Orleans jazz, is a style of jazz music which developed in New Orleans at the start of the 20th century, and was spread to Chicago and New York City by New Orleans bands in the 1910s.Well-known jazz standard songs from the...
jazz. However urban contemporary gospel
Urban contemporary gospel
Traditional black gospel is music that is written to express either personal or a communal belief regarding Christian life, as well as to give a Christian alternative to mainstream secular music...
was stressing the back beat much earlier with hand-clapping and tambourine
Tambourine
The tambourine or marine is a musical instrument of the percussion family consisting of a frame, often of wood or plastic, with pairs of small metal jingles, called "zils". Classically the term tambourine denotes an instrument with a drumhead, though some variants may not have a head at all....
s. There is a hand-clapping back beat on "Roll 'Em Pete
Roll 'Em Pete
"Roll 'Em Pete" is a rhythm and blues song originally recorded in 1938 by Big Joe Turner and pianist Pete Johnson. The recording is regarded as one of the most important precursors of what later became known as "rock and roll".-Original recording:...
" by Pete Johnson
Pete Johnson
Pete Johnson was an American boogie-woogie and jazz pianist.Journalist Tony Russell stated in his book The Blues - From Robert Johnson to Robert Cray, that "Johnson shared with the other members of the 'Boogie Woogie Trio' the technical virtuosity and melodic fertility that can make this the most...
and Big Joe Turner
Big Joe Turner
Big Joe Turner was an American blues shouter from Kansas City, Missouri. According to the songwriter Doc Pomus, "Rock and roll would have never happened without him." Although he came to his greatest fame in the 1950s with his pioneering rock and roll recordings, particularly "Shake, Rattle and...
, recorded in 1938. A distinctive back beat can be heard on "Back Beat Boogie" by Harry James
Harry James
Henry Haag “Harry” James was a trumpeter who led a jazz swing band during the Big Band Era of the 1930s and 1940s. He was especially known among musicians for his astonishing technical proficiency as well as his superior tone.-Biography:He was born in Albany, Georgia, the son of a bandleader of a...
And His Orchestra, recorded in late 1939. Other early recorded examples include the final verse of "Grand Slam" by Benny Goodman
Benny Goodman
Benjamin David “Benny” Goodman was an American jazz and swing musician, clarinetist and bandleader; widely known as the "King of Swing".In the mid-1930s, Benny Goodman led one of the most popular musical groups in America...
in 1942 and some sections of The Glenn Miller Orchestra
Glenn Miller Orchestra
The Glenn Miller Orchestra was originally formed in 1938 by Glenn Miller. It was arranged around a clarinet and tenor saxophone playing melody, while three other saxophones played the harmony...
's "(I've Got A Girl In) Kalamazoo", while tapes of Charlie Christian
Charlie Christian
Charles Henry "Charlie" Christian was an American swing and jazz guitarist.Christian was an important early performer on the electric guitar, and is cited as a key figure in the development of bebop and cool jazz. He gained national exposure as a member of the Benny Goodman Sextet and Orchestra...
jamming at Minton's Playhouse
Minton's Playhouse
Minton’s Playhouse is a jazz club and bar located on the first floor of the Cecil Hotel at 210 West 118th Street in Harlem. Minton’s was founded by tenor saxophonist Henry Minton in 1938...
around the same time have a sustained snare-drum back-beat on the hottest choruses.

Country music
Country music is a popular American musical style that began in the rural Southern United States in the 1920s. It takes its roots from Western cowboy and folk music...
" musicians the Delmore Brothers were turning out boogie tunes with a hard driving back beat, such as the #2 hit "Freight Train Boogie" in 1946, as well as in other boogie songs they recorded. Similarly Fred Maddox’s
Maddox Brothers and Rose
The Maddox Brothers and Rose, known as America’s Most Colorful Hillbilly Band from the 1930s to the 1950s, consisted of four brothers, Fred, Cal, Cliff and Don Maddox, along with their sister Rose. Cliff died in 1949 and was replaced by brother Henry...
trademark back beat, a slapping bass
Slapping
In music, the term slapping is often used to refer to two different playing techniques used on the double bass and on the bass guitar.-Double bass:...
style, helped drive a rhythm that came to be known as rockabilly
Rockabilly
Rockabilly is one of the earliest styles of rock and roll music, dating to the early 1950s.The term rockabilly is a portmanteau of rock and hillbilly, the latter a reference to the country music that contributed strongly to the style's development...
, one of the early forms of rock and roll
Rock and roll
Rock and roll is a genre of popular music that originated and evolved in the United States during the late 1940s and early 1950s, primarily from a combination of African American blues, country, jazz, and gospel music...
. Maddox had used this style as early as 1937.
In today's popular music the snare drum
Snare drum
The snare drum or side drum is a melodic percussion instrument with strands of snares made of curled metal wire, metal cable, plastic cable, or gut cords stretched across the drumhead, typically the bottom. Pipe and tabor and some military snare drums often have a second set of snares on the bottom...
is typically used to play the backbeat pattern. Early funk music often delayed one of the backbeats so as, "to give a 'kick' to the [overall] beat".
Some songs, such as The Beatles
The Beatles
The Beatles were an English rock band, active throughout the 1960s and one of the most commercially successful and critically acclaimed acts in the history of popular music. Formed in Liverpool, by 1962 the group consisted of John Lennon , Paul McCartney , George Harrison and Ringo Starr...
' "Please Please Me
Please Please Me
Please Please Me is the debut album by the English rock band The Beatles. Parlophone rush-released the album on 22 March 1963 in the United Kingdom to capitalise on the success of singles "Please Please Me" and "Love Me Do" .Of the album's fourteen songs, eight were written by Lennon–McCartney...
" and "I Want to Hold Your Hand
I Want to Hold Your Hand
"I Want to Hold Your Hand" is a song by the English rock band The Beatles. Written by John Lennon and Paul McCartney, and recorded in October 1963, it was the first Beatles record to be made using four-track equipment....
", The Knack
The Knack
The Knack was an American New Wave rock quartet based in Los Angeles that rose to fame with their first single, "My Sharona", an international number one hit in 1979.-Founding :...
's "Good Girls Don't
Good Girls Don't (song)
"Good Girls Don't" is a 1979 hit single written by Doug Fieger and released by the rock band The Knack, off their album Get the Knack. It was the follow-up to the group's No. 1 single, "My Sharona." It reached #11 on the Billboard Hot 100 chart and #66 on the British charts. It also reached #20...
" and Blondie
Blondie (band)
Blondie is an American rock band, founded by singer Deborah Harry and guitarist Chris Stein. The band was a pioneer in the early American New Wave and punk scenes of the mid-1970s...
's cover of The Nerves
The Nerves
The Nerves were a mid-'70s American power pop trio based in Los Angeles, featuring guitarist Jack Lee, bassist Peter Case, and drummer Paul Collins. All three members composed songs and sang. They managed an international tour in the U.S. and Canada, including dates with The Ramones, and...
' "Hanging on the Telephone
Hanging on the Telephone
"Hanging on the Telephone" is a song written by Jack Lee and first performed by Lee's short-lived US West Coast power pop trio The Nerves, who placed it as the lead-off track on their 1976 EP, the band's only release. New Wave band Blondie popularised the song when it was released as the second...
", employ a double backbeat pattern. In a double backbeat, one of the off beats is played as two eighth notes rather than one quarter note.
Hyperbeat
A hyperbeat is one unit of hypermeter, generally a measure. "Hypermeter is meter, with all its inherent characteristics, at the level where measures act as beats."Related concepts
- Afterbeat refers to a percussionPercussion instrumentA percussion instrument is any object which produces a sound when hit with an implement or when it is shaken, rubbed, scraped, or otherwise acted upon in a way that sets the object into vibration...
style where a strong accent is sounded on the second, third and fourth beats of the bar, following the downbeat. - In ReggaeReggaeReggae is a music genre first developed in Jamaica in the late 1960s. While sometimes used in a broader sense to refer to most types of Jamaican music, the term reggae more properly denotes a particular music style that originated following on the development of ska and rocksteady.Reggae is based...
music, the term One DropOne drop rhythmOne drop rhythm is a drumset playing style of reggae, popularized by Carlton Barrett, long-time drummer of Bob Marley and the Wailers, created by Winston Grennan, in which the backbeat is characterized by the dominant snare drum stroke and bass drum both sounding on the third beat of every measure...
reflects the complete de-emphasis (to the point of silence) of the first beat in the cycle. - James BrownJames BrownJames Joseph Brown was an American singer, songwriter, musician, and recording artist. He is the originator of Funk and is recognized as a major figure in the 20th century popular music for both his vocals and dancing. He has been referred to as "The Godfather of Soul," "Mr...
’s signature funkFunkFunk is a music genre that originated in the mid-late 1960s when African American musicians blended soul music, jazz and R&B into a rhythmic, danceable new form of music. Funk de-emphasizes melody and harmony and brings a strong rhythmic groove of electric bass and drums to the foreground...
groove emphasized the downbeatDownbeatDownbeat, down beat or Down Beat may refer to:*Downbeat, the first beat of a measure in music. This terms originated from orchestral conducting, where the lowest point on the baton signals the first downbeat in a given measure...
– that is, with heavy emphasis "on the one" (the first beat of every measure) – to etch his distinctive sound, rather than the back beat (familiar to many R&B musicians) which places the emphasis on the second beat.

